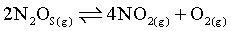Chemical Kinetics Test (20-12-2016) - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Kinetics Test (20-12-2016)
The value of the rate constant for the gas phase reaction,
2NO2 + F2 → 2NO2F is 38 dm3 mol-1 S-1 at 300 K. The order of the reaction.
The activation energy for a chemical reaction is independent upon:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Given that k is the rate constant for some order of any reaction at temperature. T, then the value of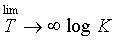 lin log k, [where A is the Arhenious constant ] is:
lin log k, [where A is the Arhenious constant ] is:
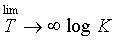 lin log k, [where A is the Arhenious constant ] is:
lin log k, [where A is the Arhenious constant ] is:Two different first order reaction have rate constant K1 and K2 at T1 (k1 > k2). If temperature is increased from T1 to T2, then new constants become K3 to K4 respectively: which among the following relation is correct?
The decomposition of N2O5 according to the equation,
N2O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Is a first order reaction. After 30 minutes from the start of the decomposition in a closed vessel, the total pressure developed is found to be 284.4 mmHg and on completion, the total pressure is 584.5 mmHg. Calculate the Rate constant of the reaction.
The addition of a catalyst to the reaction system
A monoatomic gas, X, adsorbed on a surface, follows Langmuir adsoption isotherm. A plot of the fraction of surface coverage, θ, against the concentration of the gas [X], for very low concentration fo the gas is described by the equation
Ozone depletion take place as:
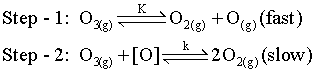
Order of Rxn will be:
Chemical reaction occurs as a result of collisions between reacting molecules. Therefore, the reaction rate is given by:
Which of the following factors are responsible for the increase in the rate of a surface catalysed reaction?
(I) A catalyst provides proper orientation for the reactant molecules to react.
(II) Heat of adsorption of reactants on a catalyst helps reactant molecules to overcome activation energy.
(III) The catalyst increases the activation energy of the reaction.
(IV) Adsorption increases the local concentration of reactant molecules on the surface of the catalyst.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
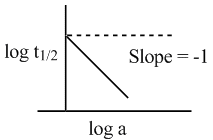
A graph between log t1/2 and log a (abscissa), a being the initial concentration of A in the reaction for reaction A → product, the rate law is:
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
A reaction rate constant is given by : 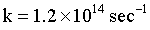 It means:
It means:
Consider the following statements, which statements is / are correct
The observed rate of a chemical reaction is substantially lower than the collision frequency. One or more of the following statements is/are true to account for this fact:
The reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → C(g) is an elementary reaction. In an experiment involving this reaction, the initial partial pressure of A and B are PA = 0.40 atm and PB = 1.0 atm respectively. When PC = 0.3 atm, the rate of the reaction relative to the initial rate is:
A certain zeroth order reaction has k = 0.025 M s-1 for the disappearance of A. what will be the concentration of A after 15s if the initial concentration is 0.50 M?
For a first order reaction, A→product, the rate of reaction at (A) = 0.2 mol-1 is 1.0 × 10-2 mol L-1 min-1 the half life period for the reaction is :
In a chemical reaction two reactants take part. The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one of them and inversely proportional to the concentration of the other. The order of the reaction is
The activation energy of a certain reaction is 87 kJ mol-1. What is the ratio of the rate constants for theis reaction when the temperature is decreased from 370C to 150C ?
In hydrogenation reaction at 25°C, it is observed that hydrogen gas pressure falls from 2 atm to 1.2 atm in 50 min. Calculate the rate of reaction in molarity per sec (in term 10-5). (R = 0.0821 litre–atm degree-1 mol-1)
Calculate the rate constants involved in the dissociation of NH4OH , vis.,
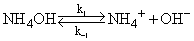 from the following data : A 0.01 molar solution of NH4OH is subjected to a sudden temperature jump terminating at 25°C, at which temperature, the equilibrium constant is 1.8 × 10–5 mol dm–3. The observed relaxation time is 0.109 μs and xe = 4.1 × 10–4 mol dm–3. (in 1010 dm3 mol–1 s–1)
from the following data : A 0.01 molar solution of NH4OH is subjected to a sudden temperature jump terminating at 25°C, at which temperature, the equilibrium constant is 1.8 × 10–5 mol dm–3. The observed relaxation time is 0.109 μs and xe = 4.1 × 10–4 mol dm–3. (in 1010 dm3 mol–1 s–1)
A substance when dissolved in water at 10–3 M concentration absorbs 10 per cent of an incident radiation in a path of 1 cm length.The concentration of the solution in order to absorb 90 per cent of the same radiation is: x × 10–2 what will be value of x :
An 18°C, the surface tension γ of an aqueous solution of butyric acid is represented by the equation γ = γ0 – 29.8 log (19.64 c2 + 1) where γ0, the surface tension of water, is 0.073 N m–1 and c2 is the bulk concentration of the solute. Calculated, using the Gibbs adsorbtion isotherm, the surface excess of butyric acid at concentration c2 equal to 0.01 mol dm–3 is 8.8 × 10–x mol m–2 what will be value of x:


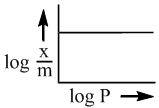
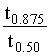 for nth order reaction is:
for nth order reaction is: