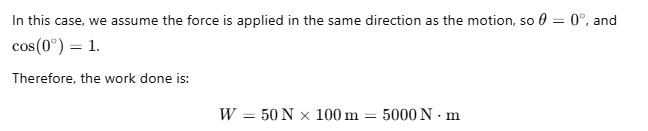Olympiad Test: Work and Energy- 1 - Class 9 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Work and Energy- 1
A coolie carries a load of 50 N to a distance of 100 m. The work done by him is
The P. E. of a body at a certain height is 200 J. The K.E. possessed by it when it just touches the surface of the earth is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The work done in lifting a 50 kg of bag from the ground to the head, height of coolie is 200 cm, by the coolie is (assume g = 10 m/s2)
A child pull a toy car by applying force of 15 N at an angel of 60°. Find the work done in pulling the toy by a distance of 20 metres.
Find the Kinetic energy of a body of mass 2 kg moving with velocity of 0.1 metre per second
An object of mass 12 kgs is at a certain height above the ground. If the P.E of the object is 480 J,
find the height at which the object is with respect to the ground. Given, g = 10 ms–2
Two objects of masses 1 × 10–3 kg and 4 × 10–3 kg have equal momentum. What is the ratio of their kinetic energies
If the speed of an object is doubled, then its kinetic energy is
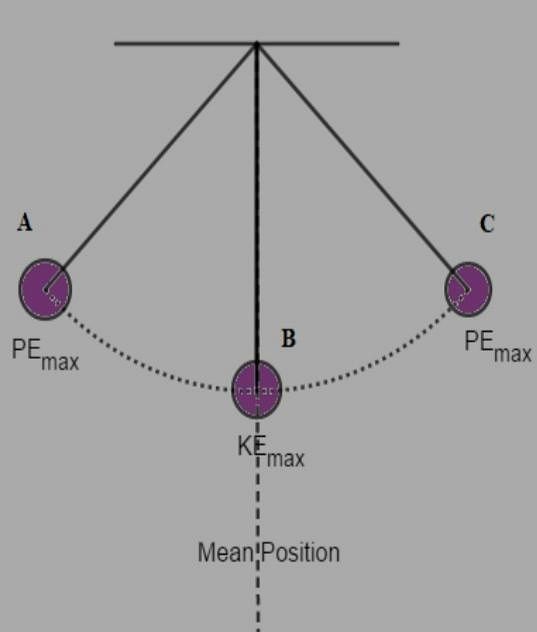
The type of energy possessed by a simple pendulum, when it is at the mean positions
A man of mass 100 kg jumps to a height of 50 cm. his potential energy at the highest point is
(g = 10 m/s2)