BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Tests > BPSC Practice Test- 1 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Practice Test- 1
BPSC Practice Test- 1 for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The BPSC Practice Test- 1 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus.The BPSC Practice Test- 1 MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for BPSC Practice Test- 1 below.
Solutions of BPSC Practice Test- 1 questions in English are available as part of our course for BPSC (Bihar) & BPSC Practice Test- 1 solutions in
Hindi for BPSC (Bihar) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt BPSC Practice Test- 1 | 150 questions in 150 minutes | Mock test for BPSC (Bihar) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for BPSC (Bihar) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 1
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 2
Which of the following is one of the key objectives of Bihar Business Connect 2024?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 3
What significant reform has the Bihar government implemented to improve the ease of doing business?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 3
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 4
Consider the following statements about methanol:
1. Methanol is regulated under Schedule I of the 1989 rules.
2. Methanol is synthesized using carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
3. Methanol exposure leads to metabolic acidosis and optic nerve damage.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. Methanol is regulated under Schedule I of the 1989 rules.
2. Methanol is synthesized using carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
3. Methanol exposure leads to metabolic acidosis and optic nerve damage.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 4
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 5
Consider the following statements regarding PM Vishwakarma scheme.
- PM Vishwakarma scheme aims to help traditional craftspeople and artisans by providing interest-free loans.
- The scheme also aims at improving the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople.
- The scheme covers rural and urban areas across India.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 5
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 6
What does the term "traumatic asphyxia," often associated with fatalities during stampedes, mean?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 6
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 7
Which of the following products is NOT part of Bihar’s ongoing efforts to secure a GI tag?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 7
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 8
Consider the following statements about lightning incidents in Bihar:
Bihar records the highest number of lightning-related deaths in India annually.
Cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning is the most dangerous type of lightning causing fatalities.
Bihar Economic Survey reported more than 400 lightning-related deaths in a single year.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Bihar records the highest number of lightning-related deaths in India annually.
Cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning is the most dangerous type of lightning causing fatalities.
Bihar Economic Survey reported more than 400 lightning-related deaths in a single year.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 8
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 9
Consider the following statements about Waqf Board properties in India:
Waqf properties are non-transferable and perpetually designated as charitable acts.
The Waqf Amendment Bill, 2024 mandates the inclusion of women representatives in Waqf Boards.
The Central Waqf Council is one of the largest landholders in India after the Railways and Defense Departments.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Waqf properties are non-transferable and perpetually designated as charitable acts.
The Waqf Amendment Bill, 2024 mandates the inclusion of women representatives in Waqf Boards.
The Central Waqf Council is one of the largest landholders in India after the Railways and Defense Departments.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 9
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 10
The Kosi River originates in which of the following regions?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 10
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 11
Which Finance Commission recommended increasing the states' share of the divisible tax pool to 42%?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 12
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 13
What penalty is prescribed under Bihar's exam law for individuals leaking exam papers?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 13
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 14
Which river merges with the Kosi River near Bornesthan, Bihar?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 14
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 15
Which Act governs the administrative control over minor minerals, including sand?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 15
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 16
Which of the following rivers is not a tributary of the Sone River?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 16
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 17
What role does Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) play in agriculture?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 17
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 18
What percentage of VTR’s total area is forested, according to the Forest Survey of India Report 2021?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 18
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 19
What is the primary objective of the Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA)?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 19
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 20
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 21
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 22
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 23
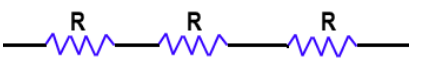
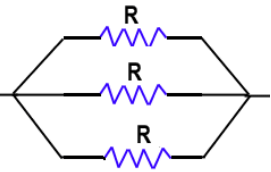
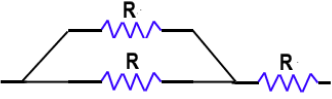
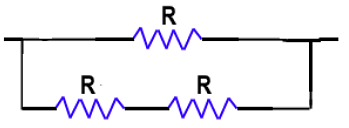
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 24
What is the maximum number of different electrical combinations possible with three equal resistances?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 24
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 25
If the earth stops rotating, the apparent value of g on the earth surface will
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 25
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 26
If the potential difference between the end of a wire of fixed resistance is doubled, by how much does the electric power increase?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 26
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 27
BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 28
Which factor is responsible for the initiation of replication in DNA?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 28
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 29
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 1 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about BPSC Practice Test- 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for BPSC Practice Test- 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for BPSC Practice Test- 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF