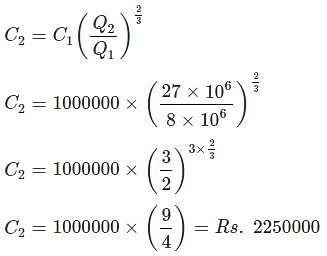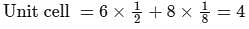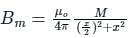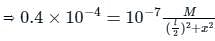Test: General Studies Engineering Aptitude - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Studies Engineering Aptitude - 1
Consider the following statements about Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve:
- Its area falls in the Malabar rainforests and is one of the noted hotspot in the Western Ghats.
- It includes the Indian eco-regions of moist deciduous forests.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which among the following pair is incorrectly matched?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Ecological hot spots present in India are ?
Consider the following statements:
- DDT
- Salts of heavy metals
- Radioactive substances
Which of these pollutants is/are non-biodegradable?
Which region is known as the "Ring of Fire" due to its high seismic activity?
What is Khetri in Rajasthan famous for?
What is the main difference between global warming and climate change?
Which of the following is not a phase of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) as per the guidelines of the International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA)?
What is the primary aim of sustainable development?
Match List I with List II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Zaire proposed "Building blocks of TQM" in which year ?
A public limited company has 9,00,000 shares outstanding at current market price of Rs. 130 per share. The company needs Rs. 2.25 crores to finance its proposed new project. The board of the company has decided to issue rights shares to raise the required money at Rs. 75 per share (as subscription price) to ensure that the rights issue is fully subscribed. How many rights are required to purchase a new share ?
What are the characteristics of job shop production ?
A. Different product types are produced
B. Very large quantities are produced
C. Single type of product is produced
D. Low quantities of product are produced
The earliest method used for planning of projects was
Planning is often called the primary management function because it:
A matrix organization is defined as
Direction: It consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Statement (I)’ and the others as ‘Statement (II)’. You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answer using the codes given below:
Statement (I): Overhead cost of Project comes under Indirect cost.
Statement (II): Allocating indirect costs to specific projects is considerably less difficult than direct costs.
Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique, commonly known as GERT, is a network analysis technique used in project management that allows
Consider the following statements:
In the critical path method of constriction planning. ‘Free Float’ can be
- greater than total float
- greater than independent float
- equal to total float
- less than independent float
Of these statements
A fluorspar plant costs Rs.10,00,000 for a 8 × 106 tonne/year facility. What would be the cost for a 27 × 106 tonnne/year facility if the rule of two-thirds was applicable?
Reproduction of objects by electrodeposition on some sort of a mould or form is known as __________
If the atomic radius of Aluminium (FCC) is r, what is the unit cell volume
A bar magnet of length 14 cm is placed in the magnetic meridian with its north pole pointing towards the geographic north pole. A neutral point is obtained at a distance of 18 cm from the centre of the magnet. If BH = 0.4 G, the magnetic moment of the magnet is
(1 G = 10-4 T)
Which of the following phase of steel is NOT present in Iron-Carbon phase diagram?
Directions: The question consists of two statements, one labeled as ‘Statement (I)’ and the other labeled as ‘Statement (II)’. You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below:
Statement (I): Indium (Z = 49) in the superconducting state will exhibit incomplete Meissner’s effect and Silsbee rule.
Statement (II): The critical current is directly proportional to the critical magnetic field.
Direction: The following item consists of two statements, one labelled as ‘Statement (I)’ and the other as ‘Statement (II)’. Examine these two statements carefully and select the answer using the code given below:
Statement (I): Electric conductivity of a solid solution alloy drops off rapidly with increased alloy content.
Statement (II): Solutes disrupt the uniform periodically potential field.
Direction: The following item consists of two statements, one labelled as ‘Statement (I)’ and the other as ‘Statement (II)’.
Examine these two statements carefully and select the answer using the code given below:
Statement (I): All the ferroelectric materials are piezoelectric materials also but the reverse statement is not true.
Statement (II): Ferro-electricity is independent of temperature.
Consider the following statements in respect of energy bands in a solid.
- Energy bands at high energy have more width than those bands at low energy.
- Low energy bands correspond to valence electrons.
- There are always some energy bands that are not filled.
Which of these statements is/are correct?