Test: The Theory of the Firm under Perfect Competition- Match Based Type Questions - Commerce MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test - Test: The Theory of the Firm under Perfect Competition- Match Based Type Questions
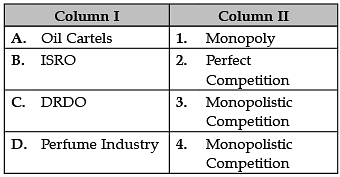
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
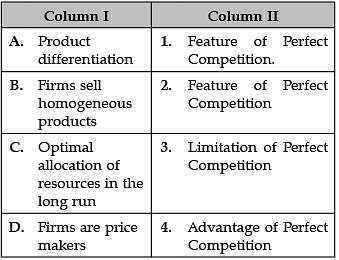

Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
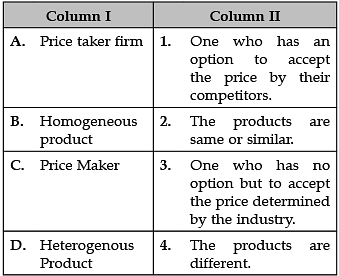
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
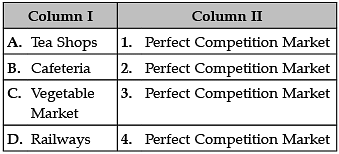

Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
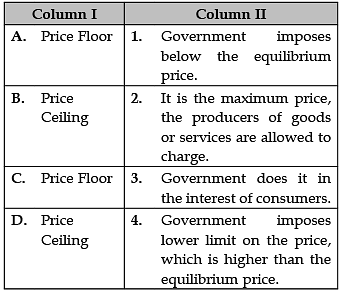
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
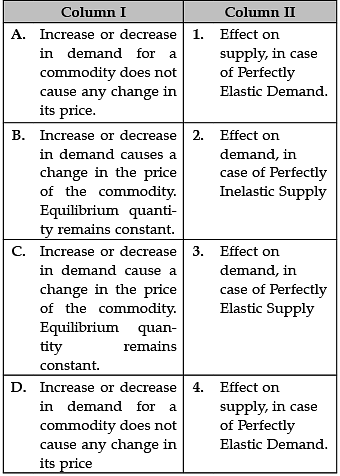
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
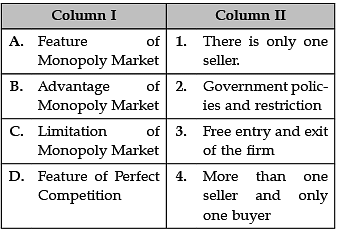
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
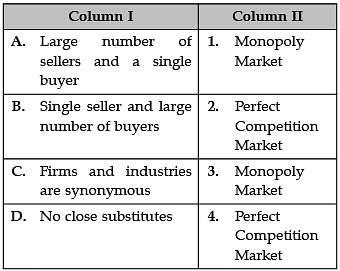
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
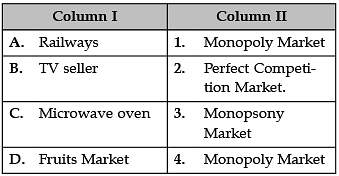
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
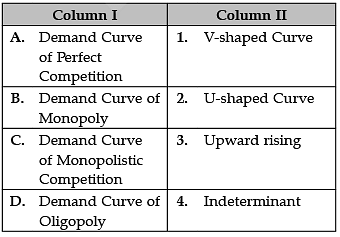
Identify the correctly matched examples from Column I to that of Column II:
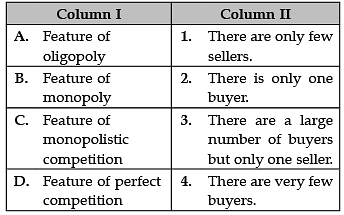
Identify the correctly matched statements from Column I to that of Column II:
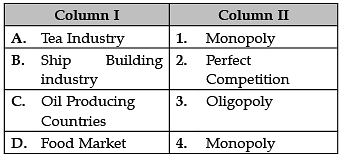
Oligopoly: The distinctive feature of an oligopoly is interdependence. Oligopolies are typically composed of a few large firms. Each firm is so large that its actions affect market conditions. Therefore, the competing firms will be aware of a firm's market actions and will respond appropriately.
Identify the correctly matched examples from Column I to type of market from Column II:
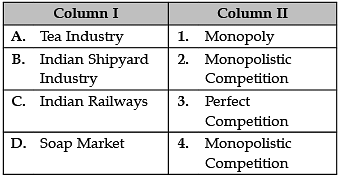
Identify the correctly matched features from Column I to that of Column II:
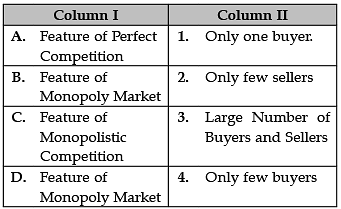
Identify the correctly matched statements from the Column I to that of Column II: