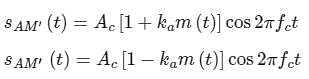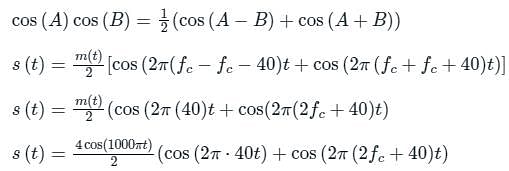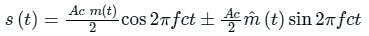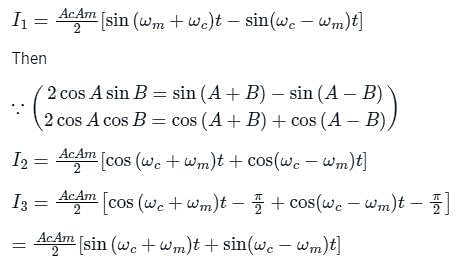Test: Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) Modulation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) Modulation
What is the power transmitted (in W) by a DSB-SC signal when the carrier wave power is 80 W and modulation index is 0.4?
An AM broadcast station is found to be transmitting modulating frequencies up to 5 kHz and the station is allowed to transmit on a frequency of 950 kHz, then what will be the bandwidth (in kHz) allotted to the station?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following equation represents the full-carrier AM (DSB-full carrier)?
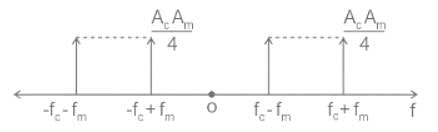
What will be the upper sideband and lower sideband frequencies for amplitude modulation of a 5-kHz signal with 40-kHz carrier frequency?
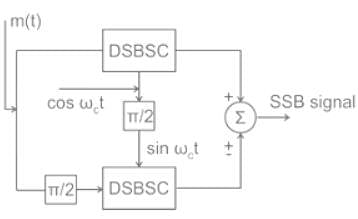
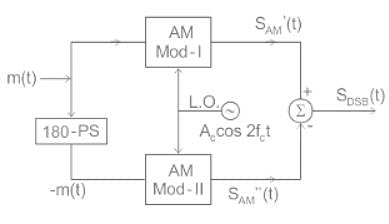
A type of amplitude modulation in which carrier is suppressed is called
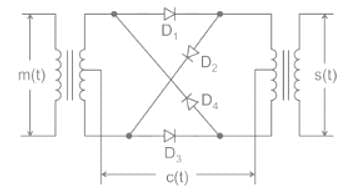
The ring modulator is generally used for generating
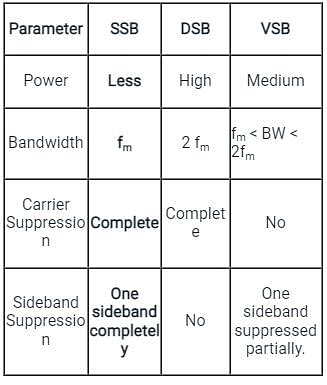
Which of the following requires the least bandwidth?
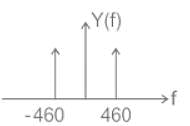
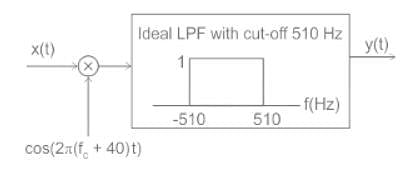
For the modulated signal x(t) = m(t) cos (2πfct), the message signal m(t) = 4 cos (1000πt) and the carrier frequency fc is 1 MHz. The signal x(t) is passed through a demodulator, as shown in the figure below. The output y(t) of the demodulator is
A DSB-SC signal is generated using the carrier signal cos (ωct + θ) and modulating signal m(t). What is the envelope detector output of this DSB-SC signal?
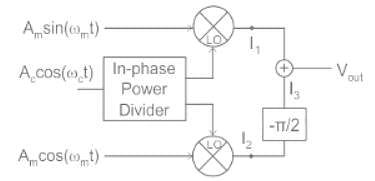
In this circuit, Vout is: