Test: Tuple Calculus - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Tuple Calculus
Consider the following tuple relational calculus:
{t | Ǝ s ε instructor (t[name] = s[name]
ᴧ Ǝ u ε department (u[dept_name] = s[dept_name]
ᴧ u[building] = “Taylor”))}
What does the given expression perform?
Find the customers having account all branches located in Hyderabad. Use the above relations and find which of the following query is not giving the same.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the given tuple calculus expressions can be used to find first name and last name of all the employees whose salary is above $15000 from the relation EMPLOYEE?
Consider the expression t ϵ instructor ∧ ∃ s ϵ department (t [dept_name] = s [dept_name]) the variables t and s are _____ respectively.
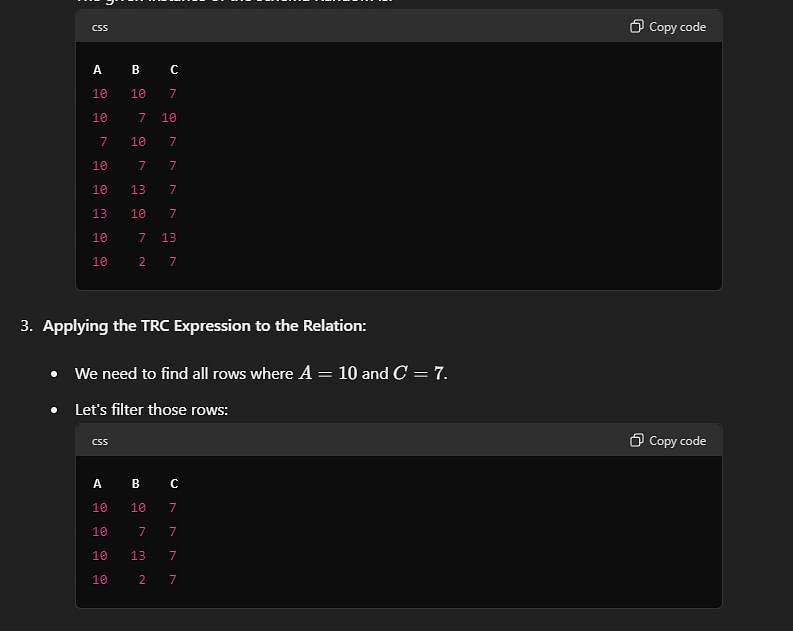
Consider a database that has the relation schema Random(A, B, C). An instance of the schema Random is as given below.
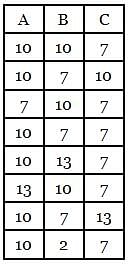
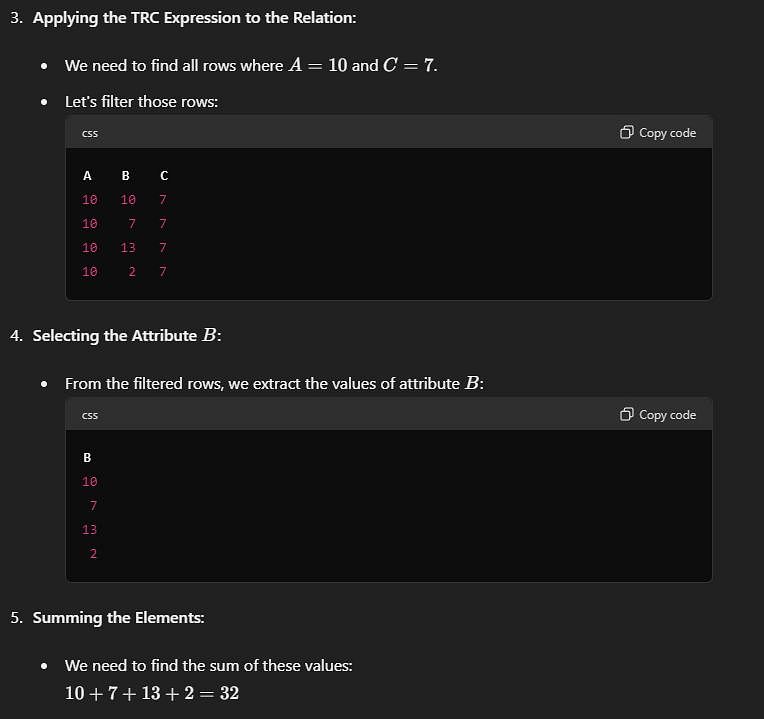
Tuple calculus expression for the above instance is given as {t.B | t ϵ r ∧ (t[A] = 10 ∧ t[C] = 7)}
What is the sum of the elements in the output row of the given expression?
Which among the following is/are false?
I. Relational algebra is more powerful than relational calculus.
II. Relational calculus is more powerful than relational algebra.
III. Relational algebra is as same power as relational calculus.
Consider the Relations COLLEGE(CollegeID, Name, Location) and FACULTY(FacultyName, FacultyID, CollegeID). Which of the following is correct tuple calculus equivalent to the following statement?
“Name all the faculties in college ‘TESTBOOK’.”
Which of the following uses domain variable that take on values from an attributes domain, rather that values for an entire tuple.?