Test: Somatosensation - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Somatosensation - 1
When a cup starts to slip from one’s hand it makes quick vibrations, which are felt through the hand. Which receptor, that is important in perceiving vibration, is being triggered?
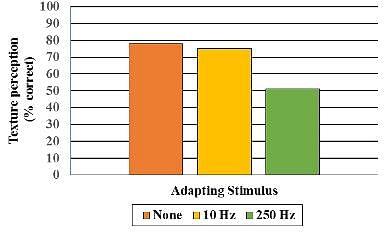
A researcher is attempting to test the hypothesis that vibrotaction is important in the perception of fine or closely spaced texture. She uses a 10 Hz vibration stimulus applied to the skin for 7 minutes to adapt the Meissner corpuscle and a 250 Hz stimulus applied for 7 minutes to adapt the Pacinian corpuscle. What effect did adaptation of the Meissner corpuscle and the Pacinian corpuscle have on the ability to perceive texture, based on the chart below?

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What term describes how a neuron down-regulates its responsiveness over time to a constant stimulus?
Which of these factors does NOT affect the perception of pain?
Tactile acuity can be measured by comparing the two-point thresholds of different parts of the body. Which of these areas would have the highest tactile acuity?
A neuroscientist conducted an investigation on his patient prior to brain surgery to remove a lesion in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1). When stimulating the ventral part of S1, she caused sensations on the face of the patient. As she moved up, the patient felt sensations in the hand, head, and leg. When she reached the dorsal S1, the patient felt sensations in the foot. What cortical map of the body is the neuroscientist tracing to determine whether the lesion affected areas of S1?
Which sense relates to the perception of motion and uses neurons in muscles, joints, and tendons?
Ménière's disease is an inner ear disorder, which affects balance and hearing. Symptoms include extreme vertigo, loss of hearing, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness or pressure that builds up in the ear. One symptom, called the “otolithic crisis of Tumarkin”, results from a mechanical deformation of the utricle and saccule. The patient’s hair cells of the otoliths are activated and he or she will suddenly feel tilted (although standing up straight). In extreme cases, the patient will fall to the ground, while still conscious, and feel as though someone violently pushed him or her down. Which statement is a likely cause of this symptom?
Which type of receptor is responsible for detecting temperature changes in the environment?
Which area of the brain is primarily involved in processing and integrating somatosensory information?

















