Test: Process- 1 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Process- 1
Consider two processors P1 and P2 executing the same instruction set. Assume that under identical conditions, for the same input, a program running on P2 takes 25% less time but incurs 20% more CPI (clock cycles per instruction) as compared to the program running on P1. If the clock frequency of P1 is 1GHz, then the clock frequency of P2 (in GHz) is _________.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the procedure below for the Producer-Consumer problem which uses semaphores:

Q. Which one of the following is TRUE?
The atomic fetch-and-set x, y instruction unconditionally sets the memory location x to 1 and fetches the old value of x n y without allowing any intervening access to the memory location x. consider the following implementation of P and V functions on a binary semaphore S.
void P (binary_semaphore *s)
{
unsigned y;
unsigned *x = &(s->value);
do
{
fetch-and-set x, y;
}
while (y);
}
void V (binary_semaphore *s)
{
S->value = 0;
}
Q. Which one of the following is true?
Barrier is a synchronization construct where a set of processes synchronizes globally i.e. each process in the set arrives at the barrier and waits for all others to arrive and then all processes leave the barrier. Let the number of processes in the set be three and S be a binary semaphore with the usual P and V functions. Consider the following C implementation of a barrier with line numbers shown on left.
void barrier (void) {
1: P(S);
2: process_arrived++;
3. V(S);
4: while (process_arrived !=3);
5: P(S);
6: process_left++;
7: if (process_left==3) {
8: process_arrived = 0;
9: process_left = 0;
10: }
11: V(S);
}
Q. The variables process_arrived and process_left are shared among all processes and are initialized to zero. In a concurrent program all the three processes call the barrier function when they need to synchronize globally. The above implementation of barrier is incorrect. Which one of the following is true?
Barrier is a synchronization construct where a set of processes synchronizes globally i.e. each process in the set arrives at the barrier and waits for all others to arrive and then all processes leave the barrier. Let the number of processes in the set be three and S be a binary semaphore with the usual P and V functions. Consider the following C implementation of a barrier with line numbers shown on left.
void barrier (void) {
1: P(S);
2: process_arrived++;
3. V(S);
4: while (process_arrived !=3);
5: P(S);
6: process_left++;
7: if (process_left==3) {
8: process_arrived = 0;
9: process_left = 0;
10: }
11: V(S);
}
Q. The variables process_arrived and process_left are shared among all processes and are initialized to zero. In a concurrent program all the three processes call the barrier function when they need to synchronize globally. Which one of the following rectifies the problem in the implementation?
Consider two processes P1 and P2 accessing the shared variables X and Y protected by two binary semaphores SX and SY respectively, both initialized to 1. P and V denote the usual semaphone operators, where P decrements the semaphore value, and V increments the semaphore value. The pseudo-code of P1 and P2 is as follows : P1 :
While true do {
L1 : ................
L2 : ................
X = X + 1;
Y = Y - 1;
V(SX);
V(SY);
}
P2 :
While true do {
L3 : ................
L4 : ................
Y = Y + 1;
X = Y - 1;
V(SY);
V(SX);
}
Q. In order to avoid deadlock, the correct operators at L1, L2, L3 and L4 are respectively
Suppose we want to synchronize two concurrent processes P and Q using binary semaphores S and T. The code for the processes P and Q is shown below.
Process P:
while (1) {
W:
print '0';
print '0';
X:
}
Process Q:
while (1) {
Y:
print '1';
print '1';
Z:
}
Q. Synchronization statements can be inserted only at points W, X, Y and Z. Which of the following will always lead to an output staring with '001100110011' ?
Suppose we want to synchronize two concurrent processes P and Q using binary semaphores S and T. The code for the processes P and Q is shown below.
Process P:
while (1) {
W:
print '0';
print '0';
X:
}
Process Q:
while (1) {
Y:
print '1';
print '1';
Z:
}
Q. Synchronization statements can be inserted only at points W, X, Y and Z Which of the following will ensure that the output string never contains a substring of the form 01n0 or 10n1 where n is odd?
Which of the following need not necessarily be saved on a context switch between processes?
The following two functions P1 and P2 that share a variable B with an initial value of 2 execute concurrently.
P1()
{
C = B – 1;
B = 2*C;
}
P2()
{
D = 2 * B;
B = D - 1;
}
The number of distinct values that B can possibly take after the execution is
The semaphore variables full, empty and mutex are initialized to 0, n and 1, respectively. Process P1 repeatedly adds one item at a time to a buffer of size n, and process P2 repeatedly removes one item at a time from the same buffer using the programs given below. In the programs, K, L, M and N are unspecified statements.
P1
while (1) { K; P(mutex); Add an item to the buffer; V(mutex); L; } P2 while (1) { M; P(mutex); Remove an item from the buffer; V(mutex); N; } The statements K, L, M and N are respectively
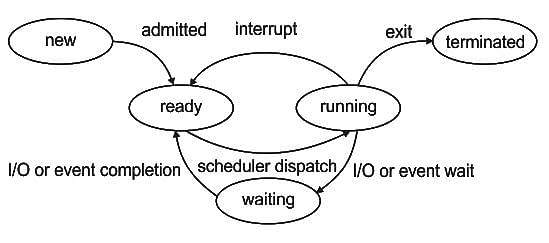
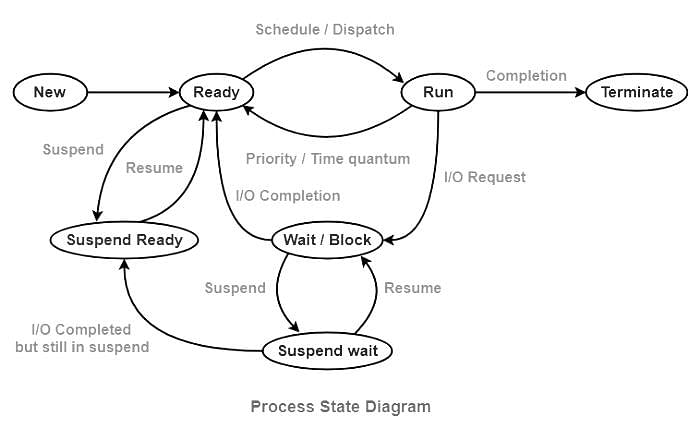
A process waiting to be assigned to a processor is considered to be in ___ state.
Consider the following two-process synchronization solution.
The shared variable turn is initialized to zero. Which one of the following is TRUE?
A _________ process is moved to the ready state when its time allocation expires.
Consider the following statements about process state transitions for a system using preemptive scheduling.
I. A running process can move to ready state.
II. A ready process can move to running state.
III. A blocked process can move to running state.
IV. A blocked process can move to ready state.
Which of the above statements are TRUE?
Which of the following DMA transfer modes and interrupt handling mechanisms will enable the highest I/O band-width?
Time taken to switch between user and kernel models is _______ the time taken to switch between two processes.
In the working-set strategy, which of the following is done by the operating system to prevent thrashing?
- It initiates another process if there are enough extra frames.
- It selects a process to suspend if the sum of the sizes of the working-sets exceeds the total number of available frames.
With respect to operating systems, which of the following is NOT a valid process state?