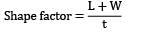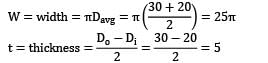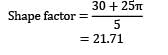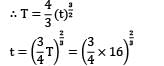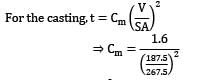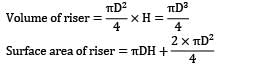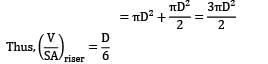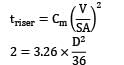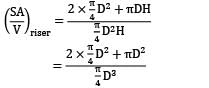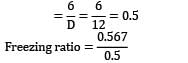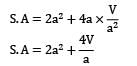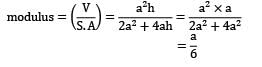Test: Casting Level - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Casting Level - 2
Which of the following sand ramming methods result into hardest layer at parting plane and around the pattern and less dense in top layers?
Recess provided in the material for locating and positioning of cores is called as:
Match the following according to the properties of moulding sand
List-I
a. Cohesiveness
b. Adhesiveness
c. Refractoriness
d. Collapsibility
List-II
i. Ability of breaking the mould with little force
ii. Ability to withstand higher temperature without losing strength
iii. Ability of bond formation of sand particles with other materials
iv. Ability to form bond between sand particles

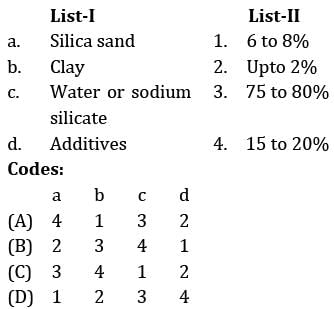
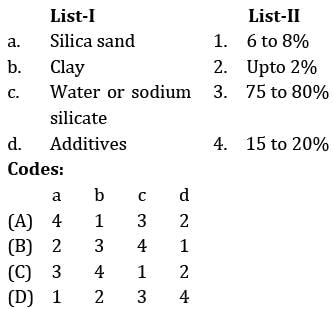
Match the four basic elements of moulding sand with its percentage
The shape factor for a casting in the form of an annular cylinder of outside diameter 30 cm, inside diameter 20 cm and height 30 cm (correction factor, k = 1 ) will be:
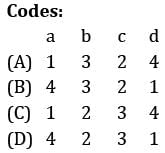
Match List-I (Type of casting) with List-II (Working principles) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
a. Die casting
b. Centrifugal casting
c. Centrifuging
d. Continuous casting
List-II
1. Molten metal is forced into the die under pressure
2. Axis of rotation does not coincide with axis of mould
3. Metal solidifies when mould is rotating
4. Continuously pouring molten metal into mould
The correct reasons for the occurrence of hot tear in casting among the following reasons will be:
i. Hindered contraction occurring immediately after metal has solidified
ii. Poor collapsibility of mould and core
iii. Too high pouring temperature
A steel slab casting of dimensions 30 cm x 30 cm x 6 cm with a side riser is to be casted horizontally into the mould. Using modulus method, the volume of the cylindrical riser is __________cm3
The rate of formation of thickness (in mm) of the metal skin frozen during solidification of pure zinc casting is found to be 2 times of square root of solidification time (in s). What will be the solidification time if thickness of the solid zinc casting is 16 mm?
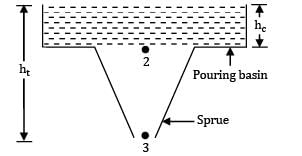
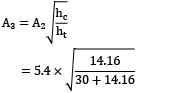
In a gating design, sprue has an area 5.4cm2 , where the pouring basin meets the sprue, sprue length is 30 cm and desired molten metal flow rate is 900 cm3 /s. The area of the sprue at the bottom to avoid air aspiration effect is:
A cylindrical side riser is used for a sand casting mold. The casting itself is a rectangular plate with dimensions 7.5 x 12.5 x 2 cm3 . The solidification time for this casting is 1.6 min. The cylinder for the riser has a diameter to height ratio equal to 1. If the riser and casting are in same mold, then for a riser solidification time of 2 min, its dimension is __________ cm
The following data is observed for a casting process:
Mass of casting = 5000 kg
Density of metal = 8000 kg/m3
Pouring time = 10 sec
Efficiency factor = 0.9
Effective had = 2 m
The chock area of the casting is ___________mm2
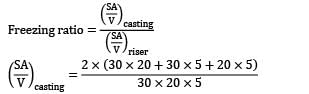
A cast steel slab of dimension 30 x 20 x 5 cm3 is poured horizontally using a side riser. The riser is cylindrical in shape with diameter and height both equal to 12 cm. The freezing ratio of mould for Caine’s empirical equation is:
What is the modulus of a optimum side riser in the shape of square parallelopiped with side a:
Following are the steps followed in a typical casting process:
i. Moulding
ii. Pattern making
iii. Melting and pouring
iv. Core making
v. Testing and inspection
vi. Fettling
The correct sequence of steps will:
In risering analysis, for finding the riser contribution, chills are used to:
Which of the following statements are true with regard to the hot chamber and cold chamber die cast machine?
i. Hot chamber die casting machine has a furnace for melting and holding the metal
ii. High melting temperature alloys of nonferrous type are best to die cast in hot chamber machines
iii. In cold chamber machine, metal is ladled by hand from a nearly holding furnace