Test: Digestion of Nutrients (Old NCERT) - JAMB MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Digestion of Nutrients (Old NCERT)
The site of action and substrate of rennin are respectively
The enzyme enterokinase helps in the conversion of
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
During prolonged fasting, in what sequence are the following organic compounds used up by the body:
Which one of the following is the correct matching of the site of action on the given substrate, the enzyme acting upon it and the end product?
Which one of the following pairs of food components in humans reaches the stomach totally undigested?
A child took sugarcane and sucked its juice. Regarding this which of the following match is correct?
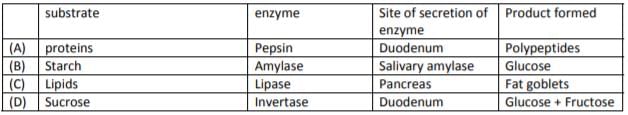
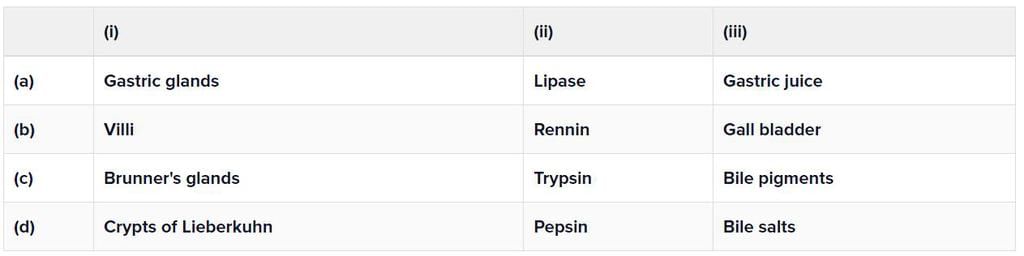
Fill in the blanks in following table by selecting the correct options
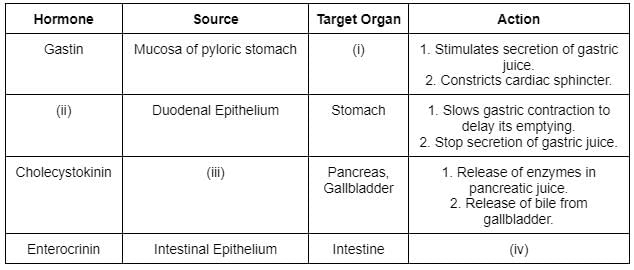
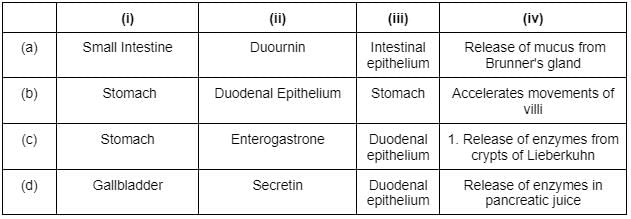
Which of the following food components will be affected if the pH of the stomach is made 7?
Which of the following is incorrectly represented?
Which of the options given below would not correctly fill the blanks in the following sentence?
In order to absorb and use _______ by the body, these must be broken down by hydrolysis into ______.
Digestion of proteins begins in the (i) and digestion of polysaccharides begins in the (ii)

Which of the following processes is helped by bile salts?
The food mixes thoroughly with the acidic gastric juice of the stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall. What do we call the food then?
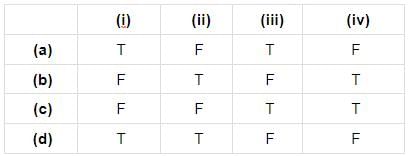
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) Salivary amylase hydrolyses proteins to amino acids.
(ii) Pancreatic amylase hydrolyses polysaccharides to disaccharides.
(iii) Enteropeptidase activates pepsinogen to pepsin.
(iv) Trypsin coagulates the milk protein casein.
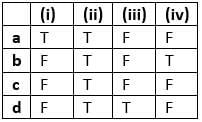
Mark the odd one in each series and select the correct option
(i) Villi, Brunner's glands, crypts of Lieberkuhn, gastric glands
(ii) Pepsin, lipase, trypsin, rennin
(iii) Bile salts, bile pigments, gall bladder, gastric juice
Consider the following four statements. and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) The stomach has the lowest pH.
(ii) The liver contains lipid emulsifier.
(iii) Large intestine secretes many enzymes.
(iv) All proteases function in the lumen of small intestine.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Deglutition starts as a reflex and then continues by voluntary action.
Statement 2 : Oesophagus has smooth muscles in the beginning and striated muscles In the rest of its wall.
Which part of the mammalian alimentary canal does not secrete any enzyme?
If pH of stomach is 1.6 then which enzyme will digest protein?
If you chew on a piece of bread long enough, it will begin to taste sweet because
Which category of compound is the most concentrated energy source?
Read the following statement and select the correct option
Statement 1: Athletes, labourers doing heavy work and mountaineers should live on high- carbohydrate diets
Statement 2: Carbohydrates need less resparatory oxygen for their oxidation than other foods
A young infant may be feeding entirely on mother's milk which is white in colour but the stools which the infant passes out is quite yellowish. The yellow colour of stool is due to
Which of the following is the function of enterogastrone?
One of the constituents of the pancreatic juice which is poured into the duodenum in humans is
The contraction of gall bladder is due to


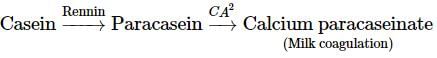
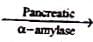 Maltose + Isomaltose + 'Limit' dextrins
Maltose + Isomaltose + 'Limit' dextrins
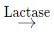 Glucose + Galactose
Glucose + Galactose














