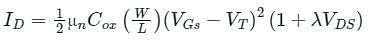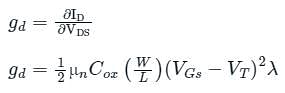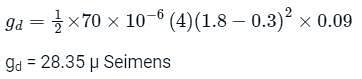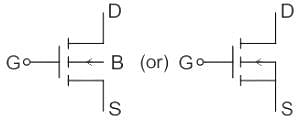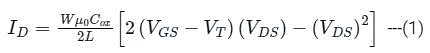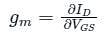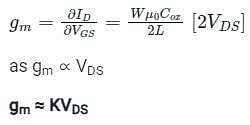Test: MOSFET-1 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: MOSFET-1
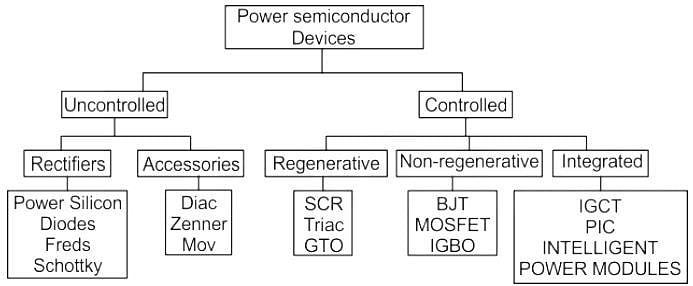
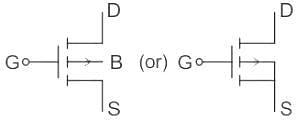
Which of the following does NOT belong to the category of semi-controlled devices?
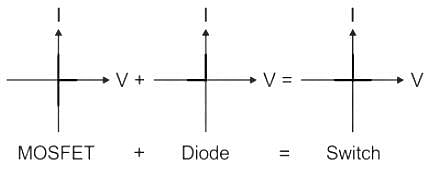
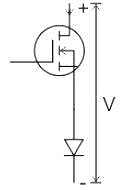
The figure shows a composite switch consisting of a power MOSFET in series with a power diode. Assuming that the MOSFET and the diode are ideal, the I-V characteristic of the composite switch is:

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
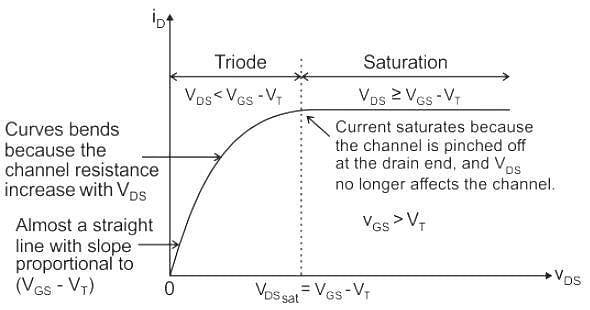
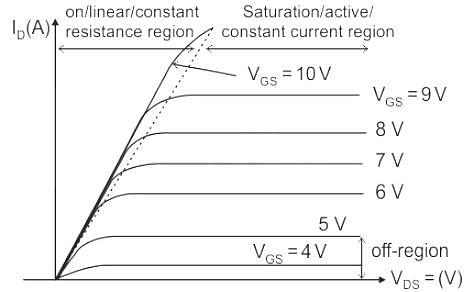
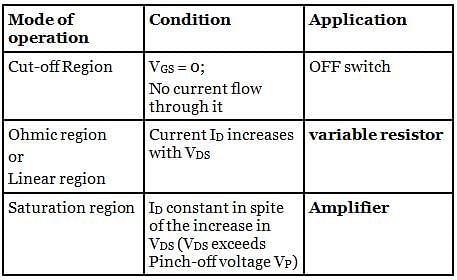
In a power MOSFET, pinch-off occurs when (VDS is the drain to source voltage, VGS is the gate to source voltage VT is the threshold voltage):
Consider an n-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) with a gate-to-source voltage of 1.8 V. Assume that W/L=4, μnCox = 70 x 10-6 AV-2, the threshold voltage is 0.3 V, and the channel length modulation parameter is 0.09 V−1. In the saturation region, the drain conductance (in micro seimens) is ________.
Given, Vgs is the gate-source voltage, Vds is the drain source voltage, and Vth is the threshold voltage of an enhancement type NMOS transistor, the conditions for transistor to be biased in saturation are
Trans conductance of MOSFET in linear region can be approximated by ______