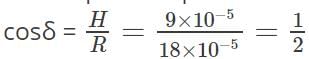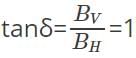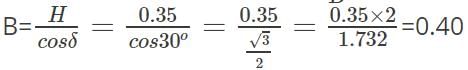Test: Earth's Magnetism - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Earth's Magnetism
How many quantities are required to specify the magnetic field of the earth?
Which of the following is the definition for magnetic meridian of Earth?
The Earth always have both horizontal and vertical components everywhere.
Identify the expression for horizontal component from the following.
At the magnetic North Pole of the Earth, what is the value of the angle of dip?
At a given place on the Earth’s surface, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is 9 × 10-5 T and the resultant magnetic field is 180 × 10-6. Calculate the angle of dip at this place.
The angle of dip at a certain place on Earth is 30o and the magnitude of Earth’s horizontal component of magnetic field is 0.35 G. Find the magnetic field at that place on Earth.
What is the relation between angle of dip and magnetic latitude?