UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 15 (Old Pattern) - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC GS I Practice Test - 15 (Old Pattern)
Consider the following pairs :
National Park Location
1. Buxa National Park - Jharkhand
2. Indravati National Park - Karnataka
3. Rajaji National Park - Uttarakhand
Which of the pairs mentioned above are incorrectly matched?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Where was the declaration of the Queen of Britain read on 1 November 1858 AD?
The Kanpur Bolshevik Conspiracy Case case was against the leaders of which movement?
Concerning the Udaygiri-Khandagiri caves, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. They are examples of the rock-cut cave tradition.
2. These caves have inscriptions of Kharavela kings.
3. The caves were primarily meant for Buddhist monks.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Where was sustainable development explained for the first time?
Consider the following events associated with reference to the Round Table Conferences held in the early 1930s:
A) Gandhi-Irwin pact
B) First Round Table Conference
C) Poona Pact
D) Communal Award
Which of the following is the correct sequence in chronological order of the given events.
Consider the following agricultural practices:
1. Contour bunding
2. Relay cropping
3. Zero tillage
In the context of global climate change, which of the above helps/helps in carbon sequestration/storage in the soil?
What is the magnitude of the maximum disturbance in the medium on either side of the mean value called?
A body of frozen gases, rock and dust traveling in an elongated orbit around the Sun is called:
Who led the archeological digging of Paleolithic culture in Uttar Pradesh?
Creation and Harmonious Application of Modern Processes for Increasing the Output and National Strength (CHAMPIONS), recently seen in news, aims to empower which of the following?
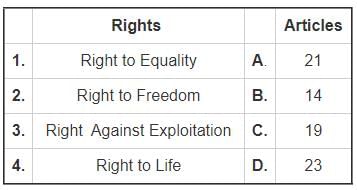
Which one of the following objectives is not embodied in the Preamble to the Constitution of India?
Consider the following statements regarding the Partition Of Bengal :
1. As per Lord Curzon, after the partition, the two provinces would be Bengal (including modern West Bengal, Odisha and Bihar) and Eastern Bengal and Assam.
2. Bengal would also lose five Hindi-speaking states to the Central Provinces.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
The National Highway which is also called the Grand Trunk Road, connects which of the following pair of cities?
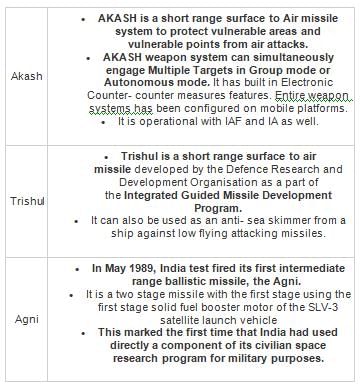
Which of the following is the first surface to surface ballistic missile of India?
Which among the following is the common basin state of Krishna and Kaveri rivers?
1. Karnataka
2. Kerala
3. Tamil Nadu
Which one of the following names is NOT related to economic theory?
Mention the correct data of the last meeting of the Constituent Assembly of India.
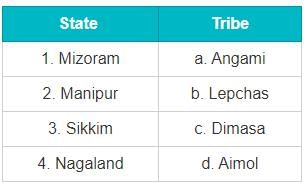
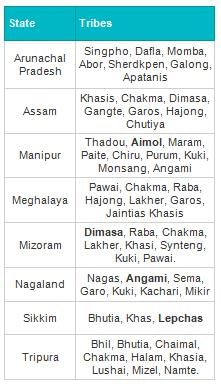
In which state is the 'Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra' located?
With reference to characteristics of natural vegetation in India, consider the following statements:
1. These are a mixture of trees and grasses.
2. Mean annual temperature of about 27°C.
3. Annual rainfall is 100 cm to 200 cm.
4. Teak, sal, shisham, hurra, mahua, amla.
Which of the following forests is best characterised by the features given above?
Which of the following is NOT based on the heating effect of current?
Consider the following statements regarding the Causes of Polluted River Stretches:
1. Rapid urbanisation and lack of efficient waste disposal systems.
2. Industrial Cities on the banks of rivers.
3. Run-off from agricultural activities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
On the bank of which river was Harappa situated?
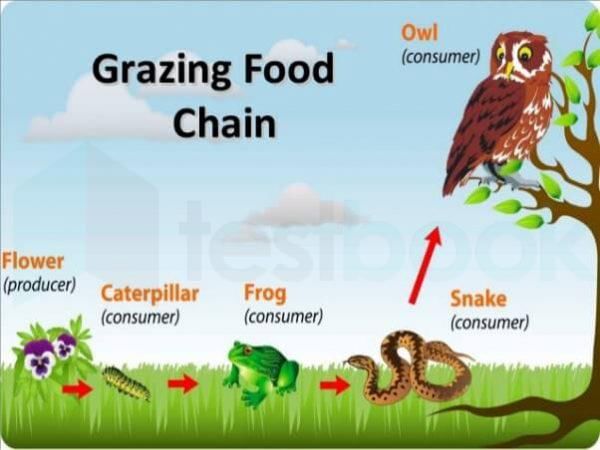
With reference to the food chains in ecosystems, which of the following kinds of an organism is/are known as decomposer organism/organisms?
1. Virus
2. Fungi
3. Bacteria
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Examine the following statements:
A. The non-cooperation movement brought all sections of Indians into the freedom struggle.
B. Violent incident took place at Chauri-Chaura
Choose the correct answer:
According to the 2011 census, what is the percentage of literacy of male in Uttar Pradesh?
Consider the following statements regarding Climate Adaptation Summit 2021.
1. The Indian government hosted an online international Climate Adaptation Summit (CAS Online) on 25 January 2021.
2. The summit will have a significant focus on securing new investments to ensure that millions of smallholder farmers can adapt to the stresses of climate on food production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?