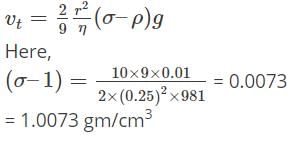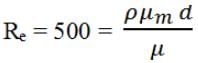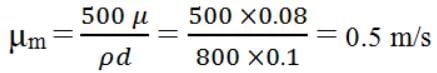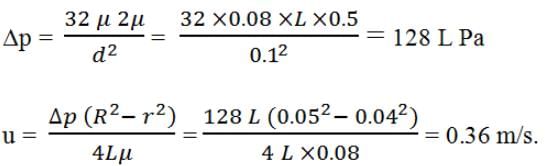Test: Measurement of Pressure, pH & Viscosity- 1 - GATE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Measurement of Pressure, pH & Viscosity- 1
If the displacement is measured with strain gauge then the number of strain gauge normally required are
A capacitive pressure sensor has a typical measurement uncertainty of
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The instruments used for the measurement of pressure is/are
Bourdon tube is used for the measurement of gauge pressure of
Dead weight gauge is used for the measurement of pressure of
The ionization gauge an instrument used for the measurement of
When a visual indication of pressure level is required then the instrument generally used is
For the measurement of high pressure with high accuracy the device used is
Advantage of passive instrument is
In a stationary fluid, how do the local pressure of the fluid vary?
Which of the following cannot be the value of absolute pressure of a fluid at any point?
A student wants to find the absolute pressure of water at a point below the surface of water. He has a barometer and a manometer pressure gauge. The barometer reads 1.3152 bar whereas the manometer pressure gauge reads 0.3152 bar. What is the absolute pressure? (Assume that pressure at one end of the manometer is atmospheric.)
In a U-tube manometer, one end is open to the atmosphere, the other end attached to a pressurized gas of gauge pressure 40 kPa. The height of the fluid column in the atmospheric side is 60 cm, and that on the gas side is 30 cm. The manometic fluid used is: (Take g = 9.8 m/s2).
In a U-tube mercury manometer, one end is exposed to the atmosphere and the other end is connected to a pressurized gas. The gauge pressure of the gas is found to be 40 kPa. Now, we change the manometric fluid to water. The height difference changes by: (ρmercury = 13600 kg/m3, ρwater = 1000 kg/m3).
A manometric liquid should suitably have _________.
A simple U-tube manometer can measure negative gauge pressures.
Both ends of a U-tube manometer are exposed to the atmosphere. There exists a possibility that the height difference of the manometer is non-zero. True or False?
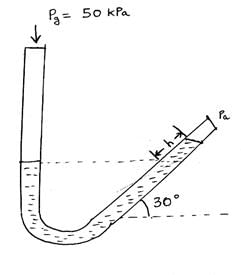
The below figure shows an inclined U-tube mercury manometer. The vertical end of the tube is exposed to a gas of gauge pressure 50 kPa and the inclined end is exposed to the atmosphere. The inclined part of the tube is at an angle of 30o with the horizontal. Find the value of h (in cm) (take g = 9.8 m/s2, ρmercury = 13600 kg/m3)
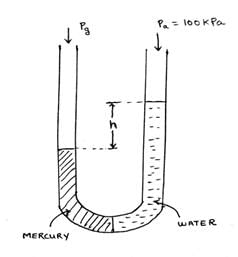
In the manometer given above, 2 immiscible fluids mercury (ρ = 13600 kg/m3) and water (ρ = 1000 kg/m3) are used as manometric fluids. The water end is exposed to the atmosphere (100 kPa) and the mercury end is exposed to a gas. At this position, the interface between the fluids is at the bottom-most point of the manometer. Ignore the width of the manometer tube and the radius of curvature. The value of h is found to be 9.45 m. The height of the mercury column is given to be 75 cm. Find the gauge pressure of the gas. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
What value of angle Φ is between the plate and cone in Cone-and-Plate viscometer?
A small spherical ball of diameter 5mm is thrown into a well of water and it moves with a terminal velocity 10cm/s. Calculate the density of the spherical ball. Given that viscosity of water is 0.01poise.
Which one of the following is not applicable to rotating spindle viscometer?
Which one of the following is not applicable to Coaxial cylinder?
Oil flows in a pipe 100 mm bore diameter with a Reynolds’ Number of 500. The density is 800 kg/m3. Calculate the velocity of a streamline at a radius of 40 mm. The viscosity µ = 0.08 Ns/m2.