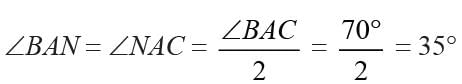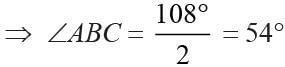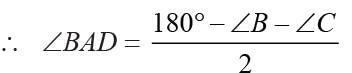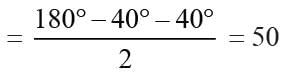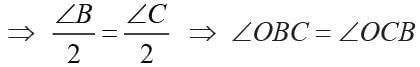Math Olympiad Test: Triangles- 2 - Class 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Math Olympiad Test: Triangles- 2
An exterior angle of a triangle is 100° and the interior opposite angles are in ratio 1 : 4. The measure of the smallest angle of the triangle is
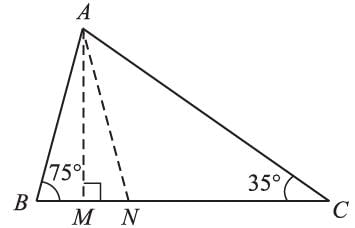
AN is the bisector of ∠A and AM ⊥ BC. Then a measure of ∠MAN is:

The sum of all the exterior angles of a triangle is
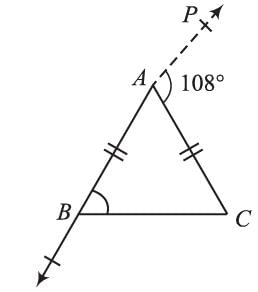
In an isosceles triangle AB = AC. Side AB is extended to P such that ∠CAP = 108°. The measure of ∠ABC is:
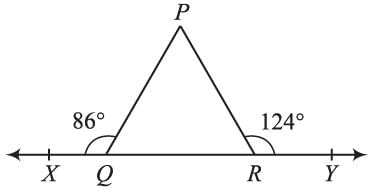
Side QR of a triangle PQR is produced both ways and the measures of exterior angles formed are 86° and 124°. The measure of ∠P is:
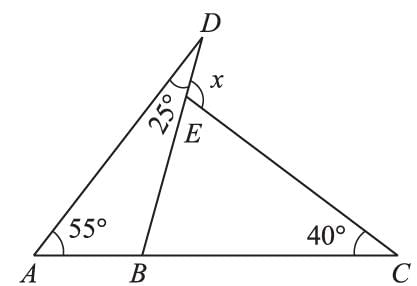
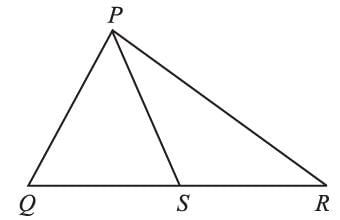
ABC is an isosceles such that AB = AC and AD is the median to base BC. Then, ∠BAD =
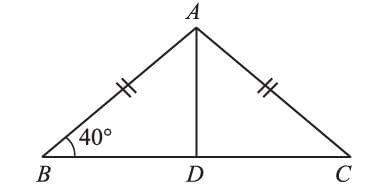
In a ΔABC, ∠A = 50°, ∠B = 60°. The longest side of the triangle will be
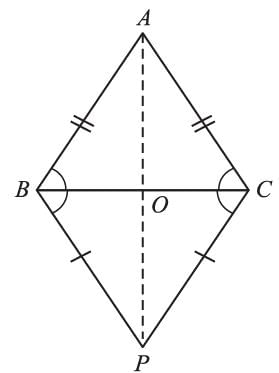
If two isosceles triangles have a common base, then the line joining their vertices will
If the length of three of the altitudes of a triangle are equal, then the triangle must be a/an
PQRS is a square and SRT is an equilateral triangle. The measure of ∠TQR is:
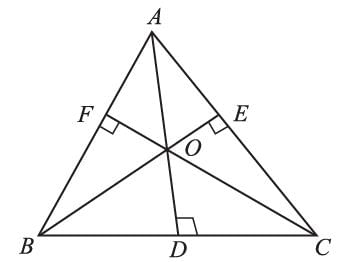
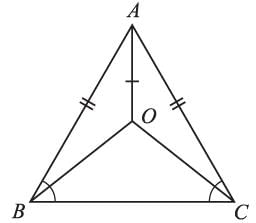
In ΔABC, AB = AC, and the bisect are of angles B and C intersect at point O, then the ray AO
P is a point equidistant from two lines l and m intersecting at point A, then