Test: ACID Properties - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: ACID Properties
Which one of the following is NOT a part of the ACID properties of database transactions?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The statement given below describes which of the ACID properties of transactions?
“The changes applied to the database by a committed transaction must persist in the database, and these changes must not be lost because of any failure”
Consider the following partial Schedule S involving two transactions T1 and T2. Only the read and the write operations have been shown. The read operation on data item P is denoted by read(P) and the write operation on data item P is denoted by write(P)
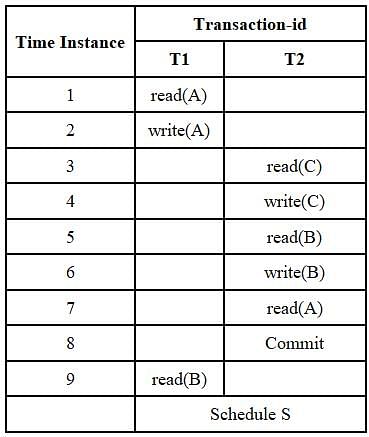
Suppose that the transaction T1 fails immediately after time instance 9. Which one of the following statements is correct?
All Oracle transactions obey the basic properties of a database transaction. What is the name of the following property?
‘All tasks of a transaction are performed or none of them are. There are no partial transactions.’
Consider the following transaction involving two bank accounts x and y.
read (x); x := x – 50 ; write (x) ; read (y) ; y≔ y + 50 ; write (y)
The constraint that the sum of the accounts x and y should remain constant is that of
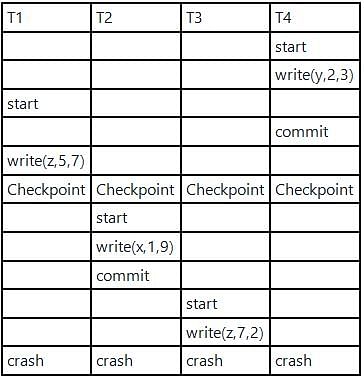
Consider a simple checkpointing protocol and the following set of operations in the log.
(start, T4); (write, T4, y, 2, 3); (start, T1); (commit, T4); (write, T1, z, 5, 7); (checkpoint);
(start, T2); (write, T2, x, 1, 9); (commit, T2); (start, T3), (write, T3, z, 7, 2);
If a crash happens now and the system tries to recover using both undo and redo operations, what are the contents of the undo list and the redo list?
Which property of database transaction create an allusion than only 1 transaction is executed in system in spite of more than one transaction is executed in parallel manner?