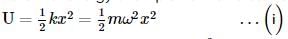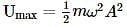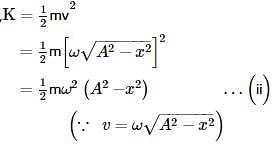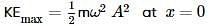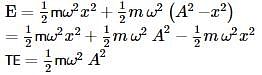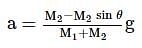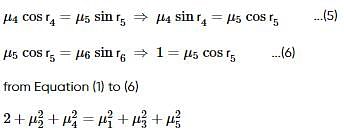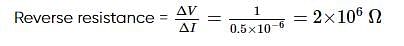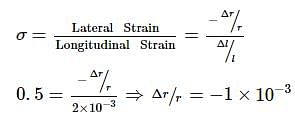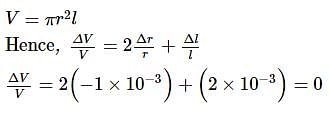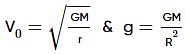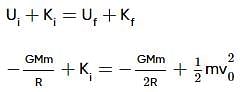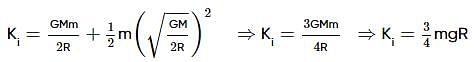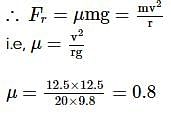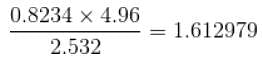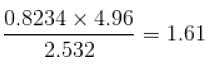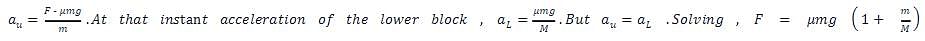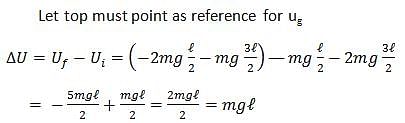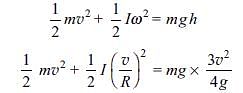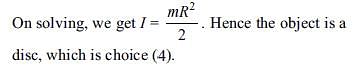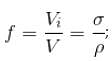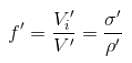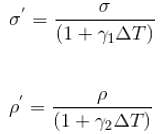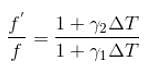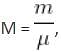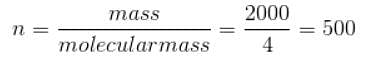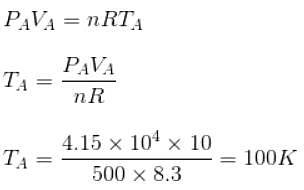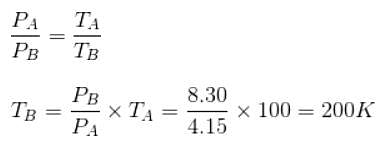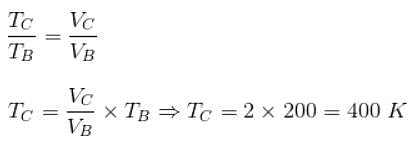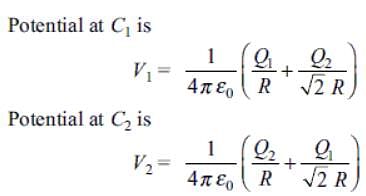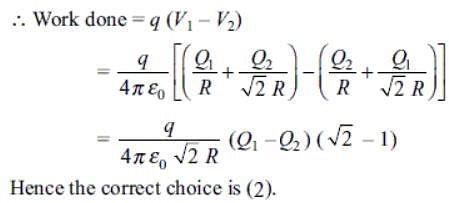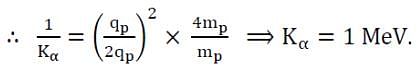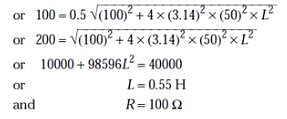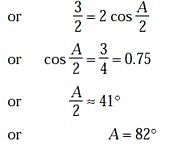BITSAT Practice Test - 9 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BITSAT Practice Test - 9
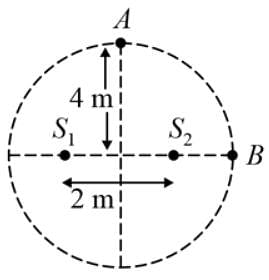
Two speakers connected to the same source of fixed frequency are placed 2.0 m apart in a box. A sensitive microphone placed at a distance of 4.0 m from their midpoint along the perpendicular bisector shows maximum response. The box is slowly rotated until the speakers are in line with the microphone. The distance between the midpoint of the speakers and the microphone remains unchanged. Exactly five maximum responses are observed in the microphone in doing this. The wavelength of the sound wave is:
A raindrop falls near the surface of the Earth with almost uniform velocity because
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
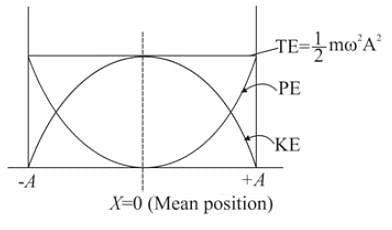
What is the correct expression for the total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator with displacement ?
What determines the emf between the two metals placed in an electrolyte?
The minimum energy required to eject an electron, from the metal surface is called
A physical quantity, associated with electrical conductivity, has the SI unit ohm-meter. Identify this physical quantity.
Two spherical bodies of mass M and 5M and radii R and 2R respectively are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body just before collision is–
Think about Gravitational Force. Which of the following statement is correct regarding it?
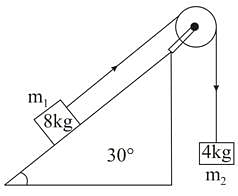
Two masses of 8 kg and 4 kg are connected by a string as shown in figure over a frictionless pulley. The acceleration of the system is
The diagram shows five isosceles right angled prisms. A light ray incident at 90o at the first face emerges at same angle with the normal from the last face. which of the following relations will hold regarding the refractive indices?

In a reverse biased diode when the applied voltage changes by 1 V, the current is found to change by 0.5 μA. The reverse bias resistance of the diode is
In the given graph shown the variation of the potential energy U by the interaction between two particles, with the distance separating them, r.
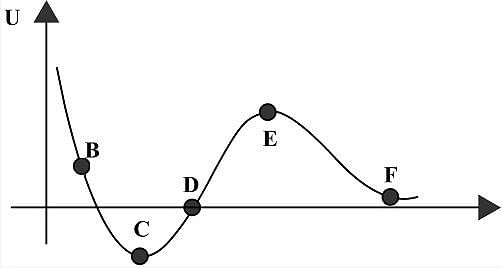
The given plot shows the variation of u, the potential energy of interaction between two particles with the distance separating them r.
1. B and D are equilibrium points
2. C is a point of stable equilibrium
3. The force is interaction between the two particles is attractive between C and D and repulsive between D and E
4. The force of interaction between particles is repulsive between points E and F.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A material has Poisson's ratio 0.50. If a uniform rod of it suffers a longitudinal strain of 2x10−3, then the percentage change in volume is
A satellite of mass m, initially at rest on the earth, is launched into a circular orbit at a height equal to the radius of the earth. The minimum energy required is
A car of mass 1500 kg is moving with a speed of 12.5 m/s on a circular path of a radius 20 m on a level road. What should be the coefficient of friction between the car and the road, so that the car does not slip?
The expression 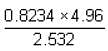 up to correct significant figures is equal to
up to correct significant figures is equal to
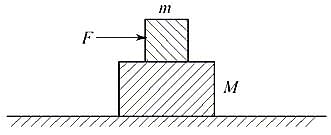
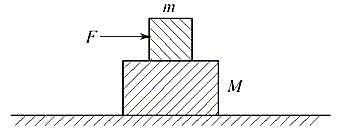
A block of mass m is lying on a another block of mass M, lying on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown in Figure. If the coefficient static friction between the two blocks is μs , the minimum horizontal force F that must be applied to block of mass m so that it moves over block of mass M is
A rope of length l and mas 'm' is connected to a chain of length 'l' and mass 2 M and hung vertically as shown in the figure. What is the change in gravitational potential energy if the system is inverted and hung from same point?

A small object of uniform density rolls up a curved surface with an initial velocity v. It reaches up to a maximum length 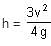 with respect to the initial position. The object is a
with respect to the initial position. The object is a
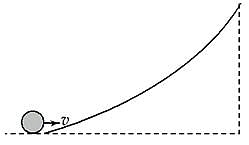
A body is projected vertically upwards from the surface of a planet of radius R, with a velocity equal to one-third of the escape velocity of the planet. The maximum height attained by the body is
A piece of metal floats on mercury. The coefficients of volume expansion of the metal and mercury are γ1 and γ2 respectively. If the temperature of both mercury and metal are increased by an amount Δt, the fraction of the volume of the metal submerged in mercury changes by the factor.
Two blocks A and B are connected to each other by a string and a spring of force constant k, as shown in the figure. The string passes over a frictionless pulley as shown. Block B slides over the horizontal top surface of a stationary block C and block A slides along the vertical side of C both with the same uniform speed. The coefficient of friction between the surfaces of the blocks B and C is μ
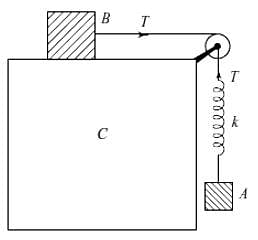
If the mass of block A is m, what is the mass of block B? .
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity one-tenth the velocity of sound. The apparent increase in frequency is
A sample of 2 kg of monatomic helium (assumed ideal) is taken through the process ABC and another sample of 2 kg of the same gas is taken through the process ADC as shown in the figure. (Molecular mass = 4 and R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1)
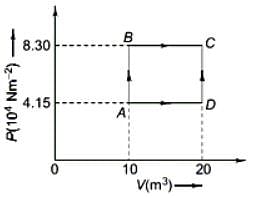
The temperature of state C is
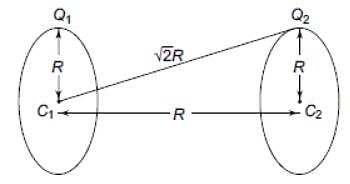
Two identical thin rings, each of radius R, are coaxially placed at a distance R apart. If Q1 and Q2 are the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q from the centre of one ring to the centre of the other is
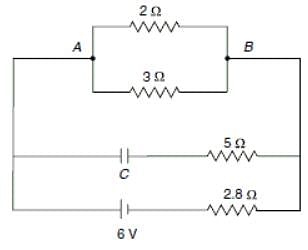
If the internal resistance of the battery is negligible and the capacitance C = 0.5μF, then what is the steady state current in the 2Ω resistor shown in the figure below?
A proton of mass m and charge +e is moving in a circular orbit in a magnetic field with energy 1 MeV. What should be the energy of an α - particle (mass 4m and charge +2e) so that it revolves in a circular orbit of the same radius in the same magnetic field?
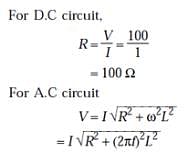
When 100 V DC is applied across a solenoid, a current of 1 A flows in it. When 100 V AC is applied across the same coil, the current drops to 0.5 A. If the frequency of the AC source is 50 Hz, the resistance and inductance of the solenoid respectively are
The angle of minimum deviation for a prism of refractive index 3/2 is equal to the angle of prism. The angle of prism is
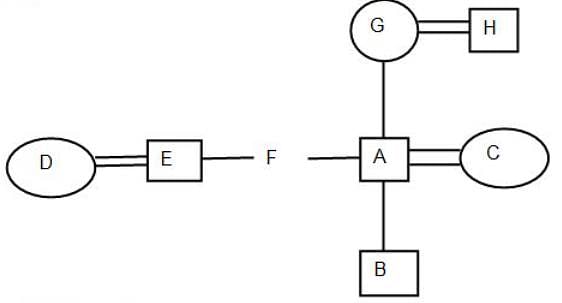
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given Questions:
P^Q-P is the child of Q
P!Q-P is the parent of Q
P*Q - P is elder to Q
P#Q-P is younger to Q
P@Q-P is brother of Q
P&Q - P is wife of Q
P+Q-P is sister-in-law of Q
Q. If A!B^C+D&E@F^G!A, if B is the son of C, then how is A related to B?