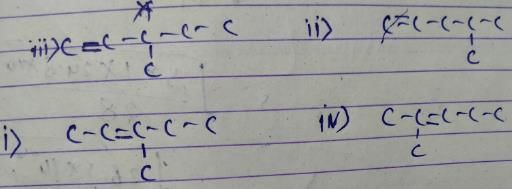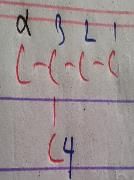Test: Chirality - JEE MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chirality
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-18) This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
The correct statement regarding a chiral compound is
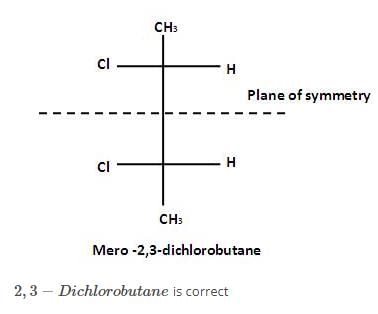
The correct statement regarding elements of symmetry and chirality of compound is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A pure enantiomer of which of the following compounds can be used for separation of racemic mixture of 2-methyl butanoic acid?
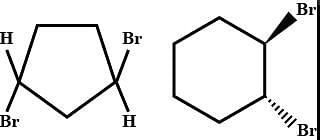
The absolute configuration of the following compound is
[AIEEE 2008]
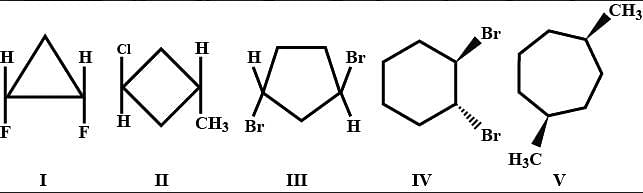
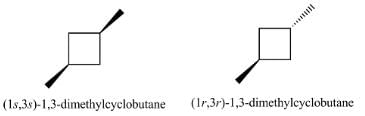
Which of the following compounds will have a meso-isomer also?
[AIEEE 2004]
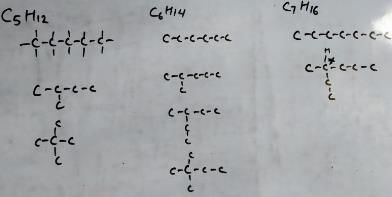
amongst the following compounds, the optically active alkane having lowest molar mass is
[AIEEE 2004]
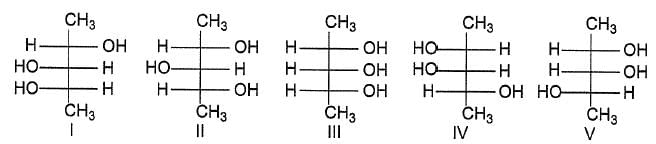
Consider the following set of molecules.
The pairs of enantiomers are
What is the molecular formula for the alkane of smallest molecular weight which possesses a stereogenic centre?
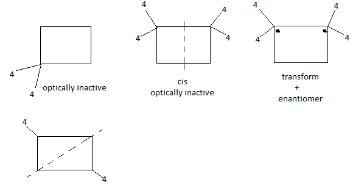
of the compounds, which correspond to the general name dichlorocyclobutane how many are optically active ?
Out of following, the alkene that exhibit optical isomerism Is
[AIEEE 2010]
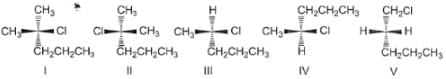
How many chiral compounds are possible on monchlorination of 2-methyl butane ?
[AIEEE 2012]
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-22) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
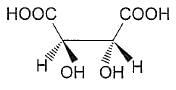
The correct statement regarding tartaric acid is/are
The correct statement(s) regarding the isomers of compound N-ethyl-N-methyl-l-propanamine is/are
Direction (Q. Nos. 23 and 24) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below
Q.
Statement I: The following compound is optically inactive
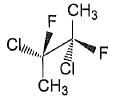
Statement II It has an axis of symmertry
Q.
Statement I : The following compound is optically inactive.
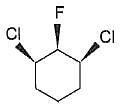
Statement II : It has two chiral carbons.


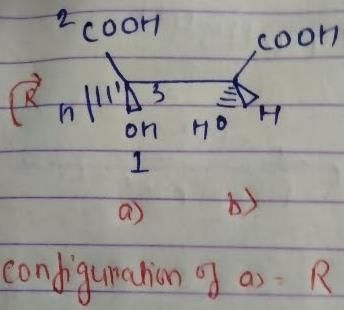
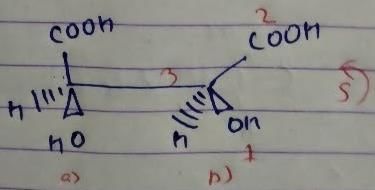 But we have done odd times interchange, so the above configuration will be reverse.
But we have done odd times interchange, so the above configuration will be reverse.