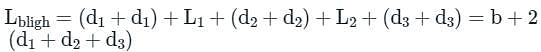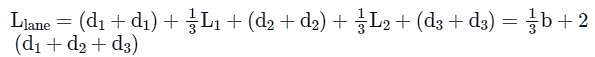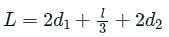Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Tests > Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test Description
6 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus.The Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory below.
Solutions of Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory questions in English are available as part of our course for Civil Engineering (CE) & Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory solutions in
Hindi for Civil Engineering (CE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory | 6 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Civil Engineering (CE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 1
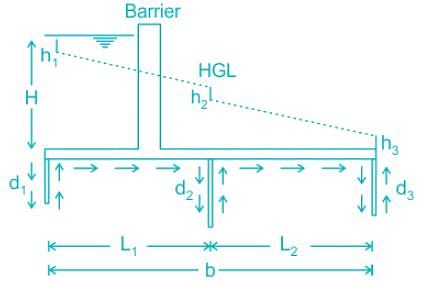
In Lane’s weighted creep theory, he suggested a weightage factor ____
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 1
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 2
In lanes weighted creep theory, weightage factor for horizontal creep is given as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 3
Who proposed the weighted creep theory in soil?
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 3
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 4
Which of the following limitation of Bligh’s theory forms the basis of Lane’s creep theory?
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 4
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 5
What is the value of Lane’s coefficient for fine sand and coarse sand?
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 5
Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 6
What is the range of Lane’s coefficient for clayey soils?
Detailed Solution for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory - Question 6
Information about Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Lane’s Weighted Creep Theory, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF