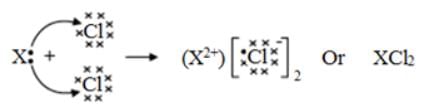Test: Periodic Classification of Elements (Medium) - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Periodic Classification of Elements (Medium)
An atom has the symbol pqX. Which value determines the position of the element in the periodic table?
Which of the following is not a noble gas?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The element placed with cerium, in the table formed by Newlands' was:
Element 'X' has twelve protons in its nucleus. To which group of the periodic table it will belong?
Which among the following elements is metalloid?
Which of the following statements can help a chemistry student to predict chemical properties of an element?
(I) Position of element in the periodic table
(II) Atomic number of the element
(III) Number of shells in the atom
(IV) Number of electrons in the outermost shell.
If the two members of a Dobereiner triad are phosphorus and antimony, the third member of this triad is:
_________were not included in Mendeleev's periodic table.
Whose name is not associated with the development of periodic Table
Which of the following forms the basis of the modern periodic table?
What happens to the electropositive character of elements moving from left to right in a periodic table?
The electronic configuration of an element M is 2, 8, 4. In modern periodic table, the element M is placed in
Which of the following is the correct order of the atomic radii of the elements oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen?
What is the other name for group 18th elements?
Which of the following is the most reactive element of the group 17?
Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is a solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as
Which group elements are called transition metals?
Which of the following elements has 2 shells and both are completely filled?
Which of the following is the atomic number of an element that forms basic oxide?