Test: Threads- 1 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Threads- 1
The atomic fetch-and-set x, y instruction unconditionally sets the memory location x to 1 and fetches the old value of x in y without allowing any intervening access to the memory location x. consider the following implementation of P and V functions on a binary semaphore
void P (binary_semaphore *s) {
unsigned y;
unsigned *x = &(s->value);
do {
fetch-and-set x, y;
} while (y);
}
void V (binary_semaphore *s) {
S->value = 0;
}
Which one of the following is true?
unsigned y;
unsigned *x = &(s->value);
do {
fetch-and-set x, y;
} while (y);
}
S->value = 0;
}
A shared variable x, initialized to zero, is operated on by four concurrent processes W, X, Y, Z as follows. Each of the processes W and X reads x from memory, increments by one, stores it to memory, and then terminates. Each of the processes Y and Z reads x from memory, decrements by two, stores it to memory, and then terminates. Each process before reading x invokes the P operation (i.e., wait) on a counting semaphore S and invokes the V operation (i.e., signal) on the semaphore S after storing x to memory. Semaphore S is initialized to two. What is the maximum possible value of x after all processes complete execution? (GATE CS 2013)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Three concurrent processes X, Y, and Z execute three different code segments that access and update certain shared variables. Process X executes the P operation (i.e., wait) on semaphores a, b and c; process Y executes the P operation on semaphores b, c and d; process Z executes the P operation on semaphores c, d, and a before entering the respective code segments. After completing the execution of its code segment, each process invokes the V operation (i.e., signal) on its three semaphores. All semaphores are binary semaphores initialized to one. Which one of the following represents a deadlock-free order of invoking the P operations by the processes?
The time taken to switch between user and kernel modes of execution be t1 while the time taken to switch between two processes be t2. Which of the following is TRUE?
Consider the methods used by processes P1 and P2 for accessing their critical sections whenever needed, as given below. The initial values of shared boolean variables S1 and S2 are randomly assigned.
Method Used by P1
while (S1 == S2) ;
Critica1 Section
S1 = S2;
Method Used by P2
while (S1 != S2) ;
Critica1 Section
S2 = not (S1);
Which one of the following statements describes the properties achieved?
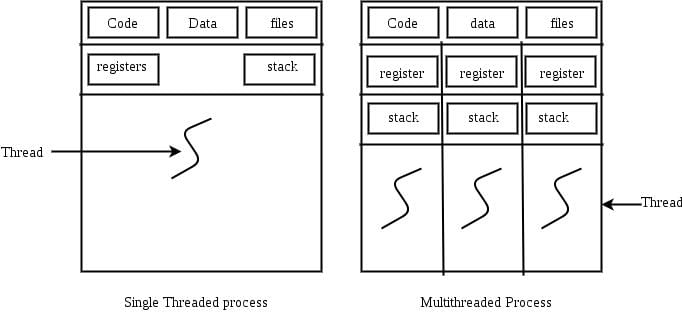
A thread is usually defined as a "light weight process" because an operating system (OS) maintains smaller data structures for a thread than for a process. In relation to this, which of the following is TRUE?
Consider the following statements about user level threads and kernel level threads. Which one of the following statement is FALSE?
Consider two processors P1 and P2 executing the same instruction set. Assume that under identical conditions, for the same input, a program running on P2 takes 25% less time but incurs 20% more CPI (clock cycles per instruction) as compared to the program running on P1. If the clock frequency of P1 is 1GHz, then the clock frequency of P2 (in GHz) is _________.
Barrier is a synchronization construct where a set of processes synchronizes globally i.e. each process in the set arrives at the barrier and waits for all others to arrive and then all processes leave the barrier. Let the number of processes in the set be three and S be a binary semaphore with the usual P and V functions. Consider the following C implementation of a barrier with line numbers shown on left.
void barrier (void) {
1: P(S);
2: process_arrived++;
3. V(S);
4: while (process_arrived !=3);
5: P(S);
6: process_left++;
7: if (process_left==3) {
8: process_arrived = 0;
9: process_left = 0;
10: }
11: V(S);
}
The variables process_arrived and process_left are shared among all processes and are initialized to zero. In a concurrent program all the three processes call the barrier function when they need to synchronize globally. The above implementation of barrier is incorrect. Which one of the following is true?
An operating system implements a policy that requires a process to release all resources before making a request for another resource. Select the TRUE statement from the following:
Consider the following C code for process P1 and P2. a=4, b=0, c=0 (initialization)
P1 P2
if (a < 0) b = 10;
c = b-a; a = -3;
else
c = b+a;
If the processes P1 and P2 executes concurrently (shared variables a, b and c), which of the following cannot be the value of ‘c’ after both processes complete?
If the time-slice used in the round-robin scheduling policy is more than the maximum time required to execute any process, then the policy will
Which of the following actions is/are typically not performed by the operating system when switching context from process A to process B?