Case Based Questions Test: Manufacturing Industries - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Manufacturing Industries
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive to each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Manufacturing industries fall in _________ and agriculture in ___________ .
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive to each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Which of the following options does not help in modernising agriculture?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive to each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. In order to attract foreign manufacturing firms, a country needs to develop:
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive to each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Manufacturing provides job opportunities to reduce dependence on agriculture. Identify which sector the following jobs belong to:
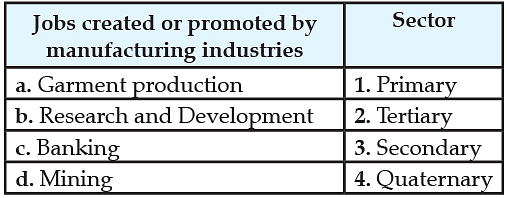
Choose the correct option:
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry since all the other industries — heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods. Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky, entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4 : 2 : 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel. Where should the steel plants be ideally located? Remember that the finished products also need an efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers. In 2016 with 95.6 million tonnes of crude steel production, India ranked 3rd among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge iron. In 2016 per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 63 kg per annum against the world average of 208 kg.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Which industry is called the basic industry of India?
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry since all the other industries — heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods. Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky, entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4 : 2 : 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel. Where should the steel plants be ideally located? Remember that the finished products also need an efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers. In 2016 with 95.6 million tonnes of crude steel production, India ranked 3rd among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge iron. In 2016 per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 63 kg per annum against the world average of 208 kg.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Explain the process of manufacturing of steel. Choose the correct option:
(i) Pig iron
(ii) Blast furnace
(iii) Shaping metal
(iv) Steel making
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry since all the other industries — heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods. Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky, entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4 : 2 : 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel. Where should the steel plants be ideally located? Remember that the finished products also need an efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers. In 2016 with 95.6 million tonnes of crude steel production, India ranked 3rd among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge iron. In 2016 per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 63 kg per annum against the world average of 208 kg.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Manufacturing steel is not every person's business. Suppose you are working in a steel industry, what will be the proportion of Iron Ore, coking coal and limestone you would use to produce steel?
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry since all the other industries — heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods. Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky, entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4 : 2 : 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel. Where should the steel plants be ideally located? Remember that the finished products also need an efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers. In 2016 with 95.6 million tonnes of crude steel production, India ranked 3rd among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge iron. In 2016 per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 63 kg per annum against the world average of 208 kg.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Index of a country is regarded on what basis? Select the appropriate option:
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced ? Some suggestions are-
(i) minimising the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(ii) harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(iii) treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(a) Primary treatment by mechanical means it involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(b) Secondary treatment by biological process.
(c) Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water.
Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. How many treatments are there for industrial effluents?
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced ? Some suggestions are-
(i) minimising the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(ii) harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(iii) treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(a) Primary treatment by mechanical means it involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(b) Secondary treatment by biological process.
(c) Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water.
Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with _______concerns.
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced ? Some suggestions are-
(i) minimising the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(ii) harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(iii) treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(a) Primary treatment by mechanical means it involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(b) Secondary treatment by biological process.
(c) Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water.
Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. _______ treatment involves biological, chemical and physical processes.
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced ? Some suggestions are-
(i) minimising the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(ii) harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(iii) treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(a) Primary treatment by mechanical means it involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(b) Secondary treatment by biological process.
(c) Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water.
Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones. The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. What could be done to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment?
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, power-looms came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill-made cloth from England. In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation. This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works. While spinning continues to be centralised in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc. India has world class production in spinning, but weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the high-quality yarn produced in the country. Weaving is done by handloom, power loom and in mills. The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Why did our traditional industries suffer a setback during the colonial period?
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, power-looms came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill-made cloth from England. In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation. This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works. While spinning continues to be centralised in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc. India has world class production in spinning, but weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the high-quality yarn produced in the country. Weaving is done by handloom, power loom and in mills. The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc., contributed towards its localisation.
Read the text given below and answer the questions that follows:
In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, power-looms came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill-made cloth from England. In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation. This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works. While spinning continues to be centralised in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc. India has world class production in spinning, but weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the high-quality yarn produced in the country. Weaving is done by handloom, power loom and in mills. The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Q. Weaving is done by:

















