Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Tests > Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test Description
5 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Estimation and Costing- 2
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus.The Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 below.
Solutions of Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Civil Engineering (CE) & Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 solutions in
Hindi for Civil Engineering (CE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 | 5 questions in 15 minutes | Mock test for Civil Engineering (CE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 1
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 2
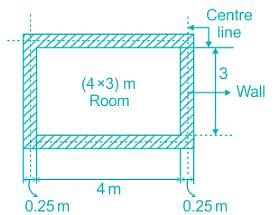
Estimate the quantity of brick masonry required for construction of a room of 4 m × 3 m internal dimensions. Thickness of wall should be 250 mm. Two windows of 2 m × 1.5 m and one door of 1.5 m × 2.2 m is to be provided to the room. Height between top of plinth beam and bottom of slab beam should be 4 m.
Detailed Solution for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 3
Determine the approximate proportion of dry cement mortar required for brick work with bricks of nominal size 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm, with 18 % extra for frog filling and wastage is : (assume 1 m3 of wet mortar = 1.3 m3 of dry mortar):
Detailed Solution for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 3
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 4
In the construction industry, contractor's profit is included in ______.
Detailed Solution for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 4
Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 5
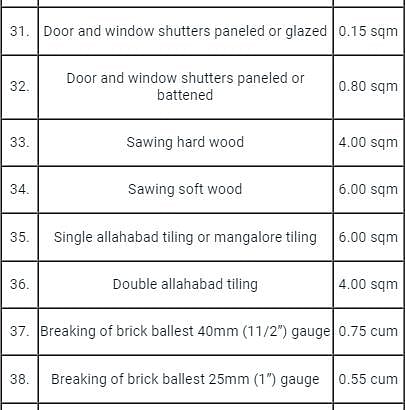
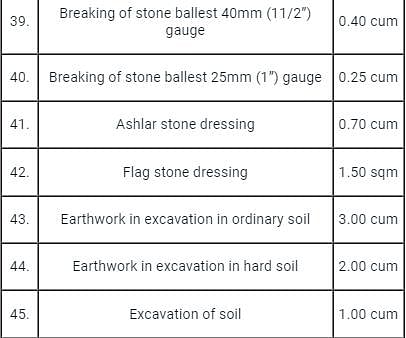
The expected out-turn of a stone cutter for an item of work “Ashlar stone dressing” is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 - Question 5
Information about Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Estimation and Costing- 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF