Chemical Kinetics (Chapter Test - Non-Medical) - Class 12 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Kinetics (Chapter Test - Non-Medical)
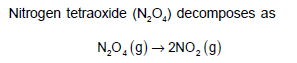
If the pressure of N2O4 falls from 0.50 atm to 0.32 atm in 30 minutes, the rate of appearance of NO2(g) is
The following mechanism has been proposed for thereaction of NO with Br2 to form NOBr.
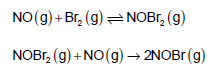
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to NO(g) is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The chemical reaction, 2O3 →3O2 , proceeds as follows
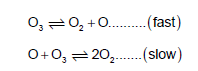
The rate law expression should be
For a reaction, R →P , the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.05 M to 0.04 M in 30 minutes. What will be the average rate of reaction in minutes ?
The rate of disappearance of SO2 in the reaction,
2SO2 +O2 → 2SO3
is 1.28 x 10–5 mol s–1. The rate of disappearance of O2 is
The reaction, is carried out in a 1 dm3 vessel and 2 dm3 vessel respectively. The ratio of reaction velocities will be
In a reaction, 2X → Y , the concentration of X decreases from 0.50 M to 0.38 M in 10 min. What is the rate of
reaction in M s–1 during this interval ?
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) dissociates into nitric oxide (NO) and oxygen (O2) as follows
If the rate of decrease of concentration of NO2 is 6.0 x 10–12 mol L–1 s–1. What will be the rate of increase of
concentration of O2 ?
Which of the following is/are correct for the first order reaction?
The smog constituents peroxyacetylnitrate (PAN) dissociate into peroxyacetyl radicals and NO2 (g) in a
first order reaction with a half-life of 30 min
If the initial concentration of PAN in an air sample is 5.0 x 1014 molecules/L. What will be concentration after
1.5 hours ?
The rate constant of first order reaction is 1.8 x 10—3 mol L—1 min—1 when initial conc. is 0.3 mol L—1. The value of rate constant in the unit of second order reaction is
For zero order reaction, variation of log t1/2 with log a may be represented as
(t1/2 = half-life, a = initial concentration of the reactants)
A graph plotted between log k versus 1/T for calculating activation energy is shown by
For a given reaction of first order, it takes 15 minutes for the concentration to drop from 0.8 M to 0.4 M. The time required for the concentration to drop from 0.1 M to 0.0125 M will be
Time required for 100% completion of a zero-order reaction is
The reaction,
follows first-order kinetics. The pressure of a vessel containing only N2O5 was found to increase from
50 mm Hg to 87.5 mm Hg in 30 min. The pressure exerted by the gases after 60 min. will be (assume
temperature remains constant)
For the non-stoichiometric reaction,
the following kinetic data were obtained in three
separate experiments, al at 298 K.

















