Test: Electromagnetic Radiations - NEET MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electromagnetic Radiations
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. FM radio broadcasts at 900 kHz. What wavelength does this corresponds to?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Moseley’s equation is represented as 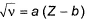 where, a and b are constants.
where, a and b are constants.
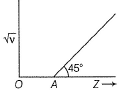
Q. If OA = 1, then atomic number of the element showing frequency of 400 Hz is
A gas absorbs photon of wavelength 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emissions is at 680 nm, the other is at
[AlEEE 2011]
The longest wavelength of light capable of breaking a single (Cl — Cl) bond in Cl2 is if
[AlEEE 2010]
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment?
Which of the following statements is not correct about the characteristics of cathode rays?
Energy of a mole of radio wave photons with a frequency of 909 kHz is
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-11) This section contains 3 multiple-choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c), and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Select the correct statement(s).
Consider the following transitions n = 1 to n = 2 and then, n = 2 to n = 3.
Then
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.
Q. Energy associated with this wave is
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.
Q. A standing wave in a string 42 cm long has a total of six nodes (including those at the ends). Wavelength of the standing wave is
Direction (Q. Nos. 14) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. The colours of visible light are at different wavelength. Match the wavelengths in Column I with their colours in Column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In Millikan’s experiment, the static electric charge on the oil drops has been obtained by shining X-rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is -1.282x 10-18 C, calculate the number of electrons present on it.
Energy change associated per mole of atoms with an atomic transition giving rise to radiations of 1 Hz is x * 10-10 J/mol. What is the value of x?

















