RBI Assistant Mains Mock Test - 3 - Banking Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RBI Assistant Mains Mock Test - 3
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
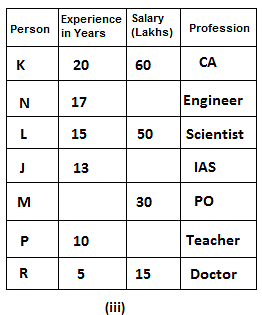
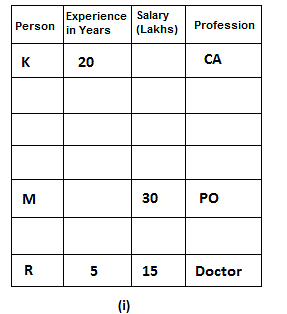
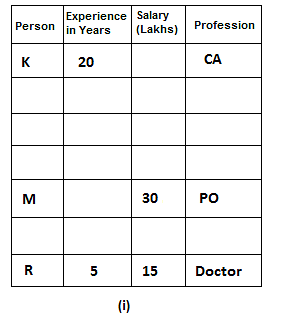
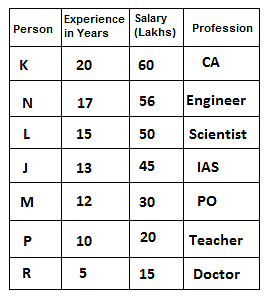
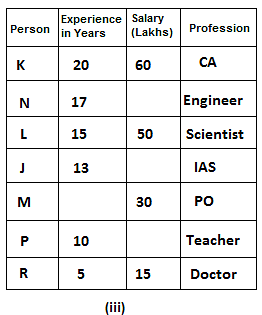
Seven friends have different professions: Scientist, Doctor, IAS, Engineer, Teacher, PO and CA, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them have different annual salaries and all of them have different experiences in their fields. One who is the most experienced has the highest annual salary.
N's annual salary is a multiple of both 7 and 8. One who is a doctor is the least experienced. Difference between salaries of the one who is a scientist and K is 10 lakh. Out of the seven friends, one has an experience of 12 years. IAS's annual salary is the sum of the annual salaries of the one who is a doctor and the one who is a PO. Difference between salaries of M and K is 30 lakh. L's experience is equal to the sum of experiences of P and R. M is a PO and 4 persons have experience more than him. L has more experience than the IAS. K has an experience of 20 years that is the highest amongst all and he is a CA. One who is a teacher has 10 years less experience than the one whose salary is 60 lakh and his annual salary is 36 lakh less than the one who is an engineer. R has an experience of 5 years and his annual salary is 15 lakh, which is 15 lakh less than the one who is a PO. N is an engineer and has 12 years more experience than the one who is a doctor. J is an IAS and has 2 years less experience than the one who is a scientist. P is neither a doctor nor a scientist. One who is a scientist has 5 years less experience than the one who is a CA.
Who is the least experienced person?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
Seven friends have different professions: Scientist, Doctor, IAS, Engineer, Teacher, PO and CA, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them have different annual salaries and all of them have different experiences in their fields. One who is the most experienced has the highest annual salary.
N's annual salary is a multiple of both 7 and 8. One who is a doctor is the least experienced. Difference between salaries of the one who is a scientist and K is 10 lakh. Out of the seven friends, one has an experience of 12 years. IAS's annual salary is the sum of the annual salaries of the one who is a doctor and the one who is a PO. Difference between salaries of M and K is 30 lakh. L's experience is equal to the sum of experiences of P and R. M is a PO and 4 persons have experience more than him. L has more experience than the IAS. K has an experience of 20 years that is the highest amongst all and he is a CA. One who is a teacher has 10 years less experience than the one whose salary is 60 lakh and his annual salary is 36 lakh less than the one who is an engineer. R has an experience of 5 years and his annual salary is 15 lakh, which is 15 lakh less than the one who is a PO. N is an engineer and has 12 years more experience than the one who is a doctor. J is an IAS and has 2 years less experience than the one who is a scientist. P is neither a doctor nor a scientist. One who is a scientist has 5 years less experience than the one who is a CA.
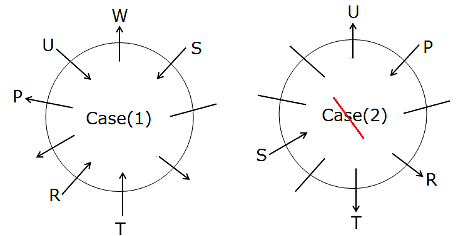
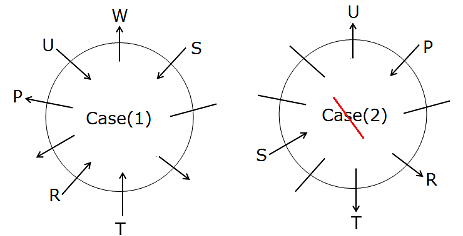
Four of the friends as below belong to a group with a distinct pattern. Find the one that does not belong to that group.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
Seven friends have different professions: Scientist, Doctor, IAS, Engineer, Teacher, PO and CA, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them have different annual salaries and all of them have different experiences in their fields. One who is the most experienced has the highest annual salary.
N's annual salary is a multiple of both 7 and 8. One who is a doctor is the least experienced. Difference between salaries of the one who is a scientist and K is 10 lakh. Out of the seven friends, one has an experience of 12 years. IAS's annual salary is the sum of the annual salaries of the one who is a doctor and the one who is a PO. Difference between salaries of M and K is 30 lakh. L's experience is equal to the sum of experiences of P and R. M is a PO and 4 persons have experience more than him. L has more experience than the IAS. K has an experience of 20 years that is the highest amongst all and he is a CA. One who is a teacher has 10 years less experience than the one whose salary is 60 lakh and his annual salary is 36 lakh less than the one who is an engineer. R has an experience of 5 years and his annual salary is 15 lakh, which is 15 lakh less than the one who is a PO. N is an engineer and has 12 years more experience than the one who is a doctor. J is an IAS and has 2 years less experience than the one who is a scientist. P is neither a doctor nor a scientist. One who is a scientist has 5 years less experience than the one who is a CA.
Who has the second highest annual salary?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
Seven friends have different professions: Scientist, Doctor, IAS, Engineer, Teacher, PO and CA, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them have different annual salaries and all of them have different experiences in their fields. One who is the most experienced has the highest annual salary.
N's annual salary is a multiple of both 7 and 8. One who is a doctor is the least experienced. Difference between salaries of the one who is a scientist and K is 10 lakh. Out of the seven friends, one has an experience of 12 years. IAS's annual salary is the sum of the annual salaries of the one who is a doctor and the one who is a PO. Difference between salaries of M and K is 30 lakh. L's experience is equal to the sum of experiences of P and R. M is a PO and 4 persons have experience more than him. L has more experience than the IAS. K has an experience of 20 years that is the highest amongst all and he is a CA. One who is a teacher has 10 years less experience than the one whose salary is 60 lakh and his annual salary is 36 lakh less than the one who is an engineer. R has an experience of 5 years and his annual salary is 15 lakh, which is 15 lakh less than the one who is a PO. N is an engineer and has 12 years more experience than the one who is a doctor. J is an IAS and has 2 years less experience than the one who is a scientist. P is neither a doctor nor a scientist. One who is a scientist has 5 years less experience than the one who is a CA.
How many persons have the annual salary less than the salary of J?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
Seven friends have different professions: Scientist, Doctor, IAS, Engineer, Teacher, PO and CA, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them have different annual salaries and all of them have different experiences in their fields. One who is the most experienced has the highest annual salary.
N's annual salary is a multiple of both 7 and 8. One who is a doctor is the least experienced. Difference between salaries of the one who is a scientist and K is 10 lakh. Out of the seven friends, one has an experience of 12 years. IAS's annual salary is the sum of the annual salaries of the one who is a doctor and the one who is a PO. Difference between salaries of M and K is 30 lakh. L's experience is equal to the sum of experiences of P and R. M is a PO and 4 persons have experience more than him. L has more experience than the IAS. K has an experience of 20 years that is the highest amongst all and he is a CA. One who is a teacher has 10 years less experience than the one whose salary is 60 lakh and his annual salary is 36 lakh less than the one who is an engineer. R has an experience of 5 years and his annual salary is 15 lakh, which is 15 lakh less than the one who is a PO. N is an engineer and has 12 years more experience than the one who is a doctor. J is an IAS and has 2 years less experience than the one who is a scientist. P is neither a doctor nor a scientist. One who is a scientist has 5 years less experience than the one who is a CA.
Which of the following combinations is incorrect?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
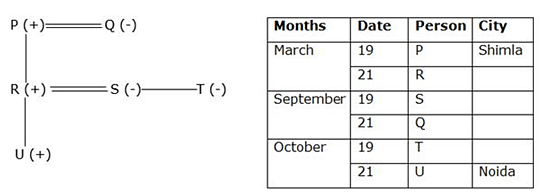
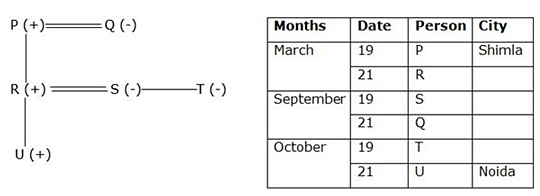
Six family members i.e. P, Q, R, S, T and U were born either on 19th or 21st in three different months i.e. March, September and October but not necessarily in the same order. All of them planned vacations for some destination.
P was the father-in-law of S and was born in the month which has 31 days. Mother of R was born on 21st September. The oldest male member of the family goes to Shimla and the youngest among them goes to Noida. T who was born on 19th of the month, was the sister-in-law of R who was born on 21st of the month. Two persons were born between R and T. S was the sister of T. No female goes to Delhi. No one was born after U who was a son of R. One of them goes to Manali. R’s mother goes to Goa. Sister-in-law of R doesn’t go to Mohali.
How is P related to U?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Six family members i.e. P, Q, R, S, T and U were born either on 19th or 21st in three different months i.e. March, September and October but not necessarily in the same order. All of them planned vacations for some destination.
P was the father-in-law of S and was born in the month which has 31 days. Mother of R was born on 21st September. The oldest male member of the family goes to Shimla and the youngest among them goes to Noida. T who was born on 19th of the month, was the sister-in-law of R who was born on 21st of the month. Two persons were born between R and T. S was the sister of T. No female goes to Delhi. No one was born after U who was a son of R. One of them goes to Manali. R’s mother goes to Goa. Sister-in-law of R doesn’t go to Mohali.
Who among the following was born on 19th March?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Six family members i.e. P, Q, R, S, T and U were born either on 19th or 21st in three different months i.e. March, September and October but not necessarily in the same order. All of them planned vacations for some destination.
P was the father-in-law of S and was born in the month which has 31 days. Mother of R was born on 21st September. The oldest male member of the family goes to Shimla and the youngest among them goes to Noida. T who was born on 19th of the month, was the sister-in-law of R who was born on 21st of the month. Two persons were born between R and T. S was the sister of T. No female goes to Delhi. No one was born after U who was a son of R. One of them goes to Manali. R’s mother goes to Goa. Sister-in-law of R doesn’t go to Mohali.
How many female members are there in the family?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Six family members i.e. P, Q, R, S, T and U were born either on 19th or 21st in three different months i.e. March, September and October but not necessarily in the same order. All of them planned vacations for some destination.
P was the father-in-law of S and was born in the month which has 31 days. Mother of R was born on 21st September. The oldest male member of the family goes to Shimla and the youngest among them goes to Noida. T who was born on 19th of the month, was the sister-in-law of R who was born on 21st of the month. Two persons were born between R and T. S was the sister of T. No female goes to Delhi. No one was born after U who was a son of R. One of them goes to Manali. R’s mother goes to Goa. Sister-in-law of R doesn’t go to Mohali.
How many persons were born between the mother of U and Q?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Six family members i.e. P, Q, R, S, T and U were born either on 19th or 21st in three different months i.e. March, September and October but not necessarily in the same order. All of them planned vacations for some destination.
P was the father-in-law of S and was born in the month which has 31 days. Mother of R was born on 21st September. The oldest male member of the family goes to Shimla and the youngest among them goes to Noida. T who was born on 19th of the month, was the sister-in-law of R who was born on 21st of the month. Two persons were born between R and T. S was the sister of T. No female goes to Delhi. No one was born after U who was a son of R. One of them goes to Manali. R’s mother goes to Goa. Sister-in-law of R doesn’t go to Mohali.
On which of the following date does S was born?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
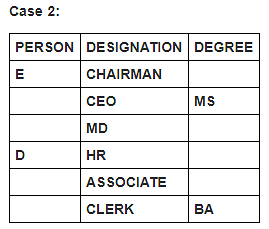
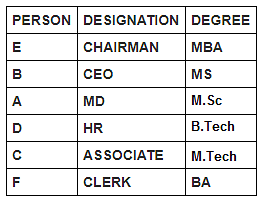
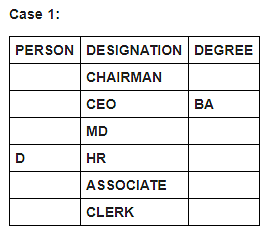
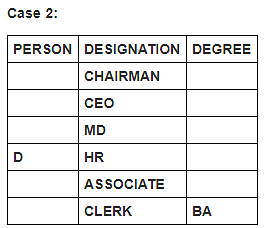
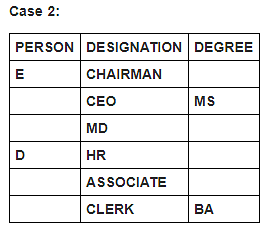
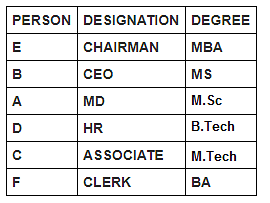
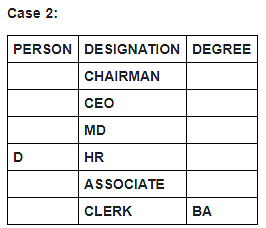
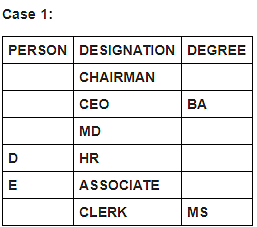
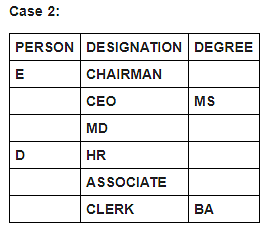
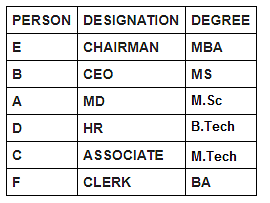
Six persons in a company have different designations. The designations in descending order are Chairman, CEO, MD, HR, Associate and Clerk. It is known that each of these persons has different degrees of specialisation.
The person having MS degree is ranked just lower than E. The person with M.Tech degree is ranked lower than the person with M.Sc degree. C is ranked just higher than F, but lower than the person with B.Tech degree. Two persons are ranked between E and the person ranked with B.Tech degree. Only one person is ranked between D and the person who has BA degree. D is HR. Three persons are ranked between one who has BA degree and the person having MS degree. B is ranked higher than A, but lower than the person having MBA degree.
Who among the following holds an MS degree?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Six persons in a company have different designations. The designations in descending order are Chairman, CEO, MD, HR, Associate and Clerk. It is known that each of these persons has different degrees of specialisation.
The person having MS degree is ranked just lower than E. The person with M.Tech degree is ranked lower than the person with M.Sc degree. C is ranked just higher than F, but lower than the person with B.Tech degree. Two persons are ranked between E and the person ranked with B.Tech degree. Only one person is ranked between D and the person who has BA degree. D is HR. Three persons are ranked between one who has BA degree and the person having MS degree. B is ranked higher than A, but lower than the person having MBA degree.
Who is the CEO?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Six persons in a company have different designations. The designations in descending order are Chairman, CEO, MD, HR, Associate and Clerk. It is known that each of these persons has different degrees of specialisation.
The person having MS degree is ranked just lower than E. The person with M.Tech degree is ranked lower than the person with M.Sc degree. C is ranked just higher than F, but lower than the person with B.Tech degree. Two persons are ranked between E and the person ranked with B.Tech degree. Only one person is ranked between D and the person who has BA degree. D is HR. Three persons are ranked between one who has BA degree and the person having MS degree. B is ranked higher than A, but lower than the person having MBA degree.
Designation of how many persons is lower than that of A?
Directions: Study the following information and answer the question given below.
Six persons in a company have different designations. The designations in descending order are Chairman, CEO, MD, HR, Associate and Clerk. It is known that each of these persons has different degrees of specialisation.
The person having MS degree is ranked just lower than E. The person with M.Tech degree is ranked lower than the person with M.Sc degree. C is ranked just higher than F, but lower than the person with B.Tech degree. Two persons are ranked between E and the person ranked with B.Tech degree. Only one person is ranked between D and the person who has BA degree. D is HR. Three persons are ranked between one who has BA degree and the person having MS degree. B is ranked higher than A, but lower than the person having MBA degree.
Which of the following is false?
Below questions contain input and final output. Certain rules are applied to each step. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Input: 389264 728369 693874 928647 642943
Step I: 386492 697382 396874 478692 294463
Step II: 294463 386492 396874 478692 697382
Step III: 181618 242418 274828 284818 542116
Step IV: 25 21 31 31 19
Based on the rules followed above find the output for the given input.
Input: 763829 469423 893246 698347 289674
Which of the following is the second lowest number in step III?
Below questions contain input and final output. Certain rules are applied to each step. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Input: 389264 728369 693874 928647 642943
Step I: 386492 697382 396874 478692 294463
Step II: 294463 386492 396874 478692 697382
Step III: 181618 242418 274828 284818 542116
Step IV: 25 21 31 31 19
Based on the rules followed above find the output for the given input.
Input: 763829 469423 893246 698347 289674
Which of the following represent step I correctly?
Below questions contain input and final output. Certain rules are applied to each step. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Input: 389264 728369 693874 928647 642943
Step I: 386492 697382 396874 478692 294463
Step II: 294463 386492 396874 478692 697382
Step III: 181618 242418 274828 284818 542116
Step IV: 25 21 31 31 19
Based on the rules followed above find the output for the given input.
Input: 763829 469423 893246 698347 289674
Which of the following number is third from the right end of step II?
Below questions contain input and final output. Certain rules are applied to each step. Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Input: 389264 728369 693874 928647 642943
Step I: 386492 697382 396874 478692 294463
Step II: 294463 386492 396874 478692 697382
Step III: 181618 242418 274828 284818 542116
Step IV: 25 21 31 31 19
Based on the rules followed above find the output for the given input.
Input: 763829 469423 893246 698347 289674
What is the sum of the second lowest and second-highest number from step IV?
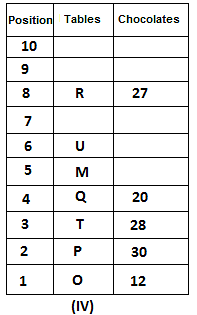
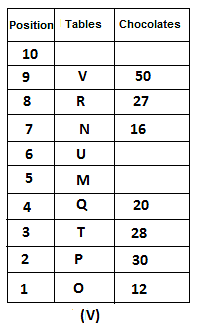
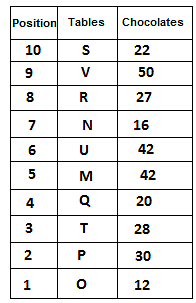
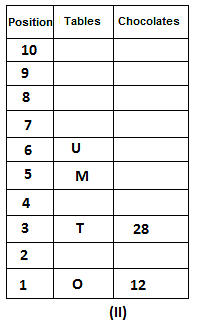
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
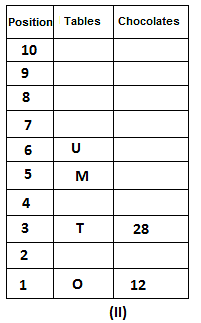
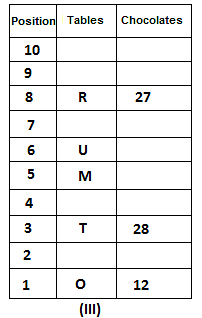
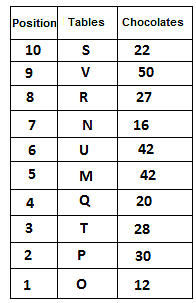
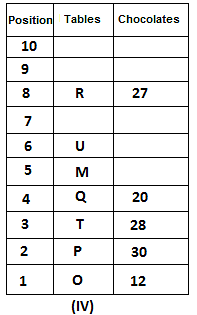
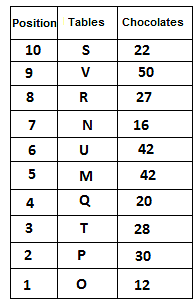
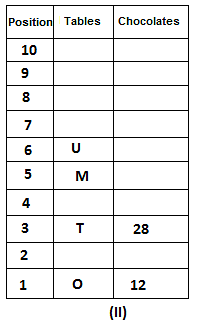
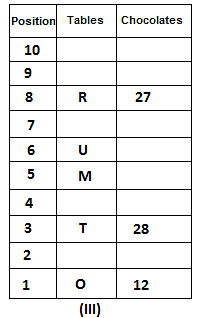
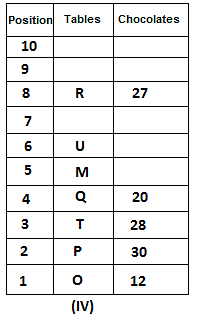
10 tables are placed one above another in such a way that the table which is placed at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and above it is numbered 2 and so on, till table numbered 10 that is the uppermost position. There are some chocolates kept on each table.
Note: The number of chocolate kept on each table is equal to the multiple of place number of table which is kept immediately above it. (E.g: The number of chocolates kept on table 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6, ….. so on and the number of chocolates kept on table 10 is a multiple of 11 i.e. 11, 22, 33, … so on)
Not more than 60 chocolates are kept on any table. Table P is placed below table M. Number of chocolates kept on table N is 16. Number of chocolates kept on table S is 5 less than the number of chocolates kept on table R. Number of tables placed above table U is the same as that below table M and the same number of chocolates are kept on both the tables. 28 chocolates are kept on table T. Three tables are placed between table M and the table on which 12 chocolates are kept. Table R is kept above table N and number of chocolates kept on table R is one less than the number of chocolates kept on table T. Number of chocolates kept on table P is a multiple of both 3 and 5, but not more than 40. Table Q is placed immediately below table M and number of chocolates kept on table Q is 8 more than the number of chocolates kept on table O, which is placed at the lowermost position. Table U is placed immediately above table M. Number of chocolates kept on table V is the sum of number of chocolates kept on tables Q and P. Number of chocolates kept on tables U and M is a multiple of both 6 and 7. 15 chocolates are not kept on any table.
Which of the following tables is placed at position 7?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
10 tables are placed one above another in such a way that the table which is placed at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and above it is numbered 2 and so on, till table numbered 10 that is the uppermost position. There are some chocolates kept on each table.
Note: The number of chocolate kept on each table is equal to the multiple of place number of table which is kept immediately above it. (E.g: The number of chocolates kept on table 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6, ….. so on and the number of chocolates kept on table 10 is a multiple of 11 i.e. 11, 22, 33, … so on)
Not more than 60 chocolates are kept on any table. Table P is placed below table M. Number of chocolates kept on table N is 16. Number of chocolates kept on table S is 5 less than the number of chocolates kept on table R. Number of tables placed above table U is the same as that below table M and the same number of chocolates are kept on both the tables. 28 chocolates are kept on table T. Three tables are placed between table M and the table on which 12 chocolates are kept. Table R is kept above table N and number of chocolates kept on table R is one less than the number of chocolates kept on table T. Number of chocolates kept on table P is a multiple of both 3 and 5, but not more than 40. Table Q is placed immediately below table M and number of chocolates kept on table Q is 8 more than the number of chocolates kept on table O, which is placed at the lowermost position. Table U is placed immediately above table M. Number of chocolates kept on table V is the sum of number of chocolates kept on tables Q and P. Number of chocolates kept on tables U and M is a multiple of both 6 and 7. 15 chocolates are not kept on any table.
What is the sum of chocolates kept on tables V and S?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
10 tables are placed one above another in such a way that the table which is placed at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and above it is numbered 2 and so on, till table numbered 10 that is the uppermost position. There are some chocolates kept on each table.
Note: The number of chocolate kept on each table is equal to the multiple of place number of table which is kept immediately above it. (E.g: The number of chocolates kept on table 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6, ….. so on and the number of chocolates kept on table 10 is a multiple of 11 i.e. 11, 22, 33, … so on)
Not more than 60 chocolates are kept on any table. Table P is placed below table M. Number of chocolates kept on table N is 16. Number of chocolates kept on table S is 5 less than the number of chocolates kept on table R. Number of tables placed above table U is the same as that below table M and the same number of chocolates are kept on both the tables. 28 chocolates are kept on table T. Three tables are placed between table M and the table on which 12 chocolates are kept. Table R is kept above table N and number of chocolates kept on table R is one less than the number of chocolates kept on table T. Number of chocolates kept on table P is a multiple of both 3 and 5, but not more than 40. Table Q is placed immediately below table M and number of chocolates kept on table Q is 8 more than the number of chocolates kept on table O, which is placed at the lowermost position. Table U is placed immediately above table M. Number of chocolates kept on table V is the sum of number of chocolates kept on tables Q and P. Number of chocolates kept on tables U and M is a multiple of both 6 and 7. 15 chocolates are not kept on any table.
Find the odd one out.
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
10 tables are placed one above another in such a way that the table which is placed at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and above it is numbered 2 and so on, till table numbered 10 that is the uppermost position. There are some chocolates kept on each table.
Note: The number of chocolate kept on each table is equal to the multiple of place number of table which is kept immediately above it. (E.g: The number of chocolates kept on table 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6, ….. so on and the number of chocolates kept on table 10 is a multiple of 11 i.e. 11, 22, 33, … so on)
Not more than 60 chocolates are kept on any table. Table P is placed below table M. Number of chocolates kept on table N is 16. Number of chocolates kept on table S is 5 less than the number of chocolates kept on table R. Number of tables placed above table U is the same as that below table M and the same number of chocolates are kept on both the tables. 28 chocolates are kept on table T. Three tables are placed between table M and the table on which 12 chocolates are kept. Table R is kept above table N and number of chocolates kept on table R is one less than the number of chocolates kept on table T. Number of chocolates kept on table P is a multiple of both 3 and 5, but not more than 40. Table Q is placed immediately below table M and number of chocolates kept on table Q is 8 more than the number of chocolates kept on table O, which is placed at the lowermost position. Table U is placed immediately above table M. Number of chocolates kept on table V is the sum of number of chocolates kept on tables Q and P. Number of chocolates kept on tables U and M is a multiple of both 6 and 7. 15 chocolates are not kept on any table.
How many tables are placed between table V and the table on which 30 chocolates are kept?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
10 tables are placed one above another in such a way that the table which is placed at lowermost position is numbered as 1 and above it is numbered 2 and so on, till table numbered 10 that is the uppermost position. There are some chocolates kept on each table.
Note: The number of chocolate kept on each table is equal to the multiple of place number of table which is kept immediately above it. (E.g: The number of chocolates kept on table 1 is a multiple of 2 i.e. 2, 4, 6, ….. so on and the number of chocolates kept on table 10 is a multiple of 11 i.e. 11, 22, 33, … so on)
Not more than 60 chocolates are kept on any table. Table P is placed below table M. Number of chocolates kept on table N is 16. Number of chocolates kept on table S is 5 less than the number of chocolates kept on table R. Number of tables placed above table U is the same as that below table M and the same number of chocolates are kept on both the tables. 28 chocolates are kept on table T. Three tables are placed between table M and the table on which 12 chocolates are kept. Table R is kept above table N and number of chocolates kept on table R is one less than the number of chocolates kept on table T. Number of chocolates kept on table P is a multiple of both 3 and 5, but not more than 40. Table Q is placed immediately below table M and number of chocolates kept on table Q is 8 more than the number of chocolates kept on table O, which is placed at the lowermost position. Table U is placed immediately above table M. Number of chocolates kept on table V is the sum of number of chocolates kept on tables Q and P. Number of chocolates kept on tables U and M is a multiple of both 6 and 7. 15 chocolates are not kept on any table.
How many chocolates are kept on table S?
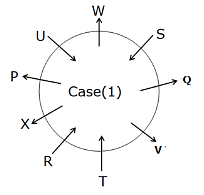
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X are sitting in a circular table in such a way that some are facing the center whereas others are facing away from the center. Not more than two persons sitting together are facing in the same direction. No two persons in alphabetical order are sitting together.
P sits third to the left of T, both are facing in opposite directions. A person sitting immediate left of P sits fourth to the right of S, who sits facing the center. U sits third to the left of R, both are facing in the same direction. Neither V nor P sits adjacent to R. U sits immediate left of W, who sits facing away from the center. Neither W nor Q sits adjacent to T. Q sits immediate left of V and facing away from the centre.
How many persons are sitting between T and Q when counted to the right of Q?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X are sitting in a circular table in such a way that some are facing the center whereas others are facing away from the center. Not more than two persons sitting together are facing in the same direction. No two persons in alphabetical order are sitting together.
P sits third to the left of T, both are facing in opposite directions. A person sitting immediate left of P sits fourth to the right of S, who sits facing the center. U sits third to the left of R, both are facing in the same direction. Neither V nor P sits adjacent to R. U sits immediate left of W, who sits facing away from the center. Neither W nor Q sits adjacent to T. Q sits immediate left of V and facing away from the centre.
Who sits second to the right of Q?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X are sitting in a circular table in such a way that some are facing the center whereas others are facing away from the center. Not more than two persons sitting together are facing in the same direction. No two persons in alphabetical order are sitting together.
P sits third to the left of T, both are facing in opposite directions. A person sitting immediate left of P sits fourth to the right of S, who sits facing the center. U sits third to the left of R, both are facing in the same direction. Neither V nor P sits adjacent to R. U sits immediate left of W, who sits facing away from the center. Neither W nor Q sits adjacent to T. Q sits immediate left of V and facing away from the centre.
What is the position of W with respect to V?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X are sitting in a circular table in such a way that some are facing the center whereas others are facing away from the center. Not more than two persons sitting together are facing in the same direction. No two persons in alphabetical order are sitting together.
P sits third to the left of T, both are facing in opposite directions. A person sitting immediate left of P sits fourth to the right of S, who sits facing the center. U sits third to the left of R, both are facing in the same direction. Neither V nor P sits adjacent to R. U sits immediate left of W, who sits facing away from the center. Neither W nor Q sits adjacent to T. Q sits immediate left of V and facing away from the centre.
If W is related to U, similarly Q is related to S, then who among the following person is related to X?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X are sitting in a circular table in such a way that some are facing the center whereas others are facing away from the center. Not more than two persons sitting together are facing in the same direction. No two persons in alphabetical order are sitting together.
P sits third to the left of T, both are facing in opposite directions. A person sitting immediate left of P sits fourth to the right of S, who sits facing the center. U sits third to the left of R, both are facing in the same direction. Neither V nor P sits adjacent to R. U sits immediate left of W, who sits facing away from the center. Neither W nor Q sits adjacent to T. Q sits immediate left of V and facing away from the centre.
Find the odd one out?
Directions: In the following question, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. The statements are followed by two conclusions. Find out which conclusion is definitely true according to the given statements.
Statements: Q ≤ U = E ≥ N; R > A ≥ E; T ≤ O ≤ N
Conclusions:
I. T ≤ E
II. R > N
Below question contains some conclusions followed by some statements. Study the following information carefully and answer which of the following statement is logically true for the given conclusion.
Conclusion: Some LED can never be Keyboard. Some Mouse not being LED is a possibility.