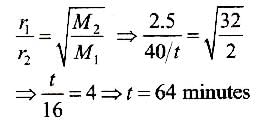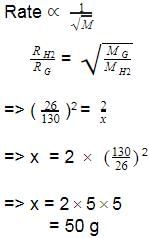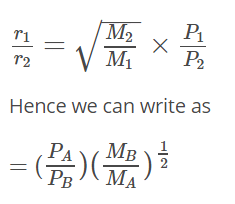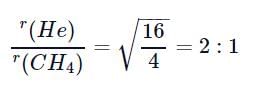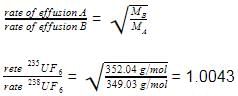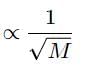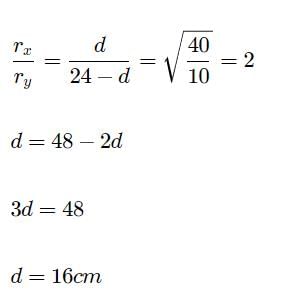Test: Diffusion of Gases (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Diffusion of Gases (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. 50 mL of H2 gas diffuse through a small hole from a vessel in 20 min. Time taken by 40 ml. of O2 gas to diffuse under similar conditions will be
It takes 26 s for 10 mL of H2 gas to effuse through a porous membrane, it takes 130 s for 10 mL of an unknown gas under identical conditions to effuse. Hence, molar mass of the unknown gas (in g mol-1) is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
100 mL of O2 gas diffuse in 10 s. 100 mL of gas X diffuse in t s. Gas X and time t respectively can be
Rate of diffusion of LPG (mixture of n-butane and propane) is 1.25 times faster than that of SO3. Hence, mole fraction of n-butane in LPG is
Assume that the air in the space vehicle cabin consists of O2 with mole fraction, 0.20. if air contains both N2 and O2, then fraction of O2 that comes out the hole is
Consider a tube that has a frilled disk sealed in its centre so that gases can effuse through it in both directions. If the left hand side contains H2 at a pressure p and temperature T and the right hand side contains He at a pressure 2p and temperature T, then initial ratio of rate of effusion is
According to Graham’s law at a given temperature, the rates of diffusion rA / rB of gases A and B is given by (where, p and M are partial pressure and molar masses)
[IIT JEE 1998, 2011]
If helium and methane are allowed to diffuse out of the container under the similar conditions of temperature and pressure, then the ratio of rate of diffusion of helium to methane is
[IIT JEE 2005]
Sulphur dioxide and oxygen were allowed to diffuse through a porous partition. 20 dm3 of SO2 diffuses through the porous partition in 60 s. The volume of O2 (in dm3) which diffuses in 30 s will be (atomic mass of sulphur = 32 u)
[JEE Main 2014]
A vessel contains 0.5 mole each of SO2, H2 and CH4. Its outlet was made open and closed after some time. Thus, order of partial pressure inside the vessel will be
Consider the following pairs of gases A and B
Q. Thus, relative rates of diffusion of gases A and B is in the order
1 mole of helium and 3 moles of N2 exert a pressure of 16 atm. Due to a hole in the vessel in which mixture is placed, mixture leaks out. Thus, composition of the mixture effusing out initially is
For 10 min each, at 27°C from two identical holes, nitrogen and an unknown gas are leaked into a common vessel of 3 L capacity. The resulting pressure is 4.18 bar and the mixture contains 0.4 mole of nitrogen gas. Thus, molar mass of the unknown gas is (g mol-1)
At the start of an experiment, one end of a U-tube of 6 mm glass tubing is immersed in concentrated ammonia solution and the other end in concentrated hydrochloric acid. At the point in the tube where vapours of ammonia and hydrochloric acid meet, white cloud is formed. At what fraction of the distance along the tube from the ammonia solution, the white cloud first form ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains 3 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Rates of diffusion of two gases A and B are rA and rB. is equal to
Ratio of the rate of diffusion of He to H2 at 0°C is same
100 mL of H2 gas diffuse in 10 s. X mL of O2 diffuses in t s. Thus, X and t respectively are
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-21) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
Uranium content of 235U in uranium ore is enriched from a mixture of 235UF6 and 238UF6 by effusion method (F - 19.0 g mol-1).
Q. Enrichment factor is
For permanent gases diffusivity the order is _________ sq.m/s
Passage II
X and Y are two volatile liquids with molar weights of 10 g mol-1 and 40 g mol-1 respectively. Two cotton plugs, one soaked in X and the other soaked in Y, are simultaneously placed at the ends of the tube of length l = 24 cm , as shown in the figure. The tube is filled with an inert gas at 1 atm pressure and temperature of 300 K. Vapours of X and Y react to form a product which is first formed at a distance, d cm from the plug soaked in X. Take X and Y to have equal molecular diameters and assume ideal behaviour for the inert gas and two vapours.
Q. The value of d in cm (shown in the figure), as estimated from Graham’s law is
Passage II
X and Y are two volatile liquids with molar weights of 10 g mol-1 and 40 g mol-1 respectively. Two cotton plugs, one soaked in X and the other soaked in Y, are simultaneously placed at the ends of the tube of length l = 24 cm , as shown in the figure. The tube is filled with an inert gas at 1 atm pressure and temperature of 300 K. Vapours of X and Y react to form a product which is first formed at a distance, d cm from the plug soaked in X. Take X and Y to have equal molecular diameters and assume ideal behaviour for the inert gas and two vapours.
Q. The experimental value of d is found to be smaller than the estimated value obtained by using Graham's law. This is due to
Direction (Q. No. 22) This section contains 1 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. At 1200°C, mixture of Cl2 and Cl-atoms (both in gaseous state) effuses 1.16 times as fast as a gas of molar mass 87.6 g mol-1, under identical conditions. What is the percentage dissociation of Cl2 into Cl-atoms ?