Test: Ionization of Acids and Bases - ACT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ionization of Acids and Bases
Acid strength increases in the order of _________.
What is the pH of the solution of sulphuric acid having a concentration of 0.01M?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the hydrolysis constant of a weak acid-weak base?
What is the reverse process of Neutralization?
A neutralization reaction results in the formation of __________.
What is the value of the ionic product of water at 298k?
Acetic acid’s pKa is 4.2 and ammonium hydroxide pKb is 3.24. What is the pH of the ammonium acetate solution?
Formic acid has a concentration of 0.1M and Ka is 1.77 x 10-4. What is the value of degree of dissociation?
Why is the aqueous solution of a salt of a weak acid and strong base is alkaline?
Which of the following has a PH greater than 7?
Write pH in terms of concentration of hydrogen ion?
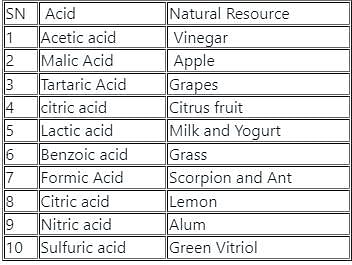
Which pair of natural source - acid is correct?
I. Tamarind - oxalic acid
II. Yogurt - lactic acid