Test: Colloids & Classification of Colloids (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Colloids & Classification of Colloids (Old NCERT)
The size of colloidal particles ranges between
Which of the following will not form a colloidal system?
Fog is an example of colloidal system of
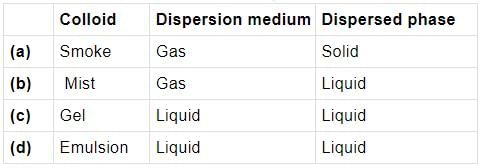
A colloidal system in which liquid is dispersed phase and solid is dispersion medium is classified as
Which of the following examples is correctly matched?
Mark the incorrect combination out of the following examples of colloidal solutions.
Lyophilic sols are also called reversible colloids because
Which of the following factors contribute towards higher stability of lyophilic colloid?
A lyophobic colloid cannot be formed by
Which of the following is not the correct difference between lyophobic and lyophillic sols?

Which of the following is not correctly matched?
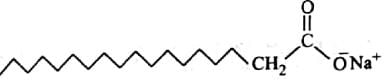
Substances which behave as normal electrolytes in solution at low concentration and exhibit colloidal properties at higher concentration are called
In these colloids, a large number of small atoms or smaller molecules of a substance aggregate to form colloidal particles having size in colloidal range. These colloids are known as
The substances which behave as colloidal solutions at higher concentration are called
The formation of micelles takes place only above
The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is defined as
At CMC (critical micelle concentration) the surface molecules:
In the given figure label the parts.
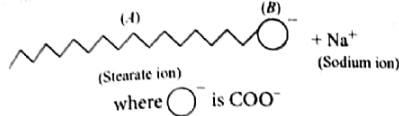
Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration behaves as
White of an egg whipped with water acts as
Colloidal solutions of metals like gold can be prepared when their salt solutions react with certain substances like SnCl2, formaldehyde, phenyl hydrazine, etc.
2AuCl3 + 3SnCl2 → 3SnCl4 + 2Ausol
The above method is an example of
In Bredigs arc method an electric arc is struck between the metal electrodes under the surface of water containing some stabilizing agent. The process involves
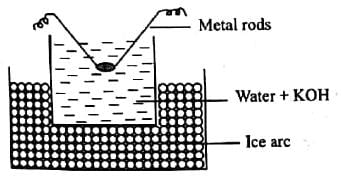
When a small quantity of FeCl3 solution is added to the fresh precipitate of Fe(OH)3, a colloidal sol is obtained. The process through which this sol is formed is known as
Which of the processes is being shown in the figure?
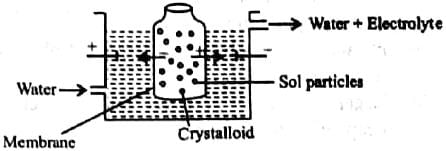
Which of the following is not a method of removing impurities from a colloidal sol?
Tyndall effect is observed only when
(i) the diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of the light used.
(ii) the refractive indices of dispersed phase and dispersion medium differ greatly in magnitude.
(iii) the size of the particles is generally between 10-11 and 10-9 m in diameter.
(iv) the dispersed phase and dispersion medium can be seen separately in the system.
When a colloidal solution is viewed from the direction at right angles of light beam, the path of the beam is illuminated due to scattering of light In the figure (A) and (B) are
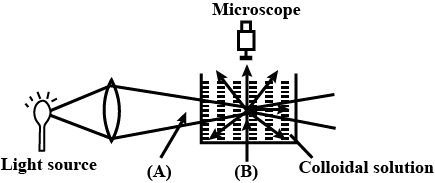
Tyndall effect is not observed in
Which of the following systems will show Tyndall effect?
The cause of Brownian movement which is not shown by true solutions or suspensions is due to