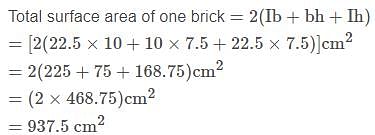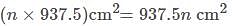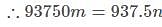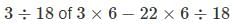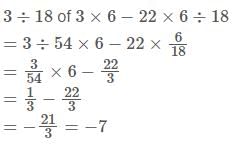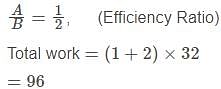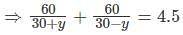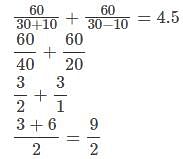BPSC Practice Test- 9 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Practice Test- 9
Dale steyn, who has announced his retirement from international cricket, belongs to which country ?
Recently two adult, one-horned rhinos were shifted from Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary to which wildlife sanctuary?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Who has been appointed as the chairman of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India?
The Netaji Award 2022, is conferred to the ex-PM of which of the following countries?
The Annamayya reservoir in Andhra Pradesh is built on which of the following rivers?
Mukhyamantri Vatsalya Yojana has been launched by which state government?
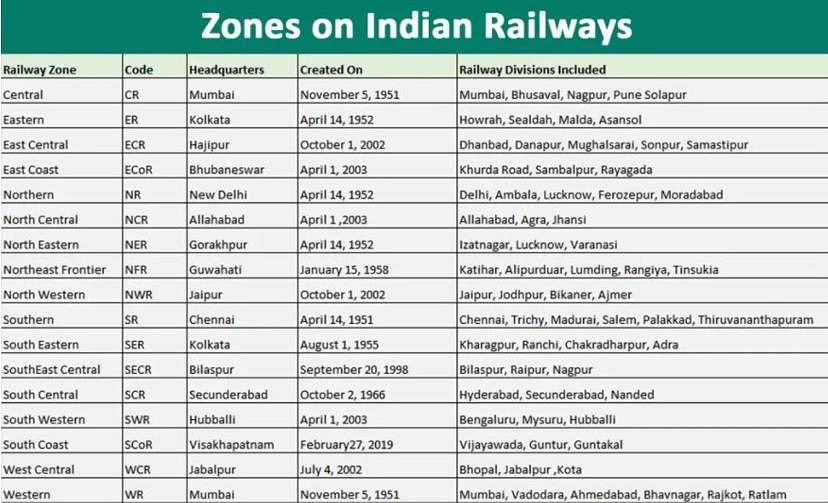
Which Zone has become the First fully electrified railway zone in the country?
With which of the following countries is India's largest export currently?
Which of the following is the most commonly used chemical for the ripening mangoes in India?
Which of the following acts as both endocrine and exocrine gland?
A mixture of camphor and KCl can be separated by which of the following processes?
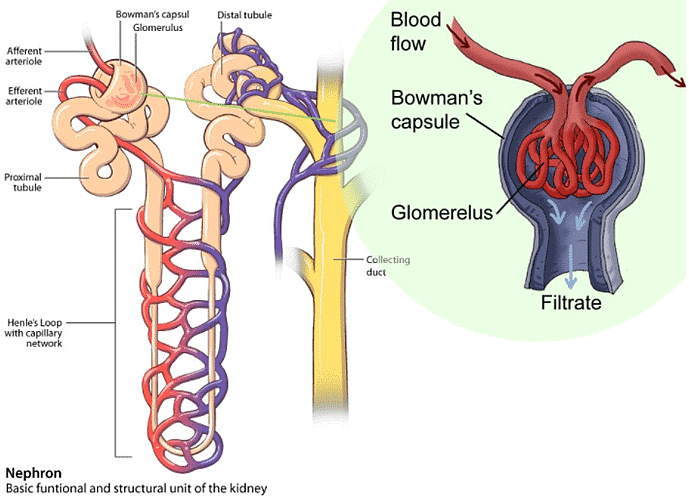
In which among the following organ, “Bowman’s Capsule” is found?
Relative strength of magnetic field at a point in the space surrounding the magnet is shown by the-
A telephone bill costs Rs. 11 for 2 minutes 30 seconds. What is the cost (in rupees) for 3 minutes 20 seconds? (Round up to one decimal)
The paint in a certain container is sufficient to paint an area equal to 9.375m2. How many bricks of dimensions 22.5cm × 10cm × 7.5cm can be painted out of this container?
A is half as good a workman as B and together they finish a piece of work in 32 days. In how many days will A alone finish the same work?
A motor boat has speed 30 km/h in still water. It goes 60 km down stream and comes back in 9/2 h. What is the speed of the stream?