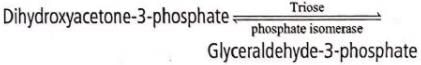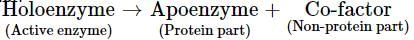Test: Enzymes (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Enzymes (NCERT)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
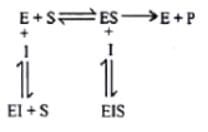
A.
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of
Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and co-factor.
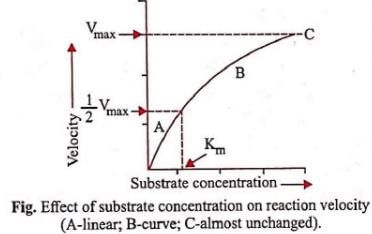
Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic activity and substrate concentration (S)?
An enzyme extract, when subjected to electric field, separates into two fractions, each catalysing the same reaction. These fractions are:
Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
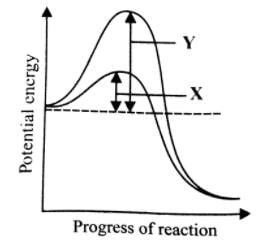
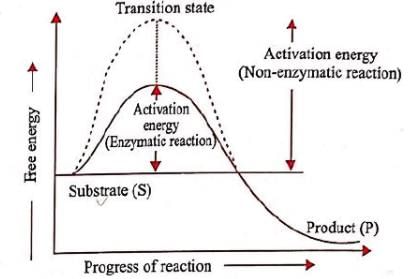
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.