Test: Sexual Reproduction (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Sexual Reproduction (Old NCERT)
Which of the following groups is formed only of the hermaphrodite organisms?
Which of the following is a dioecious organism?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
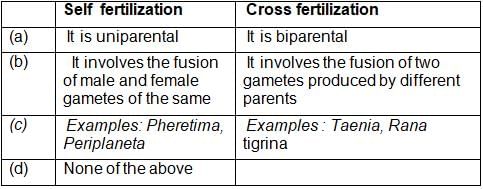
Following table summarizes the differences between self fertilization and cross-fertilization. Pick out the wrong difference.

It is observed that simple organisms like algae and fungi normally reproduce asexually but before the onset of adverse conditions they shift to sexual reproduction. It is so because sexual reproduction
The growth phase of an organism before attaining sexualmaturity is referred to as
Clear cut vegetative, reproductive and senescent phases cannot be observed in
Given figure of Hydra shows its reproductive structures and manner of fertilition
Organisms reproducing throughout the year are called ______ breeders e.g., ________, and those who show recurring sexual activity are called __________ breeders e.g., _________.
Strobilanthus Kunthiana differs from bamboo in
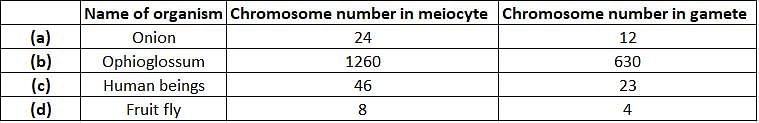
Which of the following is an incorrect combination of organism with its chromosome number in meiocyte and in gamete?
Read the following statements and select the correct option
Statement 1: In gymnosperms, endosperm is formed before fertilization and is haploid.
Statement 2: In angiosperms, endosperm is formed after fertilization and is diploid.
If a leaf cell of Agave has x chromosomes then what will be the number of chromosomes in a cell of its bulbil?
The changes that indicate reproductive maturity in humans include
Read the following statements about the reproductive cycles in mammals and select the correct ones.
(i) Oestrous cycle occurs in primate mammals
(ii) in species with oestrous cycle females are generally sexually active during estrous phase
iii) Both the cycles show monthly recurrence.
Senescent phase of an organism's life span can be recognized
If a leaf cell of Agave has x chromosomes then what will be the number of chromosomes in a cell of its bulbil?
A diploid parent plant body produces ______________gametes and a haploid parent piant body produces ___________ gametes.
Which of the following options shows bisexual animals only?
Which of the following organisms has the highest number of chromosomes?
In maize, a meiocyte has 20 chromos. What will be the number of chromosomes in its somatic cell ?
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding sexuality in organisms?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Honey bees often pollinate red coloured flowers.
Statement 2: Honey bees visit flowers for pollen grains only
If a fungal thallus has both male and female reproductive structure, it will be called
Sexual reproduction is considered more beneficial than asexual reproduction because
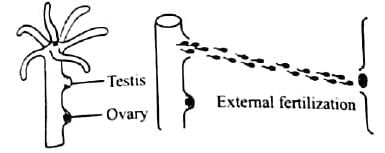
Select the incorrect statement about external fertilization.
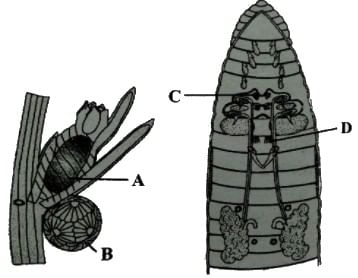
Figure P represents the reproductive organs of Chara plant and figure Q represents the reproductive organs of earthworm. Select the optikon which correctly identifies male reproductive organs of the two organisms.