Test: Measurement of High Resistance - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Measurement of High Resistance
The problem faced while measuring high resistance is/are
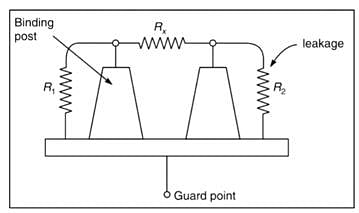
Which of the following method is used for removing the leakage current from bridges?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following are examples of measurement of high resistance?
Which among the following is not a method for measurement of High Resistance?
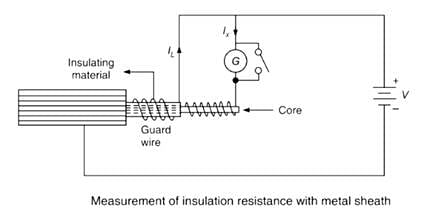
Which of the following method is most widely used for insulation resistance of the cable?
The direct deflection method uses the principle of
Which of the following statement is incorrect while taking precautions for testing the cable using the direct deflection method?
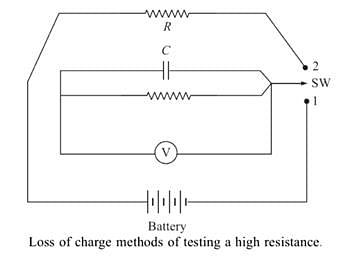
In loss of charge method _______ is connected in parallel with the insulation _______ under test.
Which of the following is/are drawbacks of the loss of charge method?
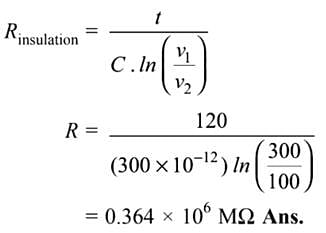
A length of cable was tested for insulation resistance using the loss of charge method. A capacitance formed by the sheath of cable of 300 pF is found to have a drop-in voltage from 300 V to 100 V in 120 seconds. What will 1. be the insulation resistance of the cable.