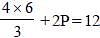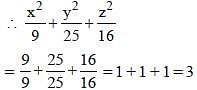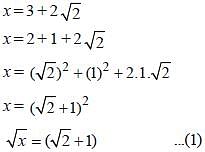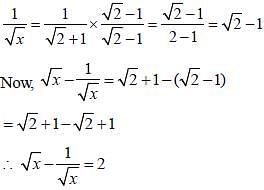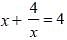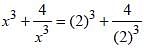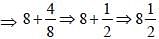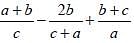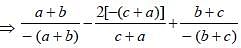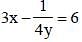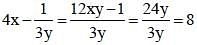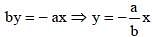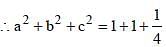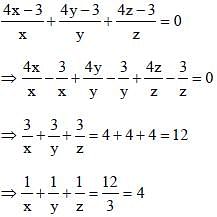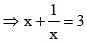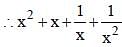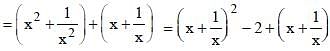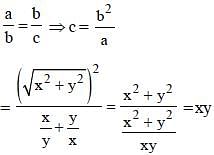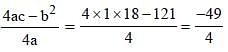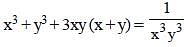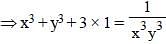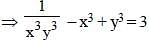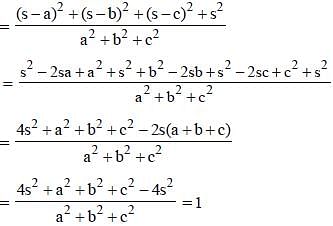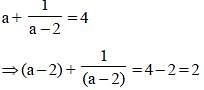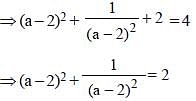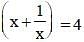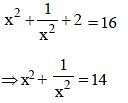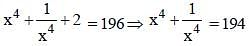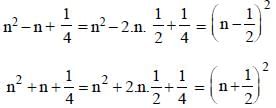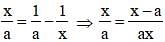SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Algebra- 4 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SSC CGL Previous Year Questions: Algebra- 4
If (4x/3) + 2P = 12 for what value of P, x = 6 ? (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If (x – 3)2 + (y – 5)2 + (z – 4)2 = 0, then the value of 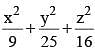 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
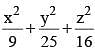 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If 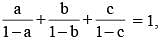 then the value of
then the value of 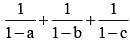 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
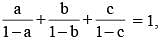 then the value of
then the value of 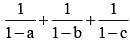 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)The total cost of 8 buckets and 5 mugs is ₹ 92 and the total cost of 5 buckets and 8 mugs is ₹ 77. Find the cost of 2 mugs and 3 buckets. (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The sum of the ages of Puneet and his father is 45 years and the product of their ages is 126. What is the age of Puneet? (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
If a = 0, b ≠ 0, c ≠ 0, then the equation ax + by + c = 0 represents a line parallel to (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
If ‘a’ be a positive number, then the least value of a + (1/a) is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If x = 3 + 2√2, then the value of 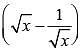 is (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
If x + (4/x) = 4, find the value of x3 + (4/x3). (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If a + b + c = 0, find the value of 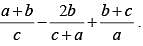 (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
(SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If 3x – 1/4y = 6, then the value of 4x – 1/3y is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The expression x4 – 2x2 + k will be a perfect square when the value of k is (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
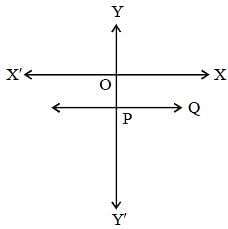
An equation of the form ax + by + c = 0 where a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0, c = 0 represents a straight line which passes through (SSC CGL1st Sit. 2013)
If a2 + b2 + 4c2 = 2(a + b – 2c) – 3 and a, b, c are real, then the value of (a2 + b2 + c2) is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If 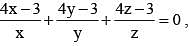 then the value of
then the value of 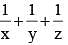 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If x2 – 3x + 1 = 0, then the value of 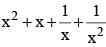 is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
The third proportional to 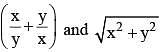 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If x + y + z = 6 and x2 + y2 + z2 = 20 then the value of x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
The minimum value of (x – 2) (x – 9) is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If a3 – b3 – c3 = 0 then the value of a9 – b9 – c9 – 3a3b3c3 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If xy (x + y) = 1 then, the value of 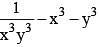 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If a + b + c = 2s, then 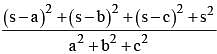 is equal to (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
is equal to (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If 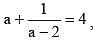 then the value of
then the value of 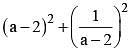 is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If the number p is 5 more than q and the sum of the squares of p and q is 55, then the product of p and q is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
If (x + 7954 × 7956) be a square number, then the value of ‘x’ is (SSC CGL 2nd Sit. 2013)
Equation of the straight line parallel to x-axis and also 3 units below x-axis is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If 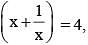 then the value of
then the value of 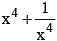 is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If 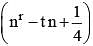 be a perfect square, then the values of t are: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
be a perfect square, then the values of t are: (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If 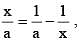 then the value of x – x2 is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
then the value of x – x2 is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)
If a2 + b2 + c2 + 3 = (2 (a – b – c), then the value of 2a – b + c is : (SSC CGL 1st Sit. 2013)