Test: Probability And Expected Value By Mathematical Expectation- 2 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Probability And Expected Value By Mathematical Expectation- 2
(Direction 1 - 15) Write down the correct answers. Each question carRies 1 mark.
Q. If x and y are independent, then
If a random variable x assumes the values x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 with corresponding probabilities p1 , p2 , p3 , p4 then the expected value of x is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
f(x), the probability mass function of a random variable x satisfies
Variance of a random variable x is given by
If two random variables x and y are related by y = 2 – 3x, then the SD of y is given by
Probability of getting a head when two unbiased coins are tossed simultaneously is
If an unbiased coin is tossed twice, the probability of obtaining at least one tail is
If an unbiased die is rolled once, the odds in favour of getting a point which is a multiple of 3 is
A bag contains 15 one rupee coins, 25 two rupee coins and 10 five rupee coins. If a coin is selected at random from the bag, then the probability of not selecting a one rupee coin is
A, B, C are three mutually independent with probabilities 0.3, 0.2 and 0.4 respectively.What is P (A ∩ B ∩ C)?
If two letters are taken at random from the word HOME, what is the Probability that none of the letters would be vowels?
If a card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards, what is the chance of getting a Spade or an ace?
If x and y are random variables having expected values as 4.5 and 2.5 respectively, then the expected value of (x–y) is
If variance of a random variable x is 23, then what is the variance of 2x+10?
What is the probability of having at least one ‘six’ from 3 throws of a perfect die?
(Direction 16 - 38) Write down the correct answers. Each question carries 2 marks.
Q.Two balls are drawn from a bag containing 5 white and 7 black balls at random. What is the probability that they would be of different colours?
What is the chance of throwing at least 7 in a single cast with 2 dice?
What is the chance of getting at least one defective item if 3 items are drawn randomly from a lot containing 6 items of which 2 are defective item?
If two unbiased dice are rolled together, what is the probability of getting no difference of points?
If A, B and C are mutually exclusive independent and exhaustive events then what is the probability that they occur simultaneously?
There are 10 balls numbered from 1 to 10 in a box.if one ofthem is selected at random whatisthe probability that the number printed onthe ball woukd be an odd number greater than 4
Following are the wages of 8 workers in rupees:
50, 62, 40, 70, 45, 56, 32, 45
If one of the workers is selected at random, what is the probability that his wage would be lower than the average wage?
A, B and C are three mutually exclusive and exhaustive events such that P (A) = 2 P (B) = 3P(C). What is P (B)?
For two events A and B, P (B) = 0.3, P (A but not B) = 0.4 and P (not A) = 0.6. The events A and B are
A bag contains 12 balls which are numbered from 1 to 12. If a ball is selected at random, what is the probability that the number of the ball will be a multiple of 5 or 6 ?
Given that for two events A and B, P(A)=3/5, P(B)=2/3 and P(A union B) =3/4, what is P(A|B)?
For two independent events A and B, what is P (A+B), given P(A) = 3/5 and P(B) = 2/3?
If P (A) = p and P (B) = q, then
If P ( 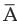 ∪ B ) = 5/6, P(A) = ½ and P (
∪ B ) = 5/6, P(A) = ½ and P ( 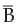 ) = 2/3, , what is P (A ∪ B) ?
) = 2/3, , what is P (A ∪ B) ?
If for two independent events A and B, P (A ∪ B) = 2/3 and P (A) = 2/5, what is P (B)?

















