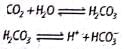Test: Exchange & Transport of Gases (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Exchange & Transport of Gases (NCERT)
What are the primary sites for the exchange of gases in the human body?
During CO2 transport, HCO3- diffuses from erythrocytes to plasma and in turn upsets the ionic balance momentarily. In order to keep the ionic balance, an equal number of Cl− pass into the erythrocytes from plasma. The process is known as
People living at sea level have around 5 million RBC per cubic millimetre of their blood whereas, those living at an altitude of 5400 metres have around 8 million. This is because at high altitude:
What is the term for the pressure contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of gases?
Why is the diffusion of CO2 more efficient than O2 in the body?
Identify the correct statement with reference to transport of respiratory gases by blood.
Which layers make up the diffusion membrane for gas exchange in the lungs?
Which of the following is true for CO2 concentration?
Which of the following statements is true about RBCs in humans?
The urge to inhale in humans results from
In which direction does the concentration gradient for oxygen exist in the body?
The factor which does not affect the rate of alveolar diffusion is
In humans, which of the following is not a step in respiration?
Which of the following is incorrect about the given graph?

Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : About 70% of CO2 that enters RBCs changes into HCO3- for transport in plasma to the lungs where it reconverts into CO2 for elimination.
Statement 2 : About 40% of CO2 that enters RBCs changes into carbaminohaemoglobin which releases O2 in the lungs.
Which of the following equations is correct?
The given graph shows an oxygen dissociation curve for haemoglobin.
Where in the body will haemoglobin be saturated at the percentages shown at points 1,2 and 3 on the graph?
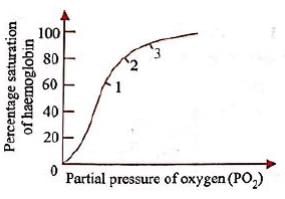
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) Expiration is normally brought about by the relaxation of inspiratory muscles.
(ii) Oxyhaemoglobin can hold much less carbon dioxide in the form of carbaminohaemoglobin than what deoxyhaemoglobin can.
(iii) A person can expel air the air from the lungs by a forceful expiration.
(iv) A rise in PCO2 increases the oxygen - affinity of haemoglobin.
Consider the following four statements (I - iv) and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) Formation of oxyhaemoglobin occurs on alveolar surface.
(ii) During gaseous exchange the gases diffuse from high particle pressure to low partial pressure.
(iii) Carbon dioxide cannot be transporteed width haemoglobin.
(iv) Earthworm respires through parapodia.
Carbon monoxide can kill a person because of it's extermely high affinity for
One haemoglobin carries how many molecules of O2?
Fetal haemoglobin has X affinity for oxygen than that of mother's haemoglobin during gestation. X is
The exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs takes place by
What factor affects the binding of carbon dioxide with haemoglobin?
The enzyme that increases the reaction rate between CO2 and H2O in red blood cell is
When temperature decreases, oxy-Hb curve becomes
During winter a person died during sleep, the room was closed and a container with burnt charcoal was found in the room. What may be the possible reason of his death?
The partial pressure of oxygen is maximum in
After taking a long deep breath we do not respire for some seconds due to
In which direction does the concentration gradient for carbon dioxide exist in the body?