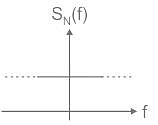
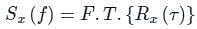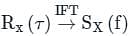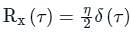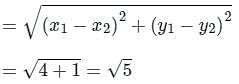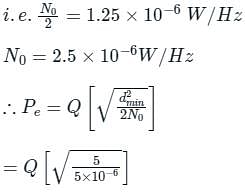Test: White Noise - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: White Noise
A binary modulation scheme used the following two signal points.
Determine the error probability in terms of Q-function if we communicate over an AWN Channel where the noise has power spectral density of 1.25 × 10-6 W/Hz
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Following are few statements regarding noise in communication system:
a) Atmospheric noise, shot noise, solar noise are examples of external noise sources
b) Noise temperature is useful in dealing with UHF noise
c) Thermal agitation is the only source of noise in receiver
Choose the correct answer:
One of the following types of noise assumes importance at high frequncies:
The noise caused by random variations in the arrival of electrons or holes at the output electrode of an amplifying device
Which type of noise is produced in a microwave tube due to random nature of emission and electron flow?