Test: Chemical Kinetics - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Kinetics
Which of the following factors affects the rate of a chemical reaction?
Given the following information, what would the overall order of the reaction be?
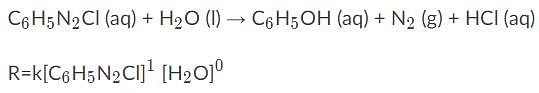
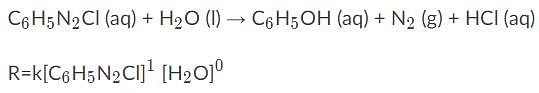
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statements is true regarding activation energy?
Which of the following are true of reaction rates?
I. The overall rate law is determined by the fastest step of a reaction
II. The presence of a catalyst will increase the number of molecules entering the transition state
III. An increase in temperature will increase the rate of a reaction
IV. Increasing the concentration of reactants will increase the rate at which products yield
The Arrhenius equation, k = Ae-Ea/(RT) gives the relationship of the rate constant of a reaction to the temperature (T) and the activation energy (Ea). If a catalyst is added that decreases the activation energy by 20 kJ/mol, and simultaneously the temperature is decreased by 20 K, which of the following will be true of the reaction?
Which of the following is true regarding the addition of a catalyst to a reaction?
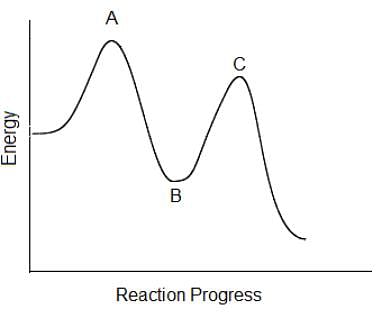
In the following reaction coordinate diagram, each point represents a state a molecule passes through as it undergoes the reaction. Which of the following could be isolated during the course of the reaction?
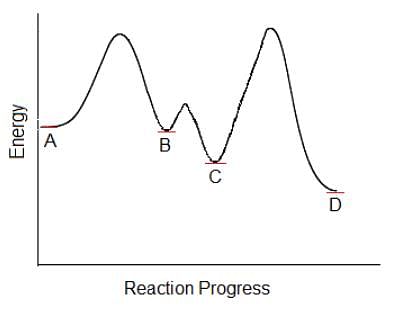
Which of the following steps in this multi-step chemical reaction will be the rate determining step?
Which of the following is an example of a zero-order reaction?
Which of the following factors would increase the rate of a gaseous reaction?

















