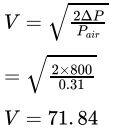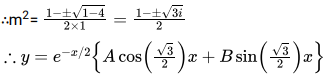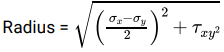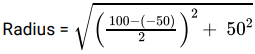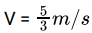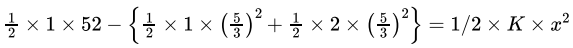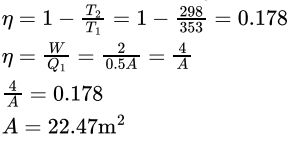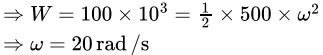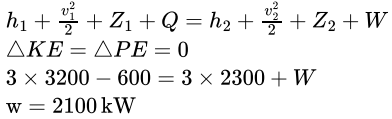Practice Test: Mechanical Engineering (ME)- 16 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Mechanical Engineering (ME)- 16
Direction: A sentence with one blank is given, indicating that something has been omitted. Choose the word that best fits the blank appropriately.
______ you have enough swimming practice, you will be able to swim well.
If price of an article increases from Rs 200 to Rs 240, when quantity demanded decreases from 1,000 units to 800 units. Find price elasticity of demand?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
With reference to India's freedom struggle consider the following statements:
1] In March 1940, the Muslim League passed a resolution committing itself to the creation of a separate nation called "Pakistan".
2] The "Salt Satyagraha" campaign began in August 1942.
3] Jayaprakash Narayan was a socialist member of the Congress and was active in the underground resistance during the Quit India Movement.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Choose the pair of words to be placed in the 2 blanks in the given sentence so that the completed sentence becomes meaningful.
After having been close friends for more than a decade, they had a _____ last year and have not _____ each other ever since.
A 200 × 100 × 50 mm3 steel block is subjected to a hydro-static stress of 15 MPa. The Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the material are 200 GPa and 0.3 respectively. The change in the volume of the block in mm3 is
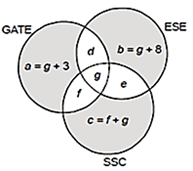
From a group of 61 students, each student appears for at least one of the 3 papers i.e. GATE, ESE or SSC. Out of the students appearing for SSC, the number of students appearing for ONLY SSC is equal to the number of students who also appear for GATE. The number of students who appear for only GATE is 3 more than the number of students who appear for all 3; number of students who appear for ESE alone is higher than the previous number by 5. If 32 students appear for ESE and 36 students appear for exactly ONE exam, then the number of students appearing for all 3 exams are ______.
Raja and Joseph start from their school to walk towards their hostel. The distance covered by Raja in 3 steps is identical to the distance covered by Joseph in 4 steps while the time taken by both of them to cover a step is identical. At a particular instance of time when both of them had covered 800 steps each, the distance between them was 300 m. Now, Raja cuts down the length of his step by 1/3rd and Joseph increase the length of his step by 20% with time taken to cover a step by both remaining identical. Both will be at the same spot at the same time in ______ more steps.
In metals, resistivity is composed of two parts: one part is characteristic of the particular substance. The other part is due to
Direction: In the given questions, two statements are given followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to consider the two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. You have to decide which of the given conclusions, if any, follow from the given statements.
Statements :
(1) Best performance in Olympics fetches a gold medal.
(2) Player ‘X’ got gold medal but later was found to be using a prohibited drug.
Conclusions :
I. ‘X’ should be allowed to keep the gold medal.
II. Gold medal should be withdrawn.
They are expert statisticians and help the Black Belts in case of issues.
A pitot tube measures a differential pressure of 0.008 bar. What is the speed of the plane, if it is flying at a height of about 12000 m.? Take density of air at this height 0.31 kg/m3
Suppose a toy car is made by a group of students for analysing the effect of various forces in running a car. The car works with help of a slider crank mechanism fitted inside the toy car. The car moves with a constant angular velocity of 10 rad/s and the crank radius is 60 mm. If the mass of the slider is 0.2 kg. Find the hammer blow acting on the car that tends to lift the car vertically upward.
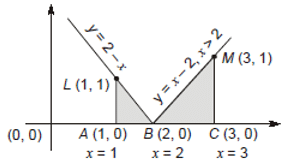
The area of the region bounded by the curves y = |x-2|, x = 1, x = 3 and the x-axis is __________.
The solution of the differential equation ![]() is
is
The demand for an item is 900 units per month and the lead time is 10 days. In the past two month, the maximum demand observed is 50 units per day. For a re-ordering system based on inventory level, the re-order level (in units) is
The solidification time for a spherical mould was 205 sec. If the radius of the mould is 5 cm, determine the mould constant.
The areas of ram and plunger of a hydraulic press are 40mm2 and 2 mm2 respectively. The plunger applies a force of 500N, determine the weight lifted based on the intensity of pressure measured at ram.
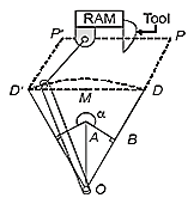
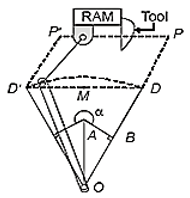
A Quick return mechanism is shown below. The value of α will be _________ (in degrees) stroke=60 cm Length of slotted lever = 50 cm
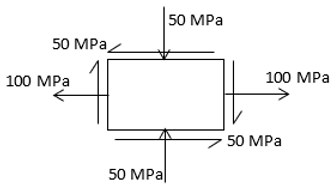
The state of stress is showing as a particular point in a stressed body. The diameter of the Mohr’s circle for this state of stress is.
Two blocks are on the frictionless surface as shown in fig. having mass 1 kg and 2 kg. The 1 kg block moves with a speed 5 m/s towards other block kept at rest. The spring is attached to 2 kg block and has a spring constant 60 N/m. The maximum compression of spring (in m) is

A heat exchanger is used to heat cold water (CP = 4.18 kJ/kg-K) entering at 15 °C at a rate of 1.2 kg/s by hot air (CP = 1.005 kJ/kg-K) entering at 90 °C at a rate of 2.5 kg/s. The highest rate of heat transfer in the heat exchanger is _____ kW.
What will be the transmission ratio of gear train?
Which of the following statement is incorrect
A solar collector receiving solar radiation at the rate of 0.5KW/m2 at temperature 80∘C and transforms it to a fluid within heat engine. The engine rejects energy as heat at temperature of 25∘C. The minimum collector area (in m2) if the plant produces 2KW of useful shaft power is
What will be the entropy change, if 1 kg of liquid water is heated from 25◦C to 100◦C. assuming constant specific heat, and compare the result with that found when using the given values.
Take: C = 4.184; sf20◦C = 0.2989 kJ/kg; sf90◦C = 1.2105 kJ/kg
Thermodynamic relation for the isothermal compressibility is
In an air standard cycle, indicated power is 80 KW and mechanical efficiency is 85%. Then the frictional power will be
Which of the following chemical formula is correct for the refrigerant designated as R12
If a body of 500 kg - m2 is rotating about its axis passing through the centre of mass and work done by the rotation of body is 100 kJ. Then the angular velocity of the body in rad/s will be
In a steady flow device, a liquid enters with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/s with enthalpy of 3200 kJ/kg. Heat lost to the environment is 600 kW. If the leaving fluid has an enthalpy of 2300 kJ/kg, calculate the work done in kW.