Case Based Questions Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - 2 - NEET MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - 2
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
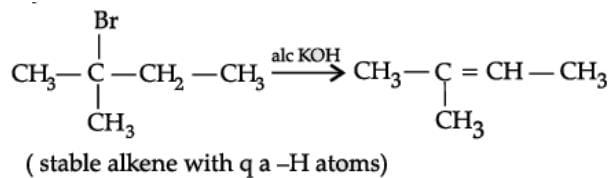
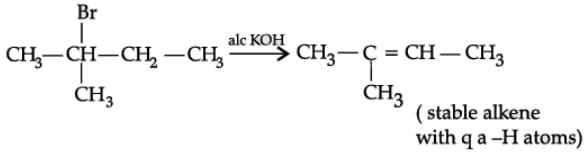
Q. Name the major monohalo product of the following reaction:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. Name the major monohalo product of the following reaction:

Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction?
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. Complete the reaction:
H3C-Br + AgF →
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. Complete the reaction:
H3C-Br + AgF →
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
Q. 2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of –OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
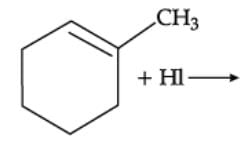
Q. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image (like a pair of hands) are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active, while the objects, which are, superimposable on their mirror images are called achiral. These molecules are optically inactive. The above test of molecular chirality can be applied to organic molecules by constructing models and its mirror images or by drawing three dimensional structures and attempting to superimpose them in our minds. There are other aids, however, that can assist us in recognising chiral molecules. One such aid is the presence of a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Q. In this questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given . Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): A racemic mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportions will have zero optical rotation.
Reason (R): This is because the rotation due to one isomer will be cancelled by the rotation due to the other isomer.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image (like a pair of hands) are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active, while the objects, which are, superimposable on their mirror images are called achiral. These molecules are optically inactive. The above test of molecular chirality can be applied to organic molecules by constructing models and its mirror images or by drawing three dimensional structures and attempting to superimpose them in our minds. There are other aids, however, that can assist us in recognising chiral molecules. One such aid is the presence of a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Q. In this questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given . Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): Propan-2-ol is an achiral molecule.
Reason (R): Carbon is called asymmetric carbon or stereocentre.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image (like a pair of hands) are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active, while the objects, which are, superimposable on their mirror images are called achiral. These molecules are optically inactive. The above test of molecular chirality can be applied to organic molecules by constructing models and its mirror images or by drawing three dimensional structures and attempting to superimpose them in our minds. There are other aids, however, that can assist us in recognising chiral molecules. One such aid is the presence of a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Q. In this questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given . Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): The stereoisomers related to each other as non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers
Reason (R): Enantiomers possess identical physical properties.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image (like a pair of hands) are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active, while the objects, which are, superimposable on their mirror images are called achiral. These molecules are optically inactive. The above test of molecular chirality can be applied to organic molecules by constructing models and its mirror images or by drawing three dimensional structures and attempting to superimpose them in our minds. There are other aids, however, that can assist us in recognising chiral molecules. One such aid is the presence of a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Q. In this questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given . Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): Butan-2-ol is a chiral molecule.
Reason (R): It has 4 different groups attached to carbon atom.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the following reasons:
(i) In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
(ii) In haloalkane, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp3 hybridised while in case of haloarene, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp2 -hybridised.
(iii) In case of haloarenes, the phenyl cation formed as a result of self-ionisation will not be stabilised by resonance.
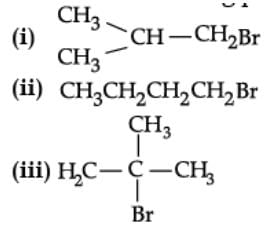
Q. Which of the following alkyl halides will undergoes SN1 reaction most readily?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the following reasons:
(i) In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
(ii) In haloalkane, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp3 hybridised while in case of haloarene, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp2 -hybridised.
(iii) In case of haloarenes, the phenyl cation formed as a result of self-ionisation will not be stabilised by resonance.
Q. Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows _______.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the following reasons:
(i) In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
(ii) In haloalkane, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp3 hybridised while in case of haloarene, the carbon atom attached to halogen is sp2 -hybridised.
(iii) In case of haloarenes, the phenyl cation formed as a result of self-ionisation will not be stabilised by resonance.
Q. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ________.