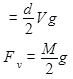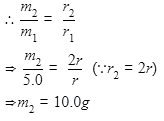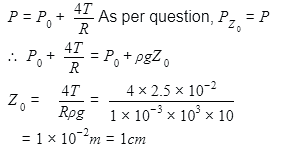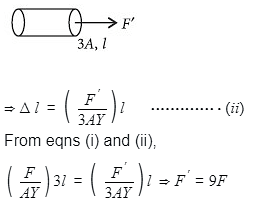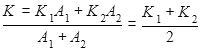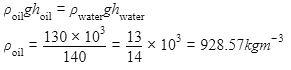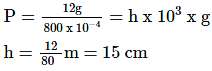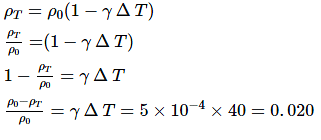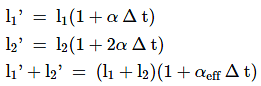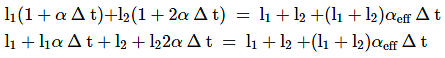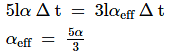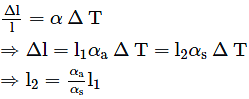NEET Minor Test - 3 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Minor Test - 3
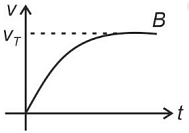
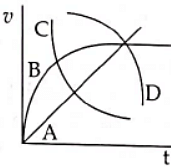
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a highly viscous liquid. The curve in the graph shown, which represents the speed of the ball (v) as a function of time (t) is

Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): The stretching of a spring is determined by the shear modulus of the material of the spring.
Reason (R): A coil spring of copper has more tensile strength than a steel spring of same dimensions.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A The terminal velocity of a copper ball of radius 5mm falling through a tank of oil at room temperature is 10cms−1. If the viscosity of oil at room temperature is 0.9kgm−1s−1, the viscous drag force is:
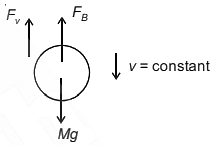
The velocity of a small ball of mass M and density d, when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is d/2, then the viscous force acting on the ball will be
A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height h. The mass of the water in the capillary is 5g. Another capillary tube of radius 2r is immersed in water. The mass of water that will rise in this tube is :
A small hole of area of cross-section 2mm2 is present near the bottom of a fully filled open tank of height 2m. Taking g = 10m/s2, the rate of flow of water through the open hole would be nearly
A soap bubble, having radius of 1 mm, is blown from a detergent solution having a surface tension of 2.5 × 10−2N/m.
The pressure inside the bubble equals at a point Z0 below the free surface of water in a container. Taking g = 10m/s2, density of water = 103kg/m3, the value of Z0 is
The stress-strain curves are drawn for two different materials X and Y. It is observed that the ultimate strength point and the fracture point are close to each other for material X but are far apart for material Y. We can say that materials X and Y are likely to be (respectively)
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. The first wire has cross-sectional area A and the second wire has cross-sectional area 3A. If the length of the first wire is increased by ∆l on applying a force F, how much force is needed to stretch the second wire by the same amount?
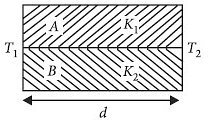
Two rods A and B of different materials are welded together as shown in figure. Their thermal conductivities are K1 and K2 The thermal conductivity of the composite rod will be
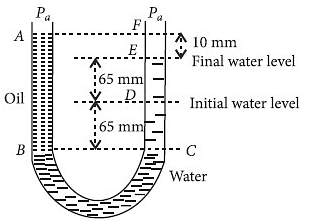
A U tube with both ends open to the atmosphere, is partially filled with water. Oil, which is immiscible with water, is poured into one side until it stands at a distance of 10 mm above the water level on the other side. Meanwhile the water rises by 65 mm from its original level (see diagram). The density of the oil is
A rectangular film of liquid is extended from (4cm × 2cm) to (5cm × 4cm). If the work done is 3 × 10−4J, the value of the surface tension of the liquid is
Two identical bodies are made of a material for which the heat capacity increases with temperature. One of these is at 100°C, while the other one is at 0°C. If the two bodies are brought into contact, then, assuming no heat loss, the final common temperature is
Coefficient of linear expansion of brass and steel rods are α1 and α2. Length of brass and steel rods are l1 and l2 respectively. If (l2 − l1) is maintained same at all temperatures, which one of the following relations holds good?
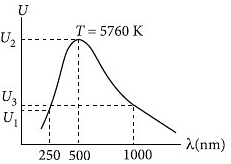
A black body is at a temperature of 5760 K. The energy of radiation emitted by the body at wavelength 250nm is U1, at wavelength 500 nm is U2 and that at 1000 nm is U3 Wien's constant, b = 2.88 × 106nmK. Which of the following is correct?
An airplane of a total wing area of 120 m2 is in a level flight at some height. If the pressure difference between the upper and lower surface is 2.5 kPa, then the mass of the airplane is: [Take g = 10 ms-2]
A liquid is poured into three vessels of the same base area and equal heights as shown in the figure, then:
If pressure at half the depth of a lake is equal to 2/3rd the pressure at the bottom of the lake, then the depth of the lake is:
The value of g at a place decreases by 2%. Then, the barometric height of mercury:
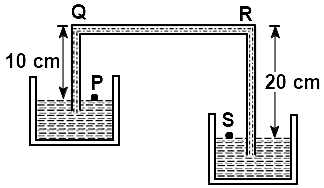
A siphon in use is demonstrated in the following figure. The density of the liquid flowing in the siphon is 1.5 gm/cc. The pressure difference between the point P and S will be:
A diver is 10 m below the surface of water. The approximate pressure experienced by the diver is-
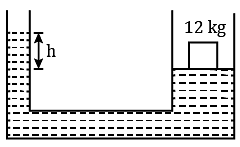
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in the figure is 800 cm2. If a mass of 12 kg is placed on the massless piston, then the difference in heights h of the levels of water in the two tubes will be:
The height of a mercury barometer is 75 cm at sea level and 50 cm at the top of a hill. The ratio of density of mercury to that of air is 104. The height of the hill is:
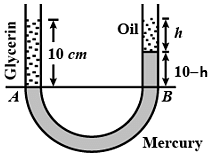
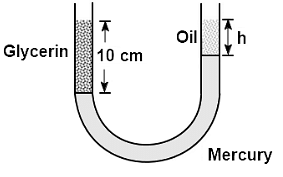
A vertical U-tube of uniform inner cross section, contains mercury in both its arms. A glycerin (density = 1.3 g/ cm3) column of length 10 cm is introduced into one of its arms. Oil of density 0.8 gm/ cm3 is poured into the other arm until the upper surfaces of the oil and glycerin are at the same horizontal level. Find the length of the oil column. [Density of mercury = 13.6 g/cm3]
The value of the coefficient of volume expansion of glycerin is 5 x 10-4 K-1. The fractional change in the density of glycerin for a temperature increase of 40°C will be:
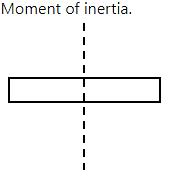
When a uniform rod is heated, which of its following properties will increase as a result of it?
If two rods of length L and 2L having coefficients of linear expansion α and 2α respectively are connected so that their total length becomes 3L, the average coefficient of linear expansion of the composition of rods equals:
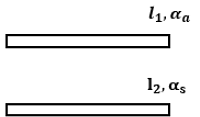
Two rods, one made of aluminium and the other made of steel, having initial lengths l1 and l2 are connected together to form a single rod of length l1 + l2. The coefficient of linear expansion for aluminium and steel are αa and αs respectively. If the length of each rod increases by the same amount when their temperature is raised by t°C, then the ratio ![]()
A large steel wheel is to be fitted onto a shaft of the same material. At 27 °C, the outer diameter of the shaft is 8.70 cm and the wheel's central hole has a diameter of 8.69 cm. The shaft is cooled using ‘dry ice’. At what temperature of the shaft does the wheel slip on the shaft? (Assume the coefficient of linear expansion of the steel to be constant over the required temperature range and α steel = 1.20 × 10−5K−1)