Case Based Questions Test: How do Organisms Reproduce? - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: How do Organisms Reproduce?
Read the following passage and answer the question :
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth
and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
Q. What should be maintained for a healthy society?
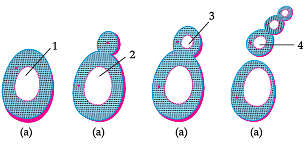
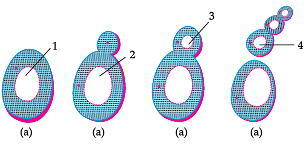
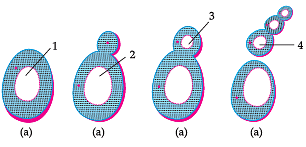
Study the diagram given below and answer the question given below :
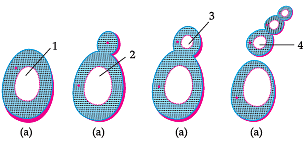
The above process.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Study the diagram given below and answer the question given below :
Q. A Planaria worm is cut horizontally in the middle into two halves P and Q such that the part P contains the whole head of the worm. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and S in such a way that both the cut pieces R and S contain half head each. Which of the cut pieces of the two Planaria worms could regenerate to form the complete respective worms?

Study the diagram given below and answer the question given below :
Q. Which organism uses the above method for reproduction?
Study the diagram given below and answer the question given below :
Q. Among the following select the statements that are true regarding the sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
(1) Fertilisation is a compulsory event
(2) It always results in the formation of zygote
(3) Offsprings formed are clones
(4) It requires two types of gametes
Study the diagram given below and answer the question given below :
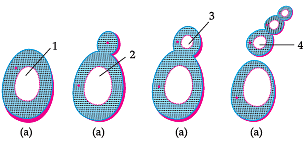
Q. An organism capable of reproducing by two asexual reproduction methods one similar to the reproduction in yeast and the other similar to the reproduction in Planaria is:
Study the process depicted in the picture given below and answer the questions :
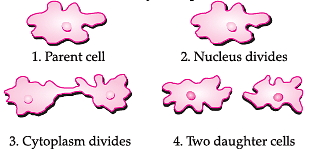
Q. Which of these organisms divides by the above process?
Study the process depicted in the picture given below and answer the questions :
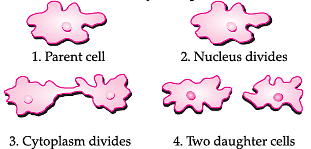
Q. Which of the following statements is correct about the above type of reproduction?
Study the process depicted in the picture given below and answer the questions :
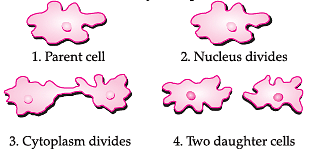
Q. Which of these are the characteristics of vegetative reproduction?
I. Involves two individuals
II. Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent.
III. The cell division is only mitotic.
Study the given diagram and answer any four questions from (a) to (e) as given below :
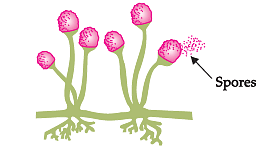
Q. Which of these plants reproduces in the same way as the given process?
Study the given diagram and answer any four questions from (a) to (e) as given below :
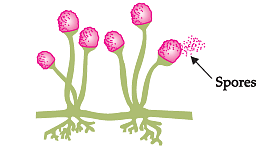
Q. The above diagram depicts:
The given diagram represents the structure of a flower. Study the structure and answer the question:
A student decides to study the impact of removing certain flower parts on fruit formation in plant species X. He chooses three separate plants that are growing in the same plot under uniform conditions. The data is given in the table below.
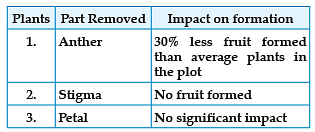
Q. Which of the following can be inferred from the above data?
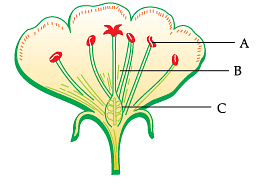
The given diagram represents the structure of a flower. Study the structure and answer the question:
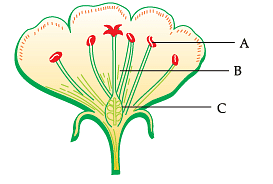
Q. The labels A, B and C are
The given diagram represents the structure of a flower. Study the structure and answer the question:
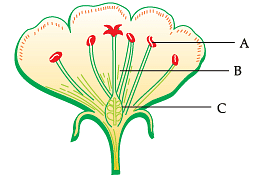
Q. When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles from the little stalks in the flowers stick to its body and when this insect sits on the flower of another plant, the particles get deposited in that flower. What are these particles?
The given diagram represents the structure of a flower. Study the structure and answer the question:
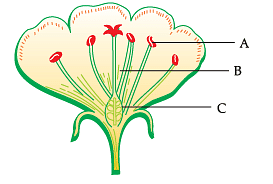
Q. Which of these is the function of a part labelled as C?
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions:
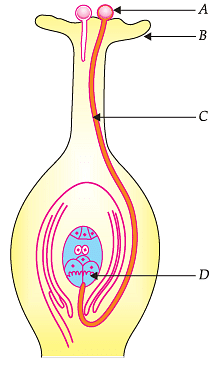
Q. Choose the incorrect statements about the reproductive system of a plant?
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions:
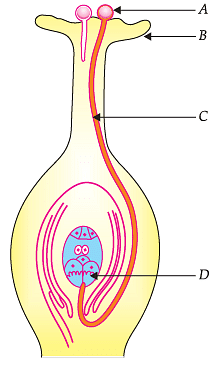
The part labelled as A in the diagram is:
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions:
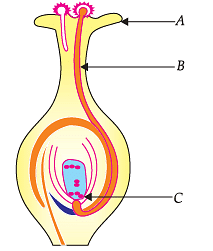
Q. How many male gametes are produced by each pollen grain?
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions:
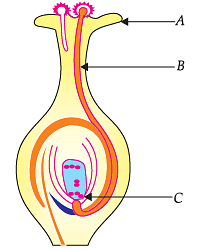
The part labelled as A is:
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions:
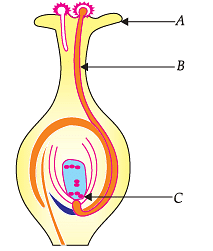
The role of part labelled as B is:

















