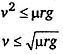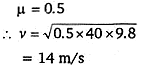DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 2 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0.8. If the frictional force on the block is 10 N, the mass of the block (in kg) is (g = 10 m/s2
[AIEEE 2004]
As per the given figure, two blocks each of mass 250 g are connected to a spring of spring constant 2 Nm-1. If both are given velocity v in opposite directions, then maximum elongation of the spring is:

A body of mass 0.5 kg travels on a straight line path with velocity v = (3x2 + 4) m/s. The net work done by the force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2 m is:
A free electron of 2.6 eV energy collides with a H+ ion. This results in the formation of a hydrogen atom in the first excited state and a photon is released. Find the frequency of the emitted photon (h = 6.6 × 10-34 J s).
When does the potential energy of a spring increase?
Two identical thin uniform rods of length L each are joined to form T shape as shown in the figure. The distance of centre of mass from D is
What is the force required to produce an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 on a body of weight 9.8N? Take g = 9.8 m/s2.
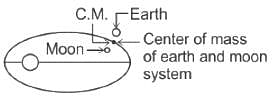
The earth attracts the moon with a gravitational force of 1020 N. Then the moon attracts the earth with the gravitational force of
Both earth and moon are subject to the gravitational force of the sun. As observed from the sun, the orbit of the moon
As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximate circular orbit. For the motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would
If a person studies about a fluid which is at rest, what will you call his domain of study?
According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law of thermal radiation for a perfect radiator, the rate of radiant energy per unit area is proportional to
Suppose we have a box filled with gas and a piston is also attached at the top of the box.What are the ways of changing the state of gas (and hence its internal energy)?
Value of gas constant, R for one mole of a gas is independent of the
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be
The electric field intensity at a point situated 4 meters from a point charge is 200 N/C. If the distance is reduced to 2 meters, the field intensity will be
Gauss Law can be used to compute which of the following?
When number of identical cells, in parallel combination are increased, the voltage of the circuit will
Which of the following statements about bar magnets is correct ?
The magnifying power of the telescope can be increased by
A lamp and a screen are set up 100 cm apart and a convex lens is placed between them. The two positions of the lens forming real images on the screen are 40 cm apart. What is the focal length of the lens ?
Shape of the wave front of light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
If the work function of a material is 2eV, then minimum frequency of light required to emit photo-electrons is
A car of mass 800 kg moves on a circular track of radius 40 m. If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, then the maximum velocity with which the car can move is



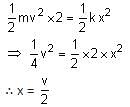
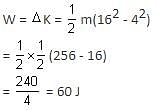

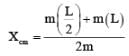
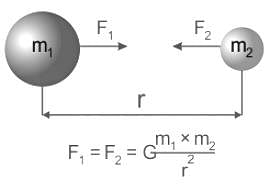
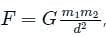 where, F is the gravitational force between bodies, m1, and m2 are the masses of the bodies, d is the distance between the centers of two bodies, and G is the universal gravitational constant.
where, F is the gravitational force between bodies, m1, and m2 are the masses of the bodies, d is the distance between the centers of two bodies, and G is the universal gravitational constant.