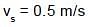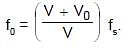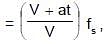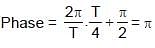NEET Part Test - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Part Test - 2
The time taken by a particle performing SHM on a straight line to pass from point A to B where it's velocities are same is 2 seconds. After another 2 seconds it returns to B. The time period of oscillation is (in seconds):
For a particle in S.H.M., if the amplitude of displacement is ‘a’ and the amplitude of velocity is ‘v’ the amplitude of acceleration is :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
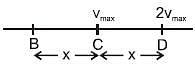
A body performs SHM along the straight line segment ABCDE with C as the mid point of segment AE (A and E are the extreme position for the SHM). Its kinetic energies at B and D are each one fourth of its maximum value. If length of segment AE is 2R, then the distance between B and D is :
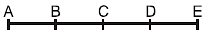
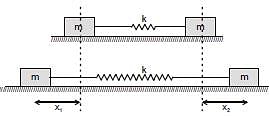
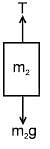
A system is shown in the figure. The time period for small oscillations of the two blocks will be :
Two light strings, each of length l, are fixed at points A and B on a fixed horizontal rod xy. A small bob is tied by both strings and in equilibrium, the strings are making angle 45° with the rod. If the bob is slightly displaced normal to the plane of the strings and released then period of the resulting small oscillation will be :
A metre stick swinging in vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis passing through its one end undergoes small oscillation of frequency f0 as shown in figure. If the bottom half of the stick were cut off, then its new frequency of small oscillation would become:
A 25 kg uniform solid sphere with a 20 cm radius is suspended by a vertical wire such that the point of suspension is vertically above the centre of the sphere. A torque of 0.10 N-m is required to rotate the sphere through an angle of 1.0 rad and then maintain the orientation. If the sphere is then released, its time period of the oscillation will be:
A rod of length l is in motion such that its ends A and B are moving along x-axis and y-axis respectively. It is given that rad/s always. P is a fixed point on the rod as shown in figure. Let M be the projection of P on x-axis. For the time interval in which q changes from 0 to π/2 ,
choose the correct statement :
Which of the following is greatest in SHM ? (assuming potential energy = 0 at mean position)
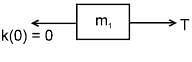
m1 & m2 are connected with a light inextensible string with m1 lying on smooth table and m2 hanging as shown in figure. m1 is also connected to a light spring which is initially unstretched and the system is released from rest :
The potential energy of a particle executing SHM changes from maximum to minimum in 5 sec. Then the time period of SHM is :
A body is executing simple harmonic motion. At a displacement x from mean position, its potential energy is E1 and at a displacement y from mean position, its potential energy is E2. The potential energy E at a displacement (x + y) from mean position is (the potential energy is zero at mean position) :
In the figure shown a block of mass m is attached at ends of two springs. The other ends of the spring are fixed. The mass m is released in the vertical plane when the spring are relaxed. The velocity of the block is maximum when:
Figure shows the kinetic energy K of a simple pendulum versus its angle θ from the vertical. The pendulum bob has mass 0.2 kg. The length of the pendulum is equal to (g = 10 m/s2) :
The equation of a wave is given by (all quantity expressed in S.I. units) Y = 5 sin10π (t – 0.01x) along the x-axis. The magnitude of phase difference between the points separated by a distance of 10 m along x- axis is :
A certain transverse sinusoidal wave of wavelength 20 cm is moving in the positive x direction. The transverse velocity of the particle at x = 0 as a function of time is shown. The amplitude of the motion is:
Two vibrating strings of same material stretched under same tension and vibrating with same frequency in the same overtone have radii 2r and r. Then the ratio of their lengths is :
A chord attached about an end to a vibrating fork divides it into 6 loops, when its tension is 36 N. The tension at which it will vibrate in 4 loops is:
Sinusoidal waves 5.00 cm in amplitude are to be transmitted along a string having a linear mass density equal to 4.00 × 10–2 kg/m. If the source can deliver a maximum power of 90 W and the string is under a tension of 100 N, then the highest frequency at which the source can operate is (take π2 = 10) :
What is the percentage change in the tension necessary in a sonometer of fixed length to produce a note one octave lower (half of original frequency) than before :`
Figure shown is a graph, at a certain time t, of the displacement function S(x,t) of three sound waves 1,2 and 3 as marked on the curves that travel along x–axis through air. If P1,P2 and P3 represent their pressure amplitudes respectively, then correct relation between them is :
Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, In which of the following gases the velocity of sound will be largest :
In a sound wave, to increase the intensity by a factor of 10, pressure amplitude must be changed by a factor of :
The two pipes are submerged in sea water, arranged as shown in figure. Pipe A with length LA = 1.5 m and one open end, contains a small sound source that sets up the standing wave with the second lowest resonant frequency of that pipe. Sound from pipe A sets up resonance in pipe B, which has both ends open. The resonance is at the second lowest resonant frequency of pipe B. The length of the pipe B is :
A source of sound of frequency 256 Hz is moving rapidly towards a wall with a velocity of 5 m/sec. If sound travels at a speed of 330 m/sec, then number of beats per second heard by an observer between the wall and the source is:
A stationary observer receives sonic oscillations from two tuning forks, one of which approaches and the other recedes with same speed. As this takes place the observer hears the beat frequency of 2 Hz. Find the speed of each tuning fork, if their oscillation frequency is 680 Hz and the velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s:
A source of frequency f is stationary and an observer starts moving towards it at t = 0 with constant small acceleration. Then the variation of observed frequency f ' registered by the observer with time is best represented as :
Two persons A and B each carrying a source of frequency 596 Hz and 600 Hz respectively are standing at rest a few metres apart. A starts moving towards B with a velocity of 2 m/s. If the speed of sound is 300 m/s. Which of the following statement is true?
In a horizontal spring–mass system, mass m is released after being displaced towards right by some distance at t = 0 on a frictionless surface. The phase angle of the motion in radian when it is first time passing through the equilibrium position is equal to :
A 75 cm string fixed at both ends produces resonant frequencies 384 Hz and 288 Hz without there being any other resonant frequency between these two. Wave speed for the string is :


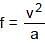

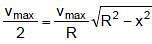 or
or 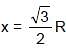
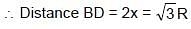
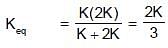


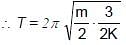


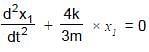

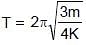
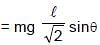
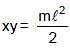
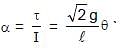
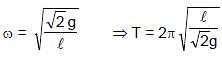
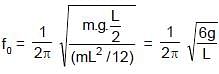

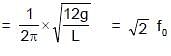
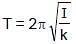
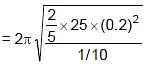
 = 4π second
= 4π second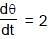 ∴ θ = 2t
∴ θ = 2t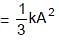
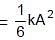
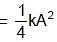

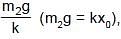 which is the new equilibrium position of the system.
which is the new equilibrium position of the system.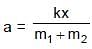 (For (m1 + m2 + spring) systeem)
(For (m1 + m2 + spring) systeem)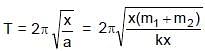
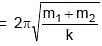


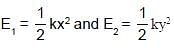
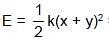
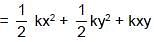

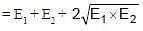

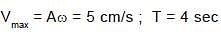
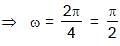
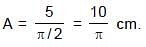
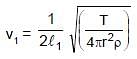 and
and 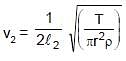
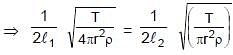
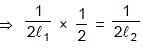
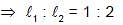
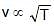 ⇒
⇒ 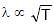
 ⇒
⇒ 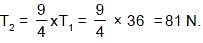

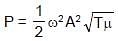
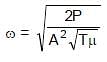 ⇒
⇒ 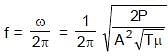
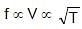 (Wave length constant for fixed length)
(Wave length constant for fixed length)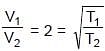 ⇒
⇒ 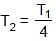
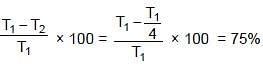
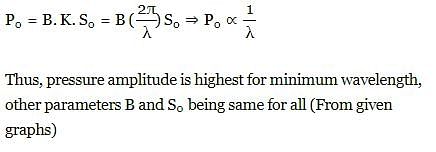
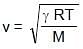
 of H2 is maximum, hence speed of sound in H2 shall be maximum.
of H2 is maximum, hence speed of sound in H2 shall be maximum.
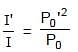 ⇒
⇒ 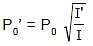
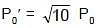
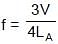
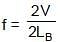
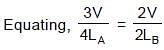
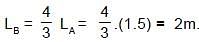
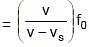
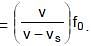
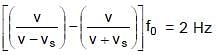 ⇒
⇒