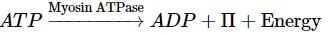Test: Mechanism of Muscle Contraction (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanism of Muscle Contraction (NCERT)
The slow twitch muscle fibres which are rich in myoglobin and have abundant mitochondria are
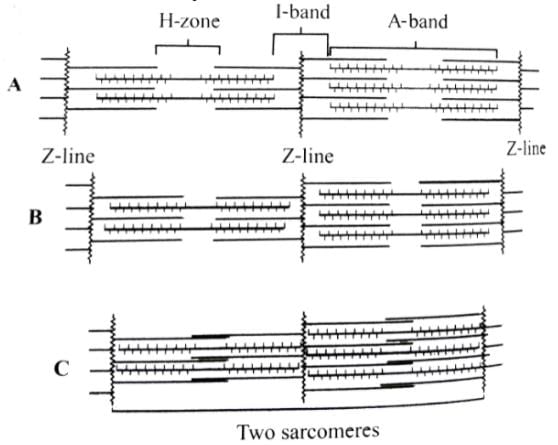
The figures given here represent three different conditions of sarcomeres. Identify these conditions and select the correct option.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is the contractile protein of a muscle?
If a stimulus, several times greater than the threshold stimulus is provided to a muscle fibre, it will
Which of the following ions help in muscle contraction?
In a muscle undergoes rapid contraction and relaxation, the sarcoplasmic reticulum extension
Which of the following is incorrect regarding muscle contraction?
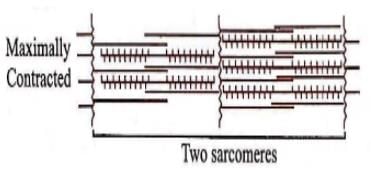
Which of the following is correct regarding changes in muscle fibre from relaxed to contracted state in the given figure?
In the resting muscle fibre, tropomyosin partially covers
Which one of the following options shown the next stage of muscle contraction after the stage given in question?
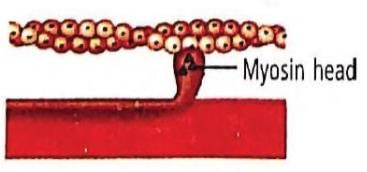
During muscular contraction, which of the following events occur?
(I) H-zoned is disappeared
(ii) A band widens
(iii) I band reduces in width
(iv) Width of A band is unaffected
(v) M line and Z line come closer.
Which of the following is the most abundant mineral element in the skeletal muscle?
Following is given a randomly arranged list of events that occur at neuromuscular junction to trigger muscle contraction.
(i) Receptor sites on sarcolemma
(ii) Nerve impulse
(iii) Release of Ca+2 from sarcoplasmic reticulum
(iv) The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released
(v) Sarcomere shortern
(vi) Synaptic cleft
(vii) Spread of impulses over sarcolemma on TT-tubules
Which of the following gives the correct sequence of these steps?
Which of the following is a source of energy for muscle contraction?