Case Based Questions Test: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - NEET MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
What are the compounds(Z)
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
What are the compounds(Z)
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. Write chemical equations leading to the conversion of 'X' to 'Y'.
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. Write chemical equations leading to the conversion of 'X' to 'Y'.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. The compound (X) is an
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. The compound (X) is an
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. Compound (Y) is
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Q. Compound (Z) is
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They act both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O-H is broken when alcohols act as nucleophiles.
(i) Alcohols as nucleophiles
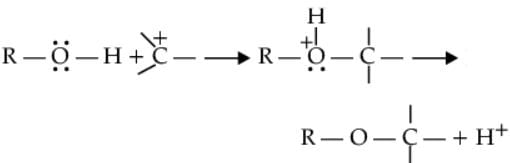
(ii) The bond between C-O is broken when they act as, electrophiles. Protonated alcohols react in this manner.
Protonated alcohols as electrophiles
R-CH2-OH+H→R-CH2+OH2
Based on the cleavage of O-H and C-O bonds, the reaction of alcohols and phenols may be divided into two groups :
(a) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond
(b) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond
Acidity of alcohols and phenols
(i) Reaction with metals :Alcohols and phenols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium and aluminium to yield corresponding alkoxide/ phenoxides and hydrogen.

Q. Name the following reaction:
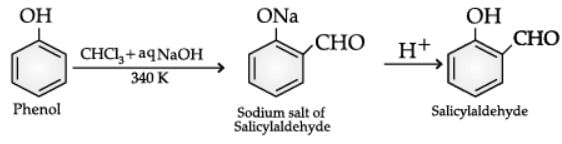
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They act both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O-H is broken when alcohols act as nucleophiles.
(i) Alcohols as nucleophiles

(ii) The bond between C-O is broken when they act as, electrophiles. Protonated alcohols react in this manner.
Protonated alcohols as electrophiles
R-CH2-OH+H→R-CH2+OH2
Based on the cleavage of O-H and C-O bonds, the reaction of alcohols and phenols may be divided into two groups :
(a) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond
(b) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond
Acidity of alcohols and phenols
(i) Reaction with metals :Alcohols and phenols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium and aluminium to yield corresponding alkoxide/ phenoxides and hydrogen.

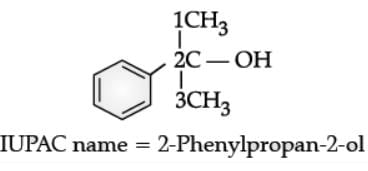
Q. Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:

Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They act both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O-H is broken when alcohols act as nucleophiles.
(i) Alcohols as nucleophiles

(ii) The bond between C-O is broken when they act as, electrophiles. Protonated alcohols react in this manner.
Protonated alcohols as electrophiles
R-CH2-OH+H→R-CH2+OH2
Based on the cleavage of O-H and C-O bonds, the reaction of alcohols and phenols may be divided into two groups :
(a) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond
(b) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond
Acidity of alcohols and phenols
(i) Reaction with metals :Alcohols and phenols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium and aluminium to yield corresponding alkoxide/ phenoxides and hydrogen.

Q. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They act both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O-H is broken when alcohols act as nucleophiles.
(i) Alcohols as nucleophiles

(ii) The bond between C-O is broken when they act as, electrophiles. Protonated alcohols react in this manner.
Protonated alcohols as electrophiles
R-CH2-OH+H→R-CH2+OH2
Based on the cleavage of O-H and C-O bonds, the reaction of alcohols and phenols may be divided into two groups :
(a) Reactions involving cleavage of O-H bond
(b) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O bond
Acidity of alcohols and phenols
(i) Reaction with metals :Alcohols and phenols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium and aluminium to yield corresponding alkoxide/ phenoxides and hydrogen.

Q. Given the descending order of acid strength of alcohols.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Oxidation of alcohols involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen double bond with cleavage of an O-H and C-H bonds.
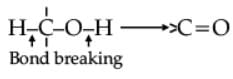
Such a cleavage and formation of bonds occur in oxidation reactions. These are also known as dehydrogenation reactions as these involve loss of dihydrogen from an alcohol molecule. Depending on the oxidising agent used, a primary alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde which in turn is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Strong oxidising agents such as acidified potassium permanganate are used for getting carboxylic acids from alcohols directly. CrO3 in anhydrous medium is used as the oxidising agent for the isolation of aldehydes.
Assertion (A): CH3CH2OH can be converted into CH3CHO by treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate.
Reason (R): PCC is a better reagent for oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Oxidation of alcohols involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen double bond with cleavage of an O-H and C-H bonds.
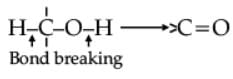
Such a cleavage and formation of bonds occur in oxidation reactions. These are also known as dehydrogenation reactions as these involve loss of dihydrogen from an alcohol molecule. Depending on the oxidising agent used, a primary alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde which in turn is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Strong oxidising agents such as acidified potassium permanganate are used for getting carboxylic acids from alcohols directly. CrO3 in anhydrous medium is used as the oxidising agent for the isolation of aldehydes.
Assertion (A): Vapours of primary and secondary alcohols are passed through heated copper an aldehyde and ketone are formed.
Reason (R): It’s a dehydration reaction.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Oxidation of alcohols involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen double bond with cleavage of an O-H and C-H bonds.
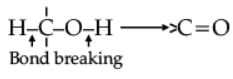
Such a cleavage and formation of bonds occur in oxidation reactions. These are also known as dehydrogenation reactions as these involve loss of dihydrogen from an alcohol molecule. Depending on the oxidising agent used, a primary alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde which in turn is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Strong oxidising agents such as acidified potassium permanganate are used for getting carboxylic acids from alcohols directly. CrO3 in anhydrous medium is used as the oxidising agent for the isolation of aldehydes.
Assertion (A): Dehydrogenation reaction of alcohols is an oxidising reaction.
Reason (R): It involves loss of dihydrogen from alcohol.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Oxidation of alcohols involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen double bond with cleavage of an O-H and C-H bonds.
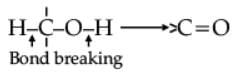
Such a cleavage and formation of bonds occur in oxidation reactions. These are also known as dehydrogenation reactions as these involve loss of dihydrogen from an alcohol molecule. Depending on the oxidising agent used, a primary alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde which in turn is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Strong oxidising agents such as acidified potassium permanganate are used for getting carboxylic acids from alcohols directly. CrO3 in anhydrous medium is used as the oxidising agent for the isolation of aldehydes.
Assertion (A): Tertiary alcohols do not undergo oxidation reactions.
Reason (R): They do not have the required C-H bond.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
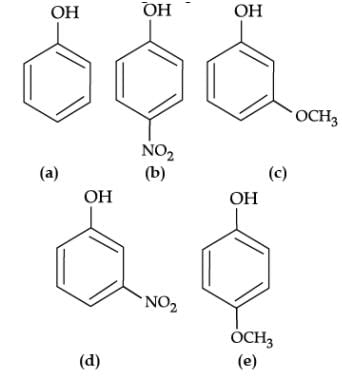
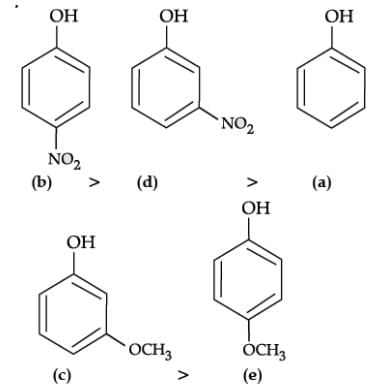
Q. Which of the following is most acidic?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
Q. Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reaction with _____
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
Q. Phenol is less acidic than_________.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.