Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Tests > Test: Bond Stresses - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test: Bond Stresses - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Bond Stresses
Test: Bond Stresses for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Test: Bond Stresses questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus.The Test: Bond Stresses MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Bond Stresses below.
Solutions of Test: Bond Stresses questions in English are available as part of our course for Civil Engineering (CE) & Test: Bond Stresses solutions in
Hindi for Civil Engineering (CE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Bond Stresses | 10 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Civil Engineering (CE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 3
Test: Bond Stresses - Question 4
If design bond stress = 1.5 N/mm2 is assumed, then the development length of an Fe 500 HYSD bar of nominal diameter 12 mm - which is fully stressed in tension - will be:
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 4
Test: Bond Stresses - Question 5
If the bond stress developed in a reinforced concrete beam is more than permissible value, it can be brought down by
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 7
Test: Bond Stresses - Question 8
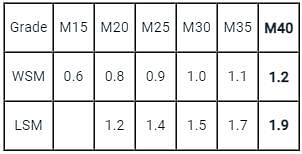
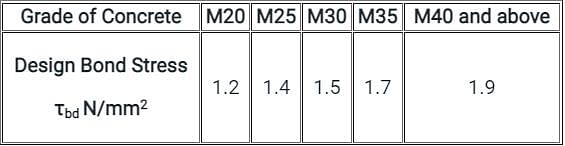
According to IS 456 ∶ 2000, the design bond stress (in N/mm2 units) in limit state method for HYSD bars (Fe415 grade) for M30 grade concrete is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 8
Test: Bond Stresses - Question 9
The magnitude of the average bond stress compared to the maximum local bond stress is considerably ______
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 9
Test: Bond Stresses - Question 10
According to Marshall the wires of 2 and 5mm diameter are stressed to ____________
Detailed Solution for Test: Bond Stresses - Question 10
Information about Test: Bond Stresses Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Bond Stresses solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Bond Stresses, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF



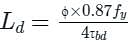
 = 543.75 mm ≈ 544 mm
= 543.75 mm ≈ 544 mm

















