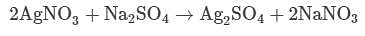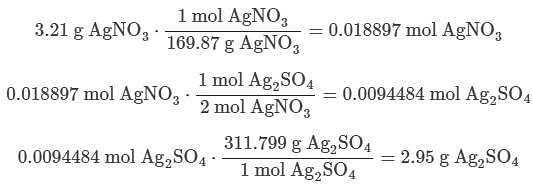Test: Chemistry - 1 - MCAT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemistry - 1
If 3.21 g of silver nitrate reacts with an excess of sodium sulfate, what mass of silver sulfate will be produced?
(MM silver nitrate = 169.87 g/mol; MM sodium sulfate = 142.04 g/mol; MM silver sulfate = 311.799 g/mol; MM sodium nitrate = 84.9947 g/mol)11.8 g
(MM silver nitrate = 169.87 g/mol; MM sodium sulfate = 142.04 g/mol; MM silver sulfate = 311.799 g/mol; MM sodium nitrate = 84.9947 g/mol)11.8 g
Which of the following statements correctly describes an exothermic reaction?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following factors affects the rate of a chemical reaction?
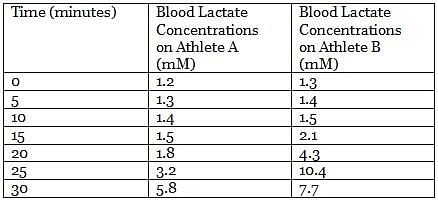
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can follow different catabolic paths depending on many factors. In animal tissues and under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD+, in a reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. During the recovery period after strenuous exercise, lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver.
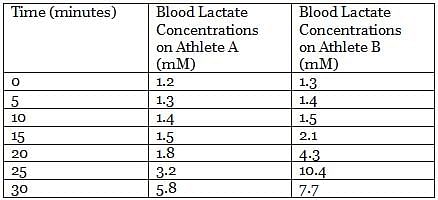
In an experiment, the lactate levels in blood for two athletes are measured at different times from the start of vigorous exercise. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below:
Q. Lactate dehydrogenase is classified as what type of enzyme? (You may consult the attachment.)
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can follow different catabolic paths depending on many factors. In animal tissues and under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD+, in a reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. During the recovery period after strenuous exercise, lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver.
In an experiment, the lactate levels in blood for two athletes are measured at different times from the start of vigorous exercise. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below:
Q. If an individual has a lactate dehydrogenase deficiency, what will be observed in a blood test during vigorous exercise? (You may utilize the attachment.)
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can follow different catabolic paths depending on many factors. In animal tissues and under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD+, in a reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. During the recovery period after strenuous exercise, lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver.
In an experiment, the lactate levels in blood for two athletes are measured at different times from the start of vigorous exercise. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below:
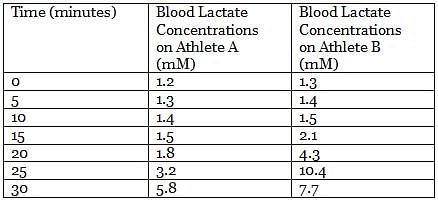
Q. From the results of the experiment (see attachment), which athlete is in the best physical shape?
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can follow different catabolic paths depending on many factors. In animal tissues and under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD+, in a reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. During the recovery period after strenuous exercise, lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver.
In an experiment, the lactate levels in blood for two athletes are measured at different times from the start of vigorous exercise. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below:
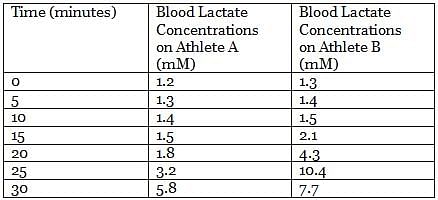
Q. Which of the following statements about lactate formation is true? (See the attachment.)
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can follow different catabolic paths depending on many factors. In animal tissues and under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD+, in a reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. During the recovery period after strenuous exercise, lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver.
In an experiment, the lactate levels in blood for two athletes are measured at different times from the start of vigorous exercise. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below:
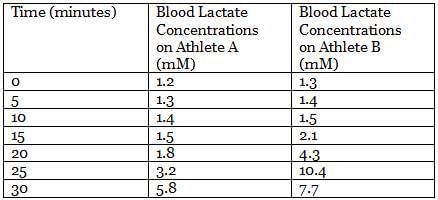
Q. What is the net yield of NADH per mole of glucose for animal tissue under anaerobic conditions? (Using the attachment may help.)
Aromatic compounds possess a π system of exceptional stability. They are defined as cyclic, planar compounds with a number of conjugated π electrons equal to 4n+2, where n is a whole number (this is known as Hückel’s rule). Aromatic compounds have low reactivity and relatively high melting and boiling points. If a compound is cyclic and planar, and has a delocalized π system that does not obey Hückel’s rule, it is called antiaromatic.
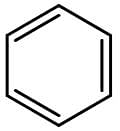
Benzene is the most well-known aromatic compound. Its chemical structure is shown on the figure below:
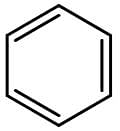
The presence of substituents on benzene can increase or decrease its reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. If the substituent is an electron donor, reactivity increases, but if the substituent is an electron acceptor, reactivity decreases. Substituents with resonance have a stronger influence on reactivity than substituents with inductive effect.
Four different organic compounds labeled from A to D are studied. Their chemical structures are shown below:
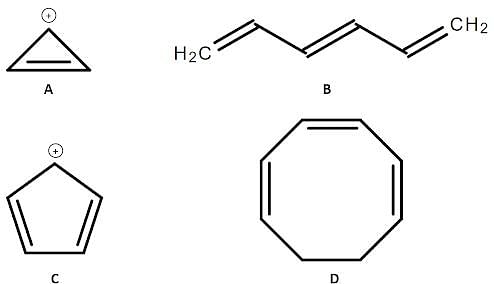
Q. Which compound in the attachment is aromatic?
Aromatic compounds possess a π system of exceptional stability. They are defined as cyclic, planar compounds with a number of conjugated π electrons equal to 4n+2, where n is a whole number (this is known as Hückel’s rule). Aromatic compounds have low reactivity and relatively high melting and boiling points. If a compound is cyclic and planar, and has a delocalized π system that does not obey Hückel’s rule, it is called antiaromatic.
Benzene is the most well-known aromatic compound. Its chemical structure is shown on the figure below:

The presence of substituents on benzene can increase or decrease its reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. If the substituent is an electron donor, reactivity increases, but if the substituent is an electron acceptor, reactivity decreases. Substituents with resonance have a stronger influence on reactivity than substituents with inductive effect.
Four different organic compounds labeled from A to D are studied. Their chemical structures are shown below:

Q. Which of the following statements regarding compounds A to D in the attachment is true?
Aromatic compounds possess a π system of exceptional stability. They are defined as cyclic, planar compounds with a number of conjugated π electrons equal to 4n+2, where n is a whole number (this is known as Hückel’s rule). Aromatic compounds have low reactivity and relatively high melting and boiling points. If a compound is cyclic and planar, and has a delocalized π system that does not obey Hückel’s rule, it is called antiaromatic.
Benzene is the most well-known aromatic compound. Its chemical structure is shown on the figure below:
The presence of substituents on benzene can increase or decrease its reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. If the substituent is an electron donor, reactivity increases, but if the substituent is an electron acceptor, reactivity decreases. Substituents with resonance have a stronger influence on reactivity than substituents with inductive effect.
Four different organic compounds labeled from A to D are studied. Their chemical structures are shown below:
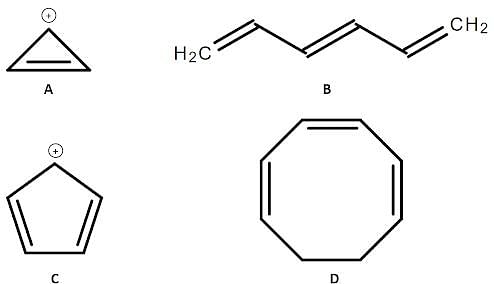
Q. Which of the following compounds will be less reactive towards electrophilic aromatic substitution? (See attachment.)
Aromatic compounds possess a π system of exceptional stability. They are defined as cyclic, planar compounds with a number of conjugated π electrons equal to 4n+2, where n is a whole number (this is known as Hückel’s rule). Aromatic compounds have low reactivity and relatively high melting and boiling points. If a compound is cyclic and planar, and has a delocalized π system that does not obey Hückel’s rule, it is called antiaromatic.
Benzene is the most well-known aromatic compound. Its chemical structure is shown on the figure below:
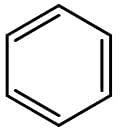
The presence of substituents on benzene can increase or decrease its reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. If the substituent is an electron donor, reactivity increases, but if the substituent is an electron acceptor, reactivity decreases. Substituents with resonance have a stronger influence on reactivity than substituents with inductive effect.
Four different organic compounds labeled from A to D are studied. Their chemical structures are shown below:

Q. Which of the 4 compounds in the attachment is/are antiaromatic?
Aromatic compounds possess a π system of exceptional stability. They are defined as cyclic, planar compounds with a number of conjugated π electrons equal to 4n+2, where n is a whole number (this is known as Hückel’s rule). Aromatic compounds have low reactivity and relatively high melting and boiling points. If a compound is cyclic and planar, and has a delocalized π system that does not obey Hückel’s rule, it is called antiaromatic.
Benzene is the most well-known aromatic compound. Its chemical structure is shown on the figure below:
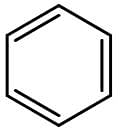
The presence of substituents on benzene can increase or decrease its reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. If the substituent is an electron donor, reactivity increases, but if the substituent is an electron acceptor, reactivity decreases. Substituents with resonance have a stronger influence on reactivity than substituents with inductive effect.
Four different organic compounds labeled from A to D are studied. Their chemical structures are shown below:
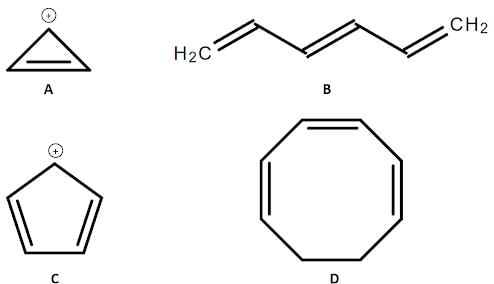
Q. Which of the following compounds will be more reactive toward electrophilic aromatic substitution? (You may consult the attachment.)
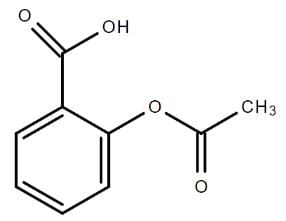
The chemical structure of aspirin is shown in the attached image. What is the IUPAC name for aspirin?