Test: Water Absorption (Old NCERT) - Grade 12 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Water Absorption (Old NCERT)
In ____ pathway, water crosses at least two membranes for each cell in its path (i.e., plasma membrane on entering and exiting).
Stomata : Transpiration : : Hydathode : ______________
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
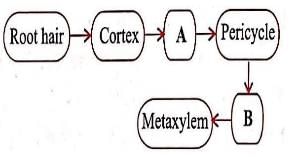
In the given flow chart, the flow of water is shown from soil to xylem of the root. Identify the tissues involved in steps A and B.

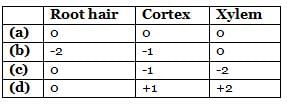
Water will move from the root hair through cortex if the water potentials are
In which of the following pathways, movement of water occurs from one cell to another cell through plasmodesmata?
In apoplast pathway, water moves exclusively through the
Concentration of minerals in the soil is usually ___________ than the concentration of minerals in the root.
In submerged hydrophytes, the absorption of water takes place through
If a soft stemmed plant is cut horizontally near the base of its stem with a sharp blade on early morning of a humid day, drop of solution ooze through cut stem. This is due to
Loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the margins and tips of leaves is called

















